Avalon Beach, New South Wales
Avalon Beach is a northern beachside suburb of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. It is 37 kilometres north of the Sydney central business district, in the local government area of Northern Beaches Council, in the Northern Beaches region. The area was previously called Avalon, with the name Avalon Beach being assigned during a change in boundaries and names in the Pittwater region in 2012.[2]
| Avalon Beach Sydney, New South Wales | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Avalon Beach, looking north | |||||||||||||||
| Population | 9,905 (2016 census)[1] | ||||||||||||||
| Established | 1921 | ||||||||||||||
| Postcode(s) | 2107 | ||||||||||||||
| Location | 37 km (23 mi) north of Sydney CBD | ||||||||||||||
| LGA(s) | Northern Beaches Council | ||||||||||||||
| State electorate(s) | Pittwater | ||||||||||||||
| Federal Division(s) | Mackellar | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
History
The Pittwater and Northern Beaches area was formerly inhabited by the Garigal or Caregal people in a region known as Guringai country.[3]
European settlement
Avalon was named after the mythical Avalon, a legendary island in Celtic languages mythology. According to legends, Avalon was an earthly paradise and the final resting place of King Arthur.[4]
The first land grant in the area was 240,000 square metres (60 acres) to John Farrell in 1827. In 1833 a 4.9-square-kilometre (1,200-acre) land grant was made to Australia's first Catholic priest, John Joseph Therry, by Governor Bourke. A further grant of 280 acres made in 1837 meant that Therry's holdings covered most of the peninsula from Newport to Whale Beach.[5] He built a church in this area but his plans for a settlement never eventuated. Therry fought hard for the recognition of the Catholic Church in the colony. After he died, the land was left to the Jesuit order and was then sold to help finance the rebuilding of St. Mary's Cathedral in Sydney.[6] In the 1920s, the area was still known as 'Priest's Flat'. Arthur J Small handled a subdivision in 1921 and chose the name Avalon.[4] Lots were sold for £100 each and included two year's free membership in the local golf club.[6]
Significant housing developments took place during the 1920s. The architect Alexander Stewart Jolly designed a number of houses that were built in the Avalon area in that period. Loggan Rock was a flamboyant log cabin combined with a stone tower; the combination of logs and rocks gave rise to the name. The house is heritage-listed.[7] Careel House is a bungalow made of stone that was quarried in the area. Nowadays it is on the Whale Beach side of the boundary. It is also heritage-listed.[8] Hy Brasil, located near Clareville, was built in 1936, but was originally known as The Gem. Later it was bought by Ted Herman, son of the painter Sali Herman, who changed the name, using the name of a mythical island west of Ireland. It is heritage-listed.[9] A sandstone cottage known as Wickham, designed by Walter Burley Griffin, was unfortunately demolished with council approval in 1994.
Another significant development was the creation of Ruskin Rowe in 1950. This street was designed as an estate by the architect Harry Ruskin Rowe, son of the architect Thomas Rowe. Rowe created covenants to preserve the character of the estate, but they have been ignored to an extent over the years. Nevertheless, the estate is heritage-listed because of its historic significance, as well as its scientific significance in preserving the bushland environment of the area.[10]
Early subdivision plans
 Avalon Beach Estate Plateau Rd, Park Reserve, 1921-1926
Avalon Beach Estate Plateau Rd, Park Reserve, 1921-1926 Avalon Beach Central Estate, Avalon Pde, Barrenjoey Rd, 1921-1926
Avalon Beach Central Estate, Avalon Pde, Barrenjoey Rd, 1921-1926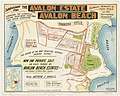 Avalon Beach Estates, Central Rd, Plateau Rd, 1921-1926
Avalon Beach Estates, Central Rd, Plateau Rd, 1921-1926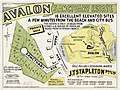 Avalon Sanctuary Estate, Park Ave, 1921-1926
Avalon Sanctuary Estate, Park Ave, 1921-1926
Heritage listings
Avalon Beach has a number of heritage-listed sites, including:
- 32 Plateau Road: Walter Burley Griffin Lodge[11]
- 111 Whale Beach Road: Loggan Rock[12]
Demographics
According to the 2016 census of Population, there were 9,905 residents in Avalon Beach. 73.3% of people were born in Australia. The next most common countries of birth were England 9.6%, New Zealand 2.0% and United States of America 1.1%. 90.2% of people only spoke English at home. The most common responses for religious affiliation were No Religion 43.0%, Catholic 19.4% and Anglican 18.6%.[1]
Commercial areas
Avalon Beach features an RSL club, bowling and sailing clubs; a golf club, a supermarket, shops, offices, cafes and a cinema. It is unique in that this large commercial centre is separated from the beach only by the road, a fact which until recently was used to argue against commercialisation of the beach side buildings themselves as restaurants and cafes were already so close to the beach.
Sport and recreation
Avalon Beach is a surfing beach and has a 25-metre salt water rock pool at the south end. Avalon Beach SLSC members patrol Avalon Beach.[13] Several former surfing world champions are also past or current Avalon residents; including Ben Player.
Avalon Soccer Club, established 1982, has over 80 teams and 1000 registered players. Avalon Junior Rugby League Club has contributed several players active in the Australian National Rugby League. Avalon also has a small nine-hole golf course.
Pittwater Council has created the Bangalley Headland Walk, which goes through part of the Careel Headland Reserve. The track starts at Whale Beach Road and goes to Marine Parade. St Michaels Cave is an interesting coastal feature.
Schools
- Barrenjoey High School
- Avalon Public School
- Maria Regina Catholic Primary School
- Montessori public school on the former grounds of Barrenjoey Highschool
Culture/politics
An episode of the American television show Baywatch was shot at Avalon Beach in the late 1990s. Producers of the show, seeking to relocate from their Californian base due to cost constraints, proposed a full relocation to Avalon and promised an upgrading of the SLSC in return, painting a huge sign saying "Avalon Beach" across the surf club. However, following complaints from residents (supported by former world surfing champion and local property owner Mark Warren), the series moved instead to Hawaii. The anti-Baywatch supporters were led by former Pittwater mayor Alex McTaggart, who was subsequently elected to NSW State Parliament for two years.
In 2011-13 there was a move by the Avalon Beach Surf Life Saving club officials, led by Christine Hopton, to replace the existing surf club. The development went ahead despite opposition from local residents in the land and environment court.
Gallery
Loggan_Rock-1.jpg) Loggan Rock, designed by Alexander Stewart Jolly
Loggan Rock, designed by Alexander Stewart JollyCareel_Head-2.jpg) Careel Head
Careel HeadBangalley_Head.jpg) Bangalley Head
Bangalley HeadSt_Marks_Avalon.jpg) St Mark's Church
St Mark's ChurchBaptist_Church_Avalon.jpg) Baptist Church
Baptist ChurchWhale_Beach_Road_house-1.jpg) Home in Whale Beach Road designed to blend in with the bush
Home in Whale Beach Road designed to blend in with the bush Avalon Beach town centre
Avalon Beach town centre
Notable residents
- Mandy Zieren (1978-), competitive bodyboarder
- Yahoo Serious, actor and director
References
- Australian Bureau of Statistics (27 June 2017). "Avalon Beach (State Suburb)". 2016 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 18 February 2018.

- Pearce, Greg. "Avalon Beach And Bilgola Beach Approved". Archived from the original on 4 April 2015. Retrieved 2015-04-23.
- "Aborigines". Pittwater Library. Retrieved 9 October 2014.
- The Book of Sydney Suburbs, Compiled by Frances Pollon, Angus & Robertson Publishers, 1990, Published in Australia ISBN 0-207-14495-8, page 13
- Messent, David (1999). Sydney's Northern Beaches. Sydney: David Messent Photography. p. 127. ISBN 0 9577124 05.
- Messent, David (1999). Sydney's Northern Beaches. Sydney: David Messent Photography. p. 128. ISBN 0 9577124 05.
- State Heritage Website
- State Heritage Website
- State Heritage Website
- State Heritage Website
- "Walter Burley Griffin Lodge". New South Wales State Heritage Register. Office of Environment and Heritage. H01510. Retrieved 18 May 2018.
- "Loggan Rock". New South Wales State Heritage Register. Office of Environment and Heritage. H01779. Retrieved 18 May 2018.
- "Avalon Beach Surf Life Saving Club". Avalonbeachslsc.com.au. 17 January 2010. Retrieved 27 January 2010.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Avalon Beach, New South Wales. |