Karpathos
Karpathos (Greek: Κάρπαθος, pronounced [ˈkarpaθos]), also Carpathos, is the second largest of the Greek Dodecanese islands, in the southeastern Aegean Sea. Together with the neighboring smaller Saria Island it forms the municipality of Karpathos, which is part of the Karpathos regional unit. Because of its remote location, Karpathos has preserved many peculiarities of dress, customs and dialect, the last resembling those of Crete and Cyprus. The island has also been called Carpathus in Latin and Scarpanto in Italian.
Karpathos Κάρπαθος | |
|---|---|
 View of the port of Pigadia | |
 Karpathos Location within the region  | |
| Coordinates: 35°35′N 27°08′E | |
| Country | Greece |
| Administrative region | South Aegean |
| Regional unit | Karpathos |
| Area | |
| • Municipality | 324.8 km2 (125.4 sq mi) |
| • Municipal unit | 219.9 km2 (84.9 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 1,215 m (3,986 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population (2011)[1] | |
| • Municipality | 6,226 |
| • Municipality density | 19/km2 (50/sq mi) |
| • Municipal unit | 5,670 |
| • Municipal unit density | 26/km2 (67/sq mi) |
| Community | |
| • Population | 2,788 (2011) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Postal code | 857 00 |
| Area code(s) | +030 22450 |
| Vehicle registration | ΚΧ, ΡΟ, ΡΚ |
| Website | www.karpathos.org |
Geography

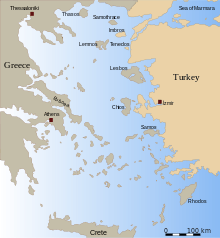
The island is located about 47 kilometres (29 miles) southwest of Rhodes, in the part of the Mediterranean which is called the Carpathian Sea (Latin: Carpathium Mare). The Sea of Crete, a sub-basin of the Mediterranean Sea, has its eastern limit defined by the island of Karpathos.[2] Karpathos' highest point is Mt. Lastos, at 1,215 metres (3,986 ft). Karpathos comprises 10 villages. Pigadia (official name Karpathos), the capital and main port of the island, is located in the southeast of the island. The capital is surrounded by the villages of Menetes, Arkasa, Aperi, Volada, Othos, and Pyles. In the north Mesochori, Spoa and Olympos. There are two ports, in Karpathos and in the north of the island next to Olympos named Diafani.
The island Saria was once united with Karpathos, but an earthquake divided them. Saria preserves many important antiquities.
Climate
The weather station of Karpathos alongside Ierapetra holds Greece's highest annual mean temperature, 20.1 °C (68 °F) (1950–1960, 1970–1975).[3]
| Climate data for Karpathos | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 15.4 (59.7) |
15.4 (59.7) |
16.7 (62.1) |
20.0 (68.0) |
23.2 (73.8) |
27.4 (81.3) |
29.0 (84.2) |
29.5 (85.1) |
27.3 (81.1) |
24.1 (75.4) |
20.4 (68.7) |
17.2 (63.0) |
22.1 (71.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 12.5 (54.5) |
12.4 (54.3) |
13.5 (56.3) |
16.6 (61.9) |
19.8 (67.6) |
24.2 (75.6) |
25.9 (78.6) |
26.8 (80.2) |
24.3 (75.7) |
20.9 (69.6) |
17.2 (63.0) |
14.3 (57.7) |
19.0 (66.3) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 9.7 (49.5) |
9.5 (49.1) |
10.4 (50.7) |
13.2 (55.8) |
16.4 (61.5) |
21.0 (69.8) |
22.9 (73.2) |
24.1 (75.4) |
21.4 (70.5) |
17.7 (63.9) |
14.1 (57.4) |
11.4 (52.5) |
16.0 (60.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 165 (6.5) |
87 (3.4) |
76 (3.0) |
25 (1.0) |
15 (0.6) |
2 (0.1) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
10 (0.4) |
60 (2.4) |
90 (3.5) |
148 (5.8) |
678 (26.7) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org [4] | |||||||||||||
Municipality

The present municipality Karpathos was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following 2 former municipalities, that became municipal units:[5]
- Karpathos
- Olympos
The municipality has an area of 324.800 km2, the municipal unit 219.924 km2.[6]
History




.jpg)
The island of Karpathos was in both ancient and medieval times closely connected with Rhodes. Its current name is mentioned, with a slight shift of one letter, in Homer's Iliad as Krapathos (οἳ δ' ἄρα Νίσυρόν τ' εἶχον Κράπαθόν τε Κάσον τε).[7] Apollonius of Rhodes, in his epic Argonautica, made it a port of call for the Argonauts travelling between Libya and Crete (Κάρπαθος: ἔνθεν δ' οἵγε περαιώσεσθαι ἔμελλον).[8] The island is also mentioned by Diodorus who claims it was a colony of the Dorians,[9] Pomponius Mela,[10] Pliny the Elder,[11] and Strabo.[12]
The Karpathians sided with Sparta in the Peloponnesian War in 431 BCE and lost their independence to Rhodes in 400 BCE. In 42 BCE, the island fell to Rome. After the division of the Roman Empire in 395 CE, the island became part of the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire.
Of its Christian bishops, the names are known of Olympius, who was a supporter of Nestorius, Zoticus (in 518), Mennas (in 553), Ioannes, Leo (in 787), and Philippus (in 879). In the 14th century, the island was a see of the Latin Church, four of whose bishops bore the name Nicolaus.[13][14] No longer a residential bishopric, Karpathos (in Latin Carpathus) is today listed by the Catholic Church as an archiepiscopal titular see.[15]
In 1304, Karpathos was given as fief to the Genoese corsairs Andrea and Lodovico Moresco, but in 1306 it fell to Andrea Cornaro, a member of the Venetian Cornaro family.[16] The Cornaro controlled Karpathos until 1538, when it passed into the possession of the Ottoman Turks.[16]
During the Greek War of Independence from 1821 to 1822, the island rebelled, but afterwards it fell again under the Ottoman rule.[16] In 1835, Sultan Mahmud II conceded to the island the privilege of the maktu tax system; that is, the tax was calculated as an annual lump sum, and not on an household basis.[16] The Ottoman rule ended on 12 May 1912, when the Italians occupied the island and the rest of the Dodecanese, during the Italo-Turkish War of 1911-12. On that day, sailors from the Regia Marina battleship Vittorio Emanuele and the destroyer Alpino landed in Karpathos.[16] With the Treaty of Lausanne (1923), Karpathos joined the other islands of the Dodecanese in the Italian possession of the Italian Aegean Islands,[16] and was ceded by Italy to Greece with the Paris Peace Treaties of 1947. The island formally joined the Kingdom of Greece on 7 March 1948, together with the other Dodecanese islands.
In the late 1940s and 1950s, due to the economic problems after World War II, a number of Karpathians emigrated to the U.S. eastern seaboard cities;. Karpathos today has a significant Greek-American constituency who have returned to their island and invested heavily. Inhabitants of the mountains to the north are more traditional.
Transportation

Karpathos Island National Airport, with its relatively large runway, is located on the south side (Afiartis area). Karpathos is connected to neighboring islands and to the mainland via ferries and airplanes. The ferries provide transport to and from Piraeus (via Crete and Rhodes). Scheduled domestic flights connect the island with Rhodes, Kasos, Crete and Athens daily. Additionally, charter flights from various European cities are frequently scheduled during the high season (April–October).
Within the island, cars are the preferred mode of transportation. The port, the airport, the main villages and other popular locations are connected by an adequate system of municipal roads, most of which are paved. During the summer months, small private boats depart from Pigadia to various locations daily, including Olympos (via Diafani) and some inaccessible beaches. Fixed-rate taxis (agoraia) and municipal buses are also available all year long.
Population
The island's 2011 census population was 6,226 inhabitants. This number more than doubles in the summer months as many Karpathian expatriates come to the island for their vacation with their families. Also, taking into consideration the number of tourists that visit, there can be up to 20,000 people on the island during the summer months. The population density is greatest during the 15th of August due to the Panagias festival (Assumption of Mary), which is considered the most important festival on the island. Individuals travel from around the world to attend the festival and view the many traditions that still remain on the island.
Census
| Town/Community | 1947 | 1951 | 1961 | 1971 | 1981 | 1991 | 2001 | 2011 | 2021 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karpathos (Pigadia) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2,788 | - |
| Menetes | 1651 | 1499 | 1413 | 1233 | 1179 | 954 | 811 | 662 | - |
| Arkasa | - | - | - | - | 390 | 394 | - | 564 | - |
| Olympos | - | - | - | - | - | - | 480 | 556 | - |
| Mesohori | - | - | - | - | 357 | 344 | - | 371 | - |
| Aperi | - | - | - | - | 457 | 402 | - | 355 | - |
| Othos | - | - | - | - | 282 | 229 | - | 281 | - |
| Volada | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 264 | - |
| Pyles | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 216 | - |
| Spoa | 339 | 340 | 380 | 293 | 251 | 254 | 341 | 169 | - |
Beaches
The beaches of Karpathos island can be divided into four large groups: the beaches on the east coast are smaller and gravelly but without wind; the beaches of the southern part of the island, near the airport, area made of fine white sand; the sandy beach on the west coast are the most exposed to the Meltemi and they are only available in low wind conditions; the beaches of the north of the island, accessible only by sea and partly by a jeep.
- East Coast: Amoopi, Karpathos Beach, Achata, Kato Latos (reachable only on foot), Kyra Panagia, Apella, Agios Nikolaos (Spoa).
- South Coast - Mihaliou o Kipos, Damatria, Diakoftis, Devils Bay, Agrilaopotamos (nude beach), Pounta beach.
- West Coast - Lefkos beach, Mesohori, Finiki, Arkasa Leucadius.
- North Coast - Diafani, Alimounta (Saria island), Palatia (Saria island), Kalamia, Vananda, Apokapos (or Papa-Mina), Opsi, Kantri, Forokli, Nati, Philios (or Agios Minas), Agnontia.
See also
- List of traditional Greek place names
Notes
- "Απογραφή Πληθυσμού - Κατοικιών 2011. ΜΟΝΙΜΟΣ Πληθυσμός" (in Greek). Hellenic Statistical Authority.
- Peter Saundry, C.Michael Hogan & Steve Baum. 2011. Sea of Crete. Encyclopedia of Earth. Eds.M.Pidwirny & C.J.Cleveland. National Council for Science and Environment. Washington DC.
- "The Climate of Magouliana of Arcadia" (PDF). The Climate of Magouliana of Arcadia (in Greek). See table 4, page 19. Academy of Athens, Research centre for Atmospheric Physics and Climatology. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-21. Retrieved 2011-02-15.
- "Climate: Karpathos". Climate-Data.org. Retrieved August 13, 2018.
- Kallikratis law Greece Ministry of Interior (in Greek)
- "Population & housing census 2001 (incl. area and average elevation)" (PDF) (in Greek). National Statistical Service of Greece. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-21.
- http://textcritical.net/work/geography/10/5/15 Geography By Strabo at TextCritical.net
- http://www.sacred-texts.com/cla/argo/argo57.htm Argonautica 4.1635-36
- Diodorus Siculus. Bibliotheca historica (Historical Library). 5.54.
- Pomponius Mela. De situ orbis. 2.7.
- Pliny. Naturalis Historia. 4.12.23, 5.31.36.
- Strabo. Geographica. x. p. 488. Page numbers refer to those of Isaac Casaubon's edition.
- Pius Bonifacius Gams, Series episcoporum Ecclesiae Catholicae, Leipzig 1931, p. 449
- Konrad Eubel, Hierarchia Catholica Medii Aevi, vol. 1, p. 439
- Annuario Pontificio 2013 (Libreria Editrice Vaticana 2013 ISBN 978-88-209-9070-1), p. 859
- Bertarelli, 137
Sources
- Bertarelli, L.V. (1929). Guida d'Italia, Vol. XVII. Consociazione Turistica Italiana, Milano.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Karpathos. |