Hockenheimring
The Hockenheimring Baden-Württemberg (German: [ˈhɔkn̩haɪmʁɪŋ ˌbaːdn̩ ˈvʏʁtəmbɛʁk] (![]()
 | |
| Location | Am Motodrom, Hockenheim, Baden-Württemberg, Germany |
|---|---|
| Time zone | UTC +1 |
| Capacity | 120,000 |
| FIA Grade | 1 |
| Broke ground | 23 March 1932 |
| Opened | 29 May 1932 |
| Major events | FIA Formula One German Grand Prix DTM World RX of Hockenheim NASCAR Whelen Euro Series NitrolympX |
| Hockenheimring (2002–present) | |
| Surface | Asphalt |
| Length | 4.574 km (2.842 mi) |
| Turns | 17 |
| Race lap record | 1:13.780 ( |
| National Circuit (2002–present) | |
| Surface | Asphalt |
| Length | 3.629 km (2.255 mi) |
| Turns | 15 |
| DTM National Circuit (2010–present) | |
| Surface | Asphalt |
| Length | 2.638 km (1.639 mi) |
| Turns | 16 |
| Hockenheimring (1965–2001) | |
| Surface | Asphalt, concrete |
| Length | 6.823 km (4.240 mi) |
| Turns | 16 |
| Race lap record | 1:41.808 ( |
| Short Course (1966–2001) | |
| Surface | Asphalt |
| Length | 2.638 km (1.639 mi) |
| Kurpfalzring (1938–1965) | |
| Surface | Asphalt |
| Length | ≈7.738 km (≈4.808 mi) |
| Hockenheimer-Dreieck (1932–1938) | |
| Surface | Asphalt |
| Length | ≈12.12 km (≈7.53 mi) |
| Website | www |
History

1932–1938
Originally called "Dreieckskurs" (triangle course), the Hockenheimring was built in 1932. The man behind it is Ernst Christ, a young timekeeper who felt that a racing track should be built in his hometown of Hockenheim. He submitted the plans to the mayor and they were approved on Christmas day, in 1931. This first layout of the track was around twelve kilometres long and consisted of a large triangle like section, a hairpin in the city and two straights connecting them.
1938–1965

In 1938, the circuit dramatically shortened, from twelve kilometres down to just over seven and a half, and the Ostkurve corner, which lasted until 2001, was introduced for the first time. In that year, the track was also renamed to "Kurpfalzring". The track was damaged by tanks during World War II. After the war, the track was repaired, and renamed to "Hockenheimring". Former DKW and NSU factory rider and world record setter Wilhelm Herz became the manager of the track in 1954 and promoted the track successfully; Grand Prix motorcycle racing events were held, with the German motorcycle Grand Prix alternating between the Hockenheimring and other tracks. This version of the circuit was just over seven and a half kilometres long and consisted of the original two long straights, with the Ostkurve in the forest and the original hairpin inside Hockenheim joining them together.
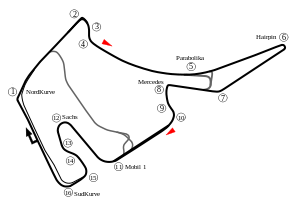
1965–2001
In 1965, when the new Autobahn A 6 separated the village from the main part of the track, a new version of Hockenheim circuit was built, with the "Motodrom" stadium section, designed by John Hugenholtz, who also designed Suzuka. After Jim Clark was killed on 7 April 1968 in a Formula 2 racing accident, two fast chicanes were added and the track was lined with crash barriers in 1970. A small memorial was placed near the first chicane (which was named after him), at the site of his accident. In 1982, another chicane was added at the Ostkurve (east curve), after Patrick Depailler was killed there in 1980, and the first chicane was made slower as well. For the 1992 German Grand Prix, the Ostkurve was changed yet again, from a quick left turn into a more complex right-left-right chicane, after Érik Comas crashed there in 1991. The second chicane was renamed after Ayrton Senna, after his death at the 1994 San Marino Grand Prix.
This version used to be quite large, with a very long and very fast section going through forests essentially consisting of four straights of roughly 1.3 km, separated by a chicane sequence, followed by a more tight and twisty "stadium" section (so called because of all the grandstands situated there) named Motodrom. This made the setting up of racing cars difficult, since a choice had to be made – whether to run low downforce to optimize speed through the straights and compromise grip in the stadium section, or vice versa. The long track length also meant that a typical Formula One race had only 45 laps, limiting the spectators' experience of the race to only that many passes through the stadium.
During the mid-1980s "turbo era" of Formula One where fuel was restricted to either 220 (1984–85), 195 (1986–87) or 150 (1988) litres for races for the turbo powered cars, Hockenheim also saw drivers, including World Champion Alain Prost, at times fail to finish due to simply running out of fuel near the end of the race. Prost ran out at the end of the 1986 race, pushing his McLaren towards the line before giving up. He was placed 3rd when he ran dry and was eventually classified 6th, gaining a valuable championship point that would help him with his second World Championship.
Many problems came to light during the 2000 German Grand Prix, where Brazilian driver Rubens Barrichello won from having started 18th on the grid, in changeable weather conditions. All the overtaking moves that took place during the race were in the chicanes of the forest sector, meaning hardly any spectators saw most of the best action. French driver Jean Alesi had a massive accident at the 3rd chicane after a collision in the braking zone with Pedro Diniz, which saw Alesi's car spin uncontrollably down the track, causing him to suffer dizziness for 3 days. A former Mercedes-Benz employee, who had been dismissed, breached the track's security barriers on the first main straight, showing vulnerable security facilities in the forest and bringing out a safety car that slowed down the Mercedes-powered McLarens.
These events prompted much protest from the FIA to greatly improve spectator viewing, safety, and security at the track, as it had become clear that the track was no longer suited to modern Formula One racing.
During the television coverage of the qualifying session of the 2002 German Grand Prix held on the new circuit, former F1 driver and current lead TV commentator for Sky Sports Formula One coverage Martin Brundle stated that he, along with other drivers of his era (mid-1980s to the mid-1990s), did not particularly enjoy racing at the old Hockenheim as the long straights often saw only seven or eight finishers from twenty-six starters, with most dropping out through engine or transmission failure caused by the long periods at high speed on the forest straights.
2002 redesign
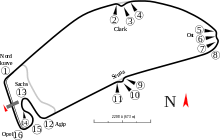
.png)
.jpg)
In the early 2000s, F1 officials demanded the 6.823 km (4.240 mi) track be shortened and threatened to discontinue racing there, due to competition from other tracks such as the EuroSpeedway Lausitz and sites in Asia. The state government of Baden-Württemberg secured the financing for the redesign by Hermann Tilke for the 2002 German Grand Prix. The stadium section remained mostly intact, despite a new surface and a tighter Turn 1 ("Nordkurve"). However, the circuit was dramatically shortened, with the long, forested straights section chopped off in favour of more tight corners. More than half of the first straight and pretty much all of the straight between the Ostkurve and Senna chicane were cut and the rest was connected with a new long straight called the "Parabolika", with a small kink being added between the first straight and the new one. A small right-left-right complex was added to the remaining part of the final straight, with a new grandstand overlooking it. In an extremely controversial move, the old forest section was torn up and replanted with trees, eliminating any chance of using the old course either for future F1 events or for historic car events.
There was and still remains a great deal of criticism of the track redesign, in terms of ruining the previous unique technical challenges of the old Hockenheim circuit and delivering a new homogenised "assembly line" circuit without the character of the previous layout, whilst being beset by the perceived problems of other Tilke circuits.[2] Several drivers and team principals, including Ron Dennis, Jarno Trulli and Juan Pablo Montoya, criticised the changes and stated their preference for the old circuit.[3]
The change in the track layout also saw the installation of a new memorial to Jim Clark. This is located at the outside of the current track's turn 2, where the old track continued out into the forests, and the new shortened track turns to the right.[4]

The new track has a seating capacity of 120,000, due to new large grandstands sponsored by Mercedes-Benz. The complex also features a quarter-mile track for drag racing. It hosts one of the largest drag racing events in Europe, known as the NitrOlympx, and was one of the last Top Fuel circuits to race to 0.25 miles (400 m) before the FIA switched the nitro categories to the now-recognised 1,000 feet (300 m) distance in 2012.
Formula One
The Hockenheim Circuit hosted the German Grand Prix for the first time in 1970 when the F1 drivers decided at the French Grand Prix to boycott the Nürburgring unless major changes were made. The next year the German Grand Prix went back to the Nürburgring until the 1976 German Grand Prix. From 1977 to 2006, the Hockenheimring hosted the German Grand Prix with the exception of 1985, when the race was held at the reconfigured Nürburgring.
In July 2006, Bernie Ecclestone announced that from 2007 onwards, there would be only one Grand Prix per year in Germany. Since 1995, there had been two Grands Prix every year in Germany; the German Grand Prix at Hockenheim, plus either the European Grand Prix or the Luxembourg Grand Prix at the Nürburgring. From 2007, the Nürburgring and Hockenheimring alternated hosting the German Grand Prix, starting with the Nürburgring in 2007.

Ongoing deficits of the Formula One races, amounting to up to 5.3 million Euro per race that had to be covered by the local communities, made it likely the contract between the Hockenheimring and Formula One Management would not be extended after the Grand Prix of 2010.[5] However, in October 2009 the contract for the circuit to hold the German GP was extended to 2018, with the FOA agreeing to cover any losses the event incurs.[6] Neither Hockenheim nor the Nürburgring hosted the 2015 German Grand Prix after the tracks failed to complete an agreement with Formula 1's commercial rights holder Bernie Ecclestone.[7]
Drag racing (NitrolympX – Rico Anthes Quartermile)
From 1986 to 1988, the start–finish straight was used for 1/8 mile drag racing. In 1989, a proper drag strip was built by connecting the Opel-Kurve and the first turn entering the Motodrom section. The finish line was at the beginning of the forest, with a very long run-off on the straight in the forest. Competitors had to travel around the full race track in opposite direction to return to the paddock.
The drag strip is only used for two events in August, the Public Race Days and the NitrolympX main event a week later. Originally named the Nitrolympics and featuring Top Fuel dragsters, it was renamed to NitrolympX.
When the Hockenheimring was shortened in 2002, the drag strip was moved back, closer to the new tall Tower stands that allow an unusual view along the drag strip.[8] Even though the run off was cut in half it remains one of the longest in drag racing. The NitrolympX usually host most European Drag Racing Championship, sanctioned by FIA or FIM, plus jet dragsters and other entertaining events on the Saturday night show that draws 40,000 spectators.[9]
The drag strip in 2008 was christened Rico Anthes Quartermile after the German former Top Fuel driver and long-time organizer of the NitrolympX had retired in 2007. As the dragstrip can only be prepared for professional drag racing after the last major circuit event, mainly the Formula One race, the grip is often sub par compared to permanent drag strips that host two Euro Championship events each year, like Santa Pod Raceway in England or Tierp Arena in Sweden. The best performances on the full quarter-mile were significantly below those in Santa Pod, and the best ET was set in 2005: 4.873 sec. and 458 km/h by Brady Kalivoda (USA).[10]
In 2012, some Pro classes could not find traction as Formula One had demanded a new surface. In subsequent years, the organizers provided a better track, with support from Santa Pod personnel and machinery. In 2016, Hockenheim, and mainland Europe, finally saw the first 3-second Top Fuel 1000 ft passes, with 3.939 sec. and 486.91 km/h by Anita Mäkelä (FIN). An overall European record for Super Street Bike was set by Garry Bowe (GB) with 7.04s 340,69 km/h.[11]
DTM
The DTM (Deutsche Tourenwagen Masters) series has regularly raced at the Hockenheimring since its revival in 2000. In most years, the DTM has competed there twice during a season.
Rallycross
Located in the stadia section of the track, the rallycross track uses a section of track from turns 11 to 16, combined with a dirt section in front of the grandstands. It hosted first ever World RX of Hockenheim, round 2 of FIA World Rallycross Championship in 2015 as supporting event of DTM. WRX also combined with the DTM for an event there in 2017.[12]
Record lap times
Official record lap times are only set during the race. The fastest ever lap on the track is 1:11.212 set by Sebastian Vettel in a Ferrari SF71H during qualifying at the 2018 German Grand Prix.
| Category | Time | Driver | Car | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formula One | 1:13.780 | McLaren MP4-19B | 2004 German Grand Prix | |
| GP2 Series | 1:23.110 | Dallara GP2/10 | 2010 Hockenheimring GP2 Series round | |
| GP3 Series | 1:31.853 | Dallara GP3/10 | 2010 Hockenheimring GP2 Series round | |
| FIA World RX | 1:43.764 | Citroën DS3 | 2015 World RX of Hockenheim |
Music events
- Michael Jackson
- Bad World Tour – 10 July 1988[13]
- HIStory World Tour – 10 August 1997[14]
- Tina Turner – Foreign Affair: The Farewell Tour – 26 August 1990
- Pink Floyd – The Division Bell Tour – 13 August 1994
- The Rolling Stones
- Voodoo Lounge Tour – 19 August 1995
- Licks Tour and 22 June 2003 with AC/DC
- AC/DC
- Stiff Upper Lip World Tour, with Buddy Guy, Die Toten Hosen & Megadeth – 10 June 2001
- Black Ice World Tour – 22 May 2009
- Rock or Bust World Tour – 16 May 2015
- Robbie Williams – Close Encounters Tour – 12–13 August 2006
- Sonisphere Festival, headlined by Metallica – 2009[15]
- Hardwell - 2016
- Ed Sheeran – ÷ Tour – 22–23 June 2019
Fatal accidents
- 1968 Jim Clark, during a Formula 2 race
- 1972 Bert Hawthorne, during a Formula 2 race
- 1980 Markus Höttinger, during a Formula 2 race
- 1980 Patrick Depailler, during a private test session
- 1986 Tony Boden, during drag racing meeting
- 2014 Albert Fleming, during Bosch Hockenheim Historic
References
- "List of FIA Licensed Circuits" (PDF). FIA. 6 February 2015. Retrieved 28 May 2015.
- "Is Hermann Tilke Slowly Killing Formula One?". Bleacher Report. 15 September 2008. Archived from the original on 15 September 2008. Retrieved 3 July 2016.
- Collantine, Keith (22 July 2010). "Changing tracks: Hockenheimring". F1Fanatic. Retrieved 9 January 2016.
- "Jim Clark Memorial, Hockenheimring". www.youtube.com.
- Hockenheim muss um Formel 1 bangen Focus Online, 12 September 2008
- Hockenheim holds on to German GP BBC Sport, 30 September 2009
- Hockenheim rules out hosting German GP motorsport.com, 17 March 2015.
- Axel Schirdewahn. "Nitrolympx 2016 Final Run Top Fuel Dragster Micke Kagered vs. Anita Mäkelä" – via YouTube.
- "NitrolympX Facebook page". Facebook.
- https://www.dragracing.de/showthread.php?1160-Hockenheim-2005-aus-Kath-Bros-Sicht!. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - "Top-Fuel-Pilotin Anita Mäkelä fährt erste 3-Sekunden-Zeit in Hockenheim - Hockenheimring Baden-Württemberg". www.hockenheimring.de.
- Red Bull WRX https://www.redbull.com/gb-en/wrx-hockenheim-report. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - Michael Jackson History Tour Dates Archived 2011-07-14 at the Wayback Machine Jackson Trader
- HIStory World Tour (1996–97) Archived 2010-01-13 at the Wayback Machine The Michael Jackson Fan Club
- "Metallica live in Hockenheim, Germany, July 4 2009 – Metal Traveller". metaltraveller.com. Retrieved 3 July 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hockenheimring. |
- The official website of the Hockenheimring (English version)
- Hockenheimring Circuit History and Statistics The Formula One Database
- Circuit Guide – Hockenheim, Germany BBC Sport, 17 February 2006
- Onboard video of one lap of Hockenheimring (MP4, 9,7 MB) Fastvoice
- Chronos Hockenheim Court Absolute Cars – Hockenheim Short Power Laps
- The Hockenheimring on Google Maps (Current Formula 1 Tracks)
- The History of the Hockenheimring Official website
- Official Facebook page
- Live webcam of the circuit Official website