Middelburg
Middelburg (Dutch: [ˈmɪdəlbʏrx] (![]()
Middelburg | |
|---|---|
City and municipality | |
Middelburg Stadhuis | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
.svg.png) Location in Zeeland | |
| Coordinates: 51°30′N 3°37′E | |
| Country | Netherlands |
| Province | Zeeland |
| City Hall | Middelburg City Hall |
| Government | |
| • Body | Municipal council |
| • Mayor | Harald Bergmann (VVD) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 53.04 km2 (20.48 sq mi) |
| • Land | 48.54 km2 (18.74 sq mi) |
| • Water | 4.50 km2 (1.74 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 3 m (10 ft) |
| Population (January 2019)[4] | |
| • Total | 48,544 |
| • Density | 1,000/km2 (3,000/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Middelburger |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postcode | 4330–4341 |
| Area code | 0118 |
| Website | www |
In terms of technology, Middelburg played a role in the Scientific Revolution at the early modern period. The city was historically a center of lens crafting in the Golden Age of Dutch science and technology. The invention of the microscope and telescope is often credited to Middelburg spectacle-makers (including Zacharias Janssen and Hans Lippershey) in the late 16th century and early 17th century.
History
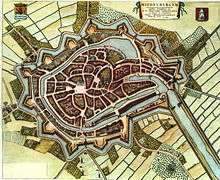
.jpg)
The city of Middelburg dates back possibly to the late 8th century or early 9th century. The first mention of Middelburg was as one of three fortified towns (borgs) erected on Walcheren (then an island) to guard against Viking raids. In 844 a monastery was built on the site, which remained an active Catholic foundation until the Reformation. Foundations for Middelburg's "stately and picturesque" main church were first laid in the 10th century; additional construction continued through the Middle Ages.
Middelburg was granted city rights in 1217. During the Middle Ages, it became an important trading centre in the commerce between England and the rising cities of Flanders. The town continued to gain in power and prestige during the 13th and 14th centuries.
From 1559 to 1603, Middelburg was the episcopal see of a Catholic bishopric covering all Zeeland. In the Eighty Years' War, Middelburg was captured from the Spanish forces during a long siege (1572–1574). The northern provinces of the original Low Countries won their independence from their former Spanish Habsburg rulers and formed The Netherlands, a Protestant state. Later, in the 17th century (the Dutch Golden Age), Middelburg became, after Holland's metropolis Amsterdam, the most important center for the East India Company of Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (VOC) or Dutch East India Company.
Middelburg played an important role in the 17th century slave trade.
Samuel Ben Israel, son of Menasseh Ben Israel, is buried in Middelburg at the Sephardic burial site located at the 'Jodengang' outside the citywall. Menasseh Ben Israel negotiated with Cromwell the opening of England, and its colonies, to the Jews. Middelburg also has an Ashkenazic burial site, which is located at the Walensingel inside the city wall. In 1994 the synagogue was restored, as it was partially destroyed during the Second World War. This synagogue was the third one to be built in the Netherlands during the Golden Age. In the hall of the railway station there is a plaque of remembrance for the Jews of Zeeland who started their journey to the death camps from the Middelburg train station.
About a third of the old city centre was devastated by bombs and fire in the early phases of World War II, on May 17, 1940. It is still not certain if German bombers or French artillery were responsible.[5] The town was captured and liberated by British troops during Operation Infatuate on 5 November 1944. After the War, as much of the destroyed part of the old town center was rebuilt and restored along pre-War lines as far as was possible. The city's archives, however, had been incinerated during the German bombardment.
Modern Middelburg has preserved and regained much of its historic and picturesque character. There are lavish 17th and 18th century merchant houses and storehouses standing along canals, of a similar style as found in cities like Amsterdam. The old city moats are still there, as are two of the city gates, the Koepoort Gate and the varkenspoort Gate. Part of the 18th century moat and defence works, however, were demolished in the 19th century to make way for a commercial canal that crosses Walcheren from Vlissingen to Veere. The medieval abbey is still in use today, as a museum and as the seat of the provincial government.
Notable locals
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
| 1398 | 6,300 | — |
| 1576 | 7,000 | +0.06% |
| 1600 | 20,000 | +4.47% |
| 1675 | 27,000 | +0.40% |
| 1739 | 25,000 | −0.12% |
| 1795 | 17,687 | −0.62% |
| Source: Lourens & Lucassen 1997, pp. 93–94 | ||
Ambrosius Bosschaert the Elder (1573–1621) was a still life painter of the Dutch Golden Age who worked most of his life in Middelburg. He had three sons, Johannes Bosschaert (1606/08– 1628/29), Ambrosius Bosschaert II (1609–1645) and Abraham Bosschaert the Younger (1612–1643) who were all Dutch Golden Age painters.
The painter Pieter Gaal, (1769–1819) was born, settled and died here, after traveling over Europe to paint
Another well-known citizen of Middelburg was the admiral and explorer Jacob Roggeveen, who was born in the city in 1659 and died there in 1729. Roggeveen discovered Easter Island (Rapa Nui) in the South Pacific Ocean on Easter Sunday, April 6, 1722. Further discoveries on the same journey included islands of the Tuamotu group, now part of French Polynesia.
Petronella Johanna de Timmerman, scientist and poet, was born here in 1723. In 1774 she was inducted as an honorary member of the academy Kunstliefde Spaart Geen Vlijt. Also, she presented the academy with poems, translated from French plays. She died in Utrecht in 1786.
.jpg)

The Arts
- Adrianus Valerius (ca.1575 – 1625) a Dutch poet and composer
- Jacob van Geel (ca.1585 – 1648) a Dutch Golden Age painter.
- Christoffel van den Berghe (ca.1590 – ca.1645) a Dutch Golden Age painter of landscapes
- Balthasar van der Ast (1593/94 – 1657) a Dutch Golden Age painter
- Pieter de Putter (ca.1600 – 1659) a Dutch still life painter
- Daniël de Blieck (ca.1610 – 1673) a Dutch Golden Age painter, draughtsman and architect
- Philips Angel I (1616–1683) a Dutch still-life painter
- Ariana Nozeman (1626/1628 – 1661) the first actress in The Netherlands
- Pieter Borsseler (ca.1633 – ca.1687) a Dutch portrait painter, prominent in England
- Pieter Bustijn (1649–1729) a composer, organist, harpsichordist and carillon player
- Adriaen Coorte (ca.1665 – ca.1707) a Dutch Golden Age painter of still-lifes
- Barend Cornelis Koekkoek (1803–1862) a Dutch landscape artist and lithographer
- Suzanna Sablairolles (1829–1867) a Dutch stage actress
- Anna Adelaïde Abrahams (1849–1930) a Dutch still life painter
- Henri Eduard Beunke (1851–1925) a Dutch writer, known for his literary regionalistic work
- Herman Johannes van der Weele (1852–1930) a Dutch painter of the 2nd Hague School
- Pieter Cornelis Boutens (1870–1943) a Dutch poet, classicist, and mystic
- Joost Baljeu (1925–1991) a Dutch painter, sculptor and writer
- Paul van der Feen (born 1978) a Dutch saxophonist
- Carolyn Lilipaly (born 1969) a Dutch news anchor and actress [6]
- Stefan de Vries (born 1970) a Dutch writer and journalist [7]

.jpg)
Public Thinking & public service
- Paul of Middelburg (1446–1534) a Flemish scientist and Bishop of Fossombrone [8]
- Philippe van Lansberge (1561–1632) a Dutch Calvinist Minister, astronomer and mathematician
- Isaac Beeckman (1588–1637) a Dutch philosopher and scientist
- Sir Balthazar Gerbier (1592–1663) an Anglo-Dutch courtier, diplomat, art advisor, miniaturist and architectural designer
- Paulus van de Perre (ca.1598 – 1653 in London) a Dutch politician and diplomat, negotiated with Oliver Cromwell
- Adam Boreel (1602–1665) a Dutch theologian and Hebrew scholar
- Margaretha Sandra (1629–1674) a Dutch military heroine in the siege of Aardenburg in 1672
- Frederik van Leenhof (1647–1715) a controversial Dutch pastor and philosopher
- Adrian Beverland (1650 — 1716 in London) a Dutch humanist scholar, banished in 1679 and settled in England
- Cornelius van Bynkershoek (1673–1743) a Dutch jurist and legal theorist [9]
- Stephanus Versluys (1694–1736) the 21st Governor of Dutch Ceylon
- Reynier de Klerck (1710–1780) Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies 1778/1780
- Laurens Pieter van de Spiegel (1736–1800) was Grand Pensionary of Zeeland
- Piet Meertens (1899–1985) a Dutch scholar of literature, dialects, and ethnology
- Etty Hillesum (1914 – 1943 in Auschwitz) the Dutch author of confessional letters and diaries
- Albert de Vries (born 1955) a Dutch politician, alderman of Middelburg 2002/2012
- Harald Bergmann (born 1965) a Dutch politician, Mayor of Middelburg since 2012


Science & Business
- Zacharias Janssen (1585 – ca.1632) a Dutch spectacle-maker, lived mostly in Middelburg.
- Alexander Daniell (1599–1668) the sole proprietor of the Manor of Alverton, Cornwall 1630/1668
- Pieter van Abeele (1608–1684) a medallist, perfected the technique of pressing hollow medals
- Jan Goedart (1617–1668) a Dutch naturalist, entomologist and painter
- Steven Blankaart (1650–1704) a Dutch physician, iatrochemist, and entomologist
- Pieter Boddaert (1730–1795) a Dutch physician and naturalist
- Franz Zacharias Ermerins (1808–1871) a Dutch physician and medical editor
- Jan Adrianus Herklots (1820–1872) a Dutch zoologist, researched carcinology and the echinoderms
- Cecil Hoare FRS (1892–1984) a British protozoologist and parasitologist
- Lili Bleeker (1897–1985) a Dutch entrepreneur and physicist, designed and made optical instruments
- Cees Maas (born 1947) former chief financial officer of the ING Group
Sport
- Jan Poortvliet (born 1955) a retired football defender with 531 club caps
- Elisabeth Willeboordse (born 1978) a female judoka, bronze medallist at the 2008 Summer Olympics
Geography
Aside from the city of Middelburg, the municipality also includes several population centres, including: Arnemuiden, Kleverskerke, Nieuw- en Sint Joosland and Sint Laurens.
Gallery
 Former city hall
Former city hall View at the Lange Jan from the station
View at the Lange Jan from the station The Londense Kaai
The Londense Kaai Near towngate, the Kuiperspoort
Near towngate, the Kuiperspoort Molen de Hoop
Molen de Hoop
Culture and recreation
When William of Orange decided to found the first university in the Netherlands in 1575, he initially considered locating it in Middelburg. Ultimately he chose Leiden, however, and Middelburg—as well as all of Zeeland—remained without a university until 2004 when University College Roosevelt (formerly known as Roosevelt Academy), affiliated with Utrecht University, was established.
Cultural institutions
Theaters and Concert halls
- Schouwburg
- Concertzaal Zeeland
- Spiegeltheater
- Minitheater
- Filmtheater Schuttershof
- UCR Stand up comedy theatre
Sightseeing
- The Abbey
- Kuiperspoort
- The "Lange Jan"
- City Hall
- Oostkerk
- Damplein
Sports
Middelburg has a rugby club, Oemoemenoe, and four football (soccer) clubs: MZVC, Zeelandia Middelburg, Jong Ambon and FC Dauwendaele. Jong Ambon is translated Young Ambon, and consists of mostly Ambonese players. FC Dauwendaele is the main club in Dauwendaele.
Transportation
Middelburg has a railway station with intercity train connections to Vlissingen, Goes, Roosendaal, Rotterdam, The Hague, Leiden, Schiphol International Airport, Amsterdam, and Almere, among others. Two trains leave every hour in both directions.
Twin cities
|
In popular culture
- In Rafael Sabatini's 1929 novel "The Romantic Prince", set in the late 1460s, Middelburg is the home town of Mister Danvelt and his son Philip. The Danvelt home is a beautiful, gabled house on the Lange Delft, not far from Middelburg's imposing abbey. Philip Danvelt inherits the house and lives there with his wife Johanna when he is arrested by Lord Claude de Rhynsault.[12]
References
- "Collegeleden" [Members of the board] (in Dutch). Gemeente Middelburg. Retrieved 4 December 2013.
- "Kerncijfers wijken en buurten" [Key figures for neighbourhoods]. CBS Statline (in Dutch). CBS. 2 July 2013. Retrieved 12 March 2014.
- "Postcodetool for 4331BK". Actueel Hoogtebestand Nederland (in Dutch). Het Waterschapshuis. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 4 December 2013.
- "Bevolkingsontwikkeling; regio per maand" [Population growth; regions per month]. CBS Statline (in Dutch). CBS. 1 January 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- "Middelburg". War over Holland. Retrieved 30 April 2016.
- IMDb Database retrieved 30 November 2019
- IMDb Database retrieved 30 November 2019
- Catholic Encyclopedia, Volume 11 (1913), Paul of Middelburg retrieved 30 November 2019
- 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica, Volume 4, Bynkershoek, Cornelius Van retrieved 27 November 2019
- Zeeuws Archief
- p166-178 of the House of Stratus edition, ch. 4. The Romantic Prince, Rafael Sabatini, 2001
Literature
- Lourens, Piet; Lucassen, Jan (1997). Inwonertallen van Nederlandse steden ca. 1300–1800. Amsterdam: NEHA. ISBN 9057420082.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Middelburg. |

- Official city website (in Dutch with a limited English section)
- Tourism Middelburg

