Socialist Republic of Serbia
The Socialist Republic of Serbia (Serbian: Социјалистичка Република Србија, romanized: Socijalistička Republika Srbija), previously known as Federal State of Serbia and People's Republic of Serbia, commonly referred to as Socialist Serbia, or simply as Serbia, was one of the six constituent republics of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and the nation state of the Serbs. It was the largest constituent republic in terms of population and territory. Its capital, Belgrade, was also the federal capital of Yugoslavia.
Socialist Republic of Serbia Социјалистичка Република Србија Socijalistička Republika Srbija | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1945–1990 | |||||||||||||||
 Serbia within Yugoslavia in 1990 | |||||||||||||||
| Status | Constituent republic of Yugoslavia | ||||||||||||||
| Capital | Belgrade | ||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Serbo-Croatian (Serbian standard) Hungarian Albanian | ||||||||||||||
| Government | 1945–1948: Marxist–Leninist one-party socialist republic 1948–1990: Titoist one-party socialist republic 1974–1990: de facto federation | ||||||||||||||
| Head of state | |||||||||||||||
• 1945–1953 (first) | Siniša Stanković | ||||||||||||||
• 1989–1990 (last) | Slobodan Milošević | ||||||||||||||
| Head of government | |||||||||||||||
• 1945–1948 (first) | Blagoje Nešković | ||||||||||||||
• 1989–1990 (last) | Stanko Radmilović | ||||||||||||||
| Legislature | National Assembly | ||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Cold War, World War II | ||||||||||||||
• ASNOS | 9–12 November 1945 | ||||||||||||||
| 8 May 1945 | |||||||||||||||
| 28 September 1990 | |||||||||||||||
• Federal Republic of Yugoslavia declared | 27 April 1992 | ||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||
| 1981 | 88,361 km2 (34,116 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||
• 1981 | 9,313,476 | ||||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | RS | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
History
World War II
After the collapse of Royal Yugoslav Army on 18 April 1941 Yugoslavia was partitioned between Axis forces. The territory of later SR Serbia was mainly occupied by German forces, with puppet Government in Belgrade. The region of Kosovo was annexed by Albania, Bačka by Hungary, Syrmia by Croatia and southeastern parts were occupied by Kingdom of Bulgaria. Banat had its own autonomous status.
In the beginning of the occupation there were two resistance armies: Chetniks and Partisans. Yet, Chetniks started open collaboration with Axis forces in 1943.
In July 1941 socialist republic was founded by partisans in western Serbia, known as Republic of Užice. However, the German offensive crushed this proto-state in December the same year. After this partisan main forces moved to Bosnia.
Together with Soviet and other allies first parts of Serbia were liberated in 1944. Many cities were heavily bombed by western allies. First major city to be liberated was Niš on 14 October, followed by capital Belgrade on 20 October 1944.
Post-World War II period
1940s–1950s
Part of a series on the |
||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History of Serbia | ||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||
In April 1945, the Anti-fascist Assembly for the National Liberation of Serbia officially created the Federated State of Serbia (Serbian: Федерална Држава Србија / Federalna Država Srbija), as a federated state within Yugoslavia. In January 1946, after the first constitution of federal Yugoslavia was adopted, the Federated State of Serbia was renamed to People's Republic of Serbia (Serbian: Народна Република Србија / Narodna Republika Srbija). It also had two autonomous units, Autonomous Province of Vojvodina and Autonomous Region of Kosovo and Metohija.
1960s
In 1966 one of the most prominent Serbs in the Communist party and also vice-president of Yugoslavia and founder of Yugoslav intelligence agency OZNA, Aleksandar Ranković was removed from positions due to allegations of spying on SFRY President Josip Broz Tito.
1970s
After the Croatian Spring in 1971, almost whole party leadership of Serbia was removed from office, under the charge of being "liberal". Latinka Perović and Marko Nikezić were marked as leaders of this liberal movement inside League of Communists of Serbia.
In 1974 new constitution was adopted, increasing the powers of provinces, and making them de facto republics. For the first time the institution of president was formed, as President of the Presidency of Socialist Republic of Serbia. Assembly was electing 15 members of the presidency and one president for a 4 -year term, and later 2-year term. The new constitution practically suspended Serbia's authority over the provinces.
After the new constitution was adopted, mistakes became obvious. Dragoslav Marković, then President of Serbia ordered a secret study on this issue. The study was completed in 1977 and was named The Blue Book.
1980s–1990s
For most of its existence in the SFRY, Serbia was loyal and generally subordinate to the federal government. This changed after the death of Josip Broz Tito in 1980, when Albanian, as well as Serbian nationalism in Kosovo arose. In 1981 a major protests erupted in Kosovo demanding the status of republic. The League of Communists was split on how to respond. At the same time, economic crisis in Yugoslavia started. The leaders of the country were unable to make any reforms, thanks to the political instability.
President of League of Communists of Serbia Slobodan Milošević visited Kosovo in April 1987 and promised rapid action in order to protect peace and Serbs of Kosovo. Ethnic tensions in Kosovo were heated up when Kosovo Albanian soldier opened fire on his fellow soldiers in Paraćin, in an event known as Paraćin massacre. Then President of Serbia Ivan Stambolić wanted to make compromise, rather than fast solution. He found himself in a clash with Milošević. This conflict culminated with 8th Session and replacement of Stambolić with Petar Gračanin as President of Serbia.
In 1988 and 1989 a successful round of coups in the Communist party leadership, known as Antibureucratic revolution, in Vojvodina, Kosovo as well as Montenegro, replaced autonomous leaderships in this regions. The coups were led by Slobodan Milošević; supporter of Serbian nationalism. The events were condemned by the communist governments of the western Yugoslav republics (especially SR Slovenia and SR Croatia), who successfully resisted the attempts to expand the revolt onto their territories, and turned against Milošević. The rising antagonism eventually resulted in the dissolution of the ruling League of Communists of Yugoslavia in 1990, and subsequently in the breakup of Yugoslavia.
In 1989, Slobodan Milošević was elected as President of Serbia. He demanded that the federal Yugoslav government act for the interests of Serbia in Kosovo by sending in the Yugoslav People's Army to suppress separatism in the province. At the same time, several reforms of federal electoral system were proposed, with Serbia supporting a "one-citizen, one-vote" system, which would have given a majority of votes to Serbs. By that time, ethnic tensions in Yugoslavia increased, and the ruling League of Communists of Yugoslavia collapsed, followed by the crisis of federal institutions. After these events, in 1989 Assembly of Socialist Republic of Serbia voted for constitution amendments that revoked high autonomy for provinces of Vojvodina and Kosovo.
After Slovenian authorities forbid a group of Serbs supporting his politics to gather in Ljubljana, Milosevic started a trade war with Socialist Republic of Slovenia in late 1989. This Serbian-Slovenian conflict culminated in January 1990 on 14th Congress of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia when Slovenians left the meeting followed by Croatian delegates.[1]
After 1990, the state was known simply as Republic of Serbia (Serbian: Република Србија / Republika Srbija), and in December of the same year, Slobodan Milošević was elected as first President of the Republic. In 1992, when the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was formed, Serbia became one of its two constituent republics. In 2003 this state union was re-formed into Serbia and Montenegro, and in 2006 Serbia became an independent republic after Montenegro separated.


Administrative divisions
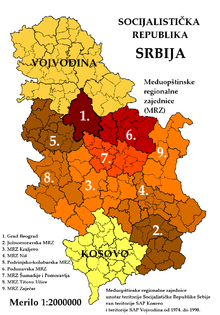
Within Socialist Republic of Serbia two autonomous provinces existed: Socialist Autonomous Province of Vojvodina and Socialist Autonomous Province of Kosovo. The central part of the Socialist Republic of Serbia located outside of the two autonomous provinces was generally known as "Serbia proper" ("Uža Srbija").
Geographically SR Serbia bordered Hungary to the north, Romania and Bulgaria to the east and Albania to the south-west. Within Yugoslavia, it bordered SR Macedonia to the south and SR Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia to the west.
Demographics
1971 census
In 1971, total population of the Socialist Republic of Serbia numbered 8,446,591 people, including:
- Serbs = 6,142,071 (72.71%)
- Albanians = 984,761 (11.66%)
- Hungarians = 430,314 (5.10%)
- Croats = 184,913 (2.19%)
- Muslims = 154,330 (1.83%)
- Yugoslavs = 123,824 (1.47%)
- Slovaks = 76,733 (0.82%)
- Romanians = 57,419 (0.62%)
- Bulgarians = 53,800 (0.58%)
- Romani = 49,894 (0.54%)
- Macedonians = 42,675 (0.46%)
- Rusyns = 20,608 (0.22%)
- Turks = 18,220 (0.20%)
- Slovenes = 15,957 (0.17%)
- Vlachs = 14,724 (0.16%)
1981 census
In 1981, total population of the Socialist Republic of Serbia numbered 9,313,677 people, including:
- Serbs = 6,331,527 (67.96%)
- Albanians = 1,303,032 (13.99%)
- Yugoslavs = 441,941 (4.75%)
- Hungarians = 390,468 (4.19%)
- Muslims = 215,166 (2.31%)
- Croats = 149,368 (1.60%)
- Romani = 110,956 (1.19%)
- Macedonians = 48,986 (0.53%)
- Slovenes = 12,006 (0.13%)
Politics
In the Socialist Republic, the only legal political party was the League of Communists of Serbia (SKS), which was part of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia (SKJ). The party remained relatively stable and loyal to the federal party until the late 1980s, when the party became split over what action to take in Kosovo when protests and fights broke out between ethnic Albanians and Serbs.
The more traditional Communists supported President Ivan Stambolic, who advocated continued neutrality as a means to solve the dispute; while more radical and nationalist-leaning members supported Slobodan Milosevic, who advocated the protection of Kosovo Serbs, who had claimed that their population was being pressured to leave Kosovo by Albanian separatists. Milosevic utilized public sentiment and opposition to Kosovo Albanian separatism to rally large numbers of supporters to help him overthrow the Communist leadership in Vojvodina, Kosovo and the Socialist Republic of Montenegro in what was known as the anti-bureaucratic revolution. Afterward, the Serbian League of Communists selected Milosevic as its leader. Milosevic took a hard stand on Albanian nationalism in Kosovo and pressured the Yugoslav government to give him emergency powers to deal with Kosovo Albanian separatists. Furthermore, he reduced the autonomy of the autonomous provinces of Kosovo and Vojvodina and installed politicians loyal to him to serve as their representatives.
In the congress of the Yugoslav League of Communists in 1990, Milosevic and his subordinate representatives for Vojvodina, Kosovo and the Socialist Republic of Montenegro attempted to silence opposition from the Socialist Republic of Slovenia who opposed the actions taken against Kosovo Albanian leadership, by blocking all reforms proposed by the Slovene representatives. The tactic failed and Slovenia, along with its ally Croatia, abdicated from the Yugoslav Communist Party. This caused the Yugoslav Communist party to fall apart, and then the state of Yugoslavia itself one year later.
Government
Until 1974, de facto head of state of SRS was President of Assembly (known as Presidium of the People's Assembly (1945-1953) and National Assembly (1953-1990)). In 1974 Constitution of Serbia collective presidency was formed. President of the Presidency served as the President of Socialist Republic of Serbia. Until 1982 President was elected on 4 years mandate, but after it was lowered to 2. In 1953 Executive Council (government) was formed. It served as the executive branch of the Assembly. President of the Executive Council had a role of Prime Minister.
Chairman of ASNOS (1944–1945)
- Siniša Stanković (12 November 1944 – 7 April 1945)
Presidents
- President of the Presidium of the People's Assembly (1945–1953)
- Siniša Stanković (7 April 1945 – March 1953)
- Presidents of the National Assembly (1953–1974)
- Petar Stambolić (December 1953 – April 1957)
- Jovan Veselinov (April 1957 – 26 June 1963)
- Dušan Petrović (26 June 1963 – 6 May 1967)
- Miloš Minić (6 May 1967 – 6 May 1969)
- Dragoslav Marković (6 May 1969 – 19 April 1974)
- Živan Vasiljević (19 April – 6 May 1974)
- Presidents of the Presidency (1974–1990)
- Dragoslav Marković (6 May 1974 – 5 May 1978)
- Dobrivoje Vidić (5 May 1978 – 5 May 1982)
- Nikola Ljubičić (5 May 1982 – 5 May 1984)
- Dušan Čkrebić (5 May 1984 – 5 May 1986)
- Ivan Stambolić (5 May 1986 – 14 December 1987)
- Petar Gračanin (14 December 1987 – 20 March 1989)
- Ljubiša Igić (20 March – 8 May 1989) (acting)
- Slobodan Milošević (8 May 1989 – 28 September 1990)
Prime Ministers
- Minister for Serbia in Yugoslav government
- Jaša Prodanović (7 March 1945 – 9 April 1945)
- President of the Government
- Blagoje Nešković (9 April 1945 – 5 September 1948)
- Petar Stambolić (5 September 1948 – 5 February 1953)
- President of the Executive Council
- Petar Stambolić (5 February 1953 – 16 December 1953)
- Jovan Veselinov (16 December 1953 – 6 April 1957)
- Miloš Minić (6 April 1957 – 9 June 1962)
- Slobodan Penezić Krcun (9 June 1962 – 6 November 1964)
- Stevan Doronjski (Acting; 6 November 1964 – 17 November 1964)
- Dragi Stamenković (17 November 1964 – 6 June 1967)
- Đurica Jojkić (6 June 1967 – 7 May 1969)
- Milenko Bojanić (7 May 1969 – 6 May 1974)
- Dušan Čkrebić (6 May 1974 – 6 May 1978)
- Ivan Stambolić (6 May 1978 – 5 May 1982)
- Branislav Ikonić (5 May 1982 – 6 May 1986)
- Desimir Jevtić (6 May 1986 – 5 December 1989)
- Stanko Radmilović (5 December 1989 – 28 September 1990)
Sources
- Bataković, Dušan T., ed. (2005). Histoire du peuple serbe [History of the Serbian People] (in French). Lausanne: L’Age d’Homme.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
References
External links

.svg.png)
.svg.png)