Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on children
Children and young people are seriously affected by COVID-19 pandemic affect multiple areas including health, safety and protection issues, educational impacts, economic impacts, impact on civic space and participation. This crisis is exacerbating existing vulnerabilities and inequalities experienced by young people, all further amplified in humanitarian contexts where fragility, conflict, and emergencies have undermined institutional capacity and limited access to services.[1][2]
| Part of a series on the |
| COVID-19 pandemic |
|---|
 |
|
|
|
International response |
|
Medical response |
|
|
|
School closures
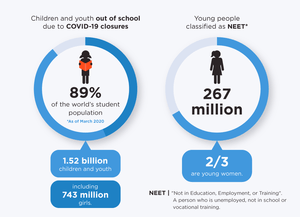
School closures and overstretched health care systems will also have acute effects on young women and girls. By the end of March 2020, UNESCO estimated that over 89 per cent of the world’s student population were out of school or university because of COVID-19 school closures, forcing many learners online with large parts of the population in low-tech or no-internet environments at a severe disadvantage. Young women and girls living in poverty, with disabilities or in rural, isolated locations are more likely to be pulled out of school first to compensate for increased care and domestic work at home.[3]
Impact on most at risk groups
Youth, especially young women, indigenous peoples, migrants and refugees, face heightened socio-economic and health impacts and an increased risk of gender-based violence due to movement restrictions, discrimination and more. They are also more prone to child marriage and other forms of violence as families find ways to alleviate economic burdens.[4][5][6][7]
Unemployment
Unemployment, too, will hit young people particularly hard: Following the 2008 economic recession, youth unemployment rates were significantly higher in many places than overall averages, and the recent expansion of the gig economy will likely heighten this disparity. Before the pandemic even hit, there was already an upward trend in the number of youth not in employment, education or training (NEET). Out of the some 267 million young people globally classified as NEET, two-thirds, or 181 million, are young women.[8][9]
Impact on young migrants
This global crisis is exacerbating existing vulnerabilities and inequalities experienced by young people, all further amplified in humanitarian contexts where fragility, conflict, and emergencies have undermined institutional capacity and limited access to services.[1][10] Young migrants, young people who are internally displaced and refugees, young people living in poor, high-density urban areas, young people without a home, young people living with disabilities, girls and young women, lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) young people and those living with HIV will be particularly affected; young people separated from, unaccompanied by, or left behind by migrant working parents face higher risks of exploitation, violence and mental health issues, and already poor access to health services and protection.[1][10]
Sources
![]()
References
- "COVID-19: Working with and for young people". www.unfpa.org. May 2020. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- Harvard Health Publishing (15 May 2020). "Coronavirus outbreak and kids". Harvard Health. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- https://plus.google.com/+UNESCO (31 March 2020). "Covid-19 school closures around the world will hit girls hardest". UNESCO. Retrieved 24 June 2020.
- "UN Secretary-General's policy brief: The impact of COVID-19 on women | Digital library: Publications". UN Women. Retrieved 24 June 2020.
- UN Women. Families in a changing world / UN Women. New York:. ISBN 1-63214-156-6. OCLC 1120137550.CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link)
- Women, U. N. "How COVID-19 impacts women and girls". interactive.unwomen.org. Retrieved 24 June 2020.
- "Gender equality matters in COVID-19 response". UN Women. Retrieved 24 June 2020.
- "Youth exclusion from jobs and training on the rise". www.ilo.org. 9 March 2020. Retrieved 24 June 2020.
- "Global Employment Trends for Youth 2020: Technology and the future of jobs". 9 March 2020. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - CDC (11 February 2020). "Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 5 June 2020.