Astrological sign
In Western astrology, astrological signs are the twelve 30° sectors of the ecliptic, starting at the vernal equinox (one of the intersections of the ecliptic with the celestial equator), also known as the First Point of Aries. The order of the astrological signs is Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius and Pisces. Each sector was named for a constellation it was passing through in times of naming.

The concept of the zodiac originated in Babylonian astrology, and was later influenced by Hellenistic culture. According to astrology, celestial phenomena relate to human activity on the principle of "as above, so below", so that the signs are held to represent characteristic modes of expression.[1] Modern discoveries about the true nature of celestial objects have undermined the theoretical basis for assigning meaning to astrological signs, and empirical scientific investigation has shown that predictions and recommendations based on these systems are not accurate.[2]:85;[3]:424 Astrology is generally regarded as pseudoscience.
Various approaches to measuring and dividing the sky are currently used by differing systems of astrology, although the tradition of the Zodiac's names and symbols remain consistent. Western astrology measures from Equinox and Solstice points (points relating to equal, longest and shortest days of the tropical year), while Jyotiṣa or Vedic astrology measures along the equatorial plane (sidereal year). Precession results in Western astrology's zodiacal divisions not corresponding in the current era to the constellations that carry similar names,[4] while Jyotiṣa measurements still correspond with the background constellations.[5]
Western zodiac signs
History and symbolism
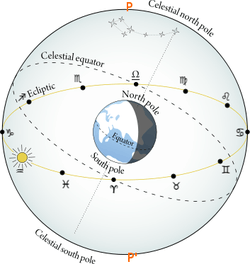
Western astrology is a direct continuation of Hellenistic astrology as recorded by Ptolemy in the 2nd century. Hellenistic astrology in turn was partly based on concepts from Babylonian tradition. Specifically, the division of the ecliptic in twelve equal sectors is a Babylonian conceptual construction.[6]
By the 4th century BC, Babylonian astronomy and its system of celestial omens had an influence on the culture of ancient Greece, as did the astronomy of Egypt by late 2nd century BC. This resulted, unlike the Mesopotamian tradition, in a strong focus on the birth chart of the individual and in the creation of Horoscopic astrology, employing the use of the Ascendant (the rising degree of the ecliptic, at the time of birth), and of the twelve houses. Association of the astrological signs with Empedocles' four classical elements was another important development in the characterization of the twelve signs.
The body of the Hellenistic astrological tradition as it stood by the 2nd century is described in Ptolemy's Tetrabiblos. This is the seminal work for later astronomical tradition not only in the West but also in India and in the Islamic sphere, and has remained a reference for almost seventeen centuries as later traditions made few substantial changes to its core teachings.
The following table enumerates the twelve divisions of celestial longitude, with the Latin names (still widely used) and the English translation (gloss), which express the constellation they are named for. The longitude intervals, are treated as closed for the first endpoint (a) and open for the second (b) – for instance, 30° of longitude is the first point of Taurus, not part of Aries. The sign numbers, 0 through 11, are seen instead of the symbols in some astronomical works.
Any association of calendar dates with these signs only makes sense when referring to Sun sign astrology.
| Sign | Symbol | Number | Ecliptic longitude (a ≤ λ < b) |
Gloss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aries | 0 | 0° to 30° | The Ram | |
| Taurus | 1 | 30° to 60° | The Bull | |
| Gemini | 2 | 60° to 90° | The Twins | |
| Cancer | 3 | 90° to 120° | The Crab | |
| Leo | 4 | 120° to 150° | The Lion | |
| Virgo | 5 | 150° to 180° | The Maiden | |
| Libra | 6 | 180° to 210° | The Scales | |
| Scorpio | 7 | 210° to 240° | The Scorpion | |
| Sagittarius | 8 | 240° to 270° | The Archer (Centaur) | |
| Capricorn | 9 | 270° to 300° | The Goat | |
| Aquarius | 10 | 300° to 330° | The Water-bearer | |
| Pisces | 11 | 330° to 360° | The Fish |
Polarity and the four elements
Empedocles, a fifth-century BC Greek philosopher, identified Fire, Earth, Air, and Water as elements. He explained the nature of the universe as an interaction of two opposing principles called love and strife manipulating the four elements, and stated that these four elements were all equal, of the same age, that each rules its own province, and each possesses its own individual character. Different mixtures of these elements produced the different natures of things. Empedocles said that those who were born with near equal proportions of the four elements are more intelligent and have the most exact perceptions.[7]
Each sign is associated with one of the classical elements (fire, air, earth, and water),[8][9] and these can also be grouped according to polarity (positive or negative): Fire and Air signs are considered positive signs while Water and Earth signs are considered negative signs. The four astrological elements are also considered as a direct equivalent to Hippocrates' personality types (sanguine = air; choleric = fire; melancholic = earth; phlegmatic = water). A modern approach looks at elements as "the energy substance of experience"[10] and the next table tries to summarize their description through keywords.[11][12]
| Polarity | Element | Symbol[13] | Keywords | Signs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive (Male) (self-expressive) |
Fire | Assertion, drive, willpower | Aries, Leo, Sagittarius | |
| Air | Communication, socialization, conceptualization | Gemini, Libra, Aquarius | ||
| Negative (Female) (self-containing) |
Earth | Practicality, caution, material world | Taurus, Virgo, Capricorn | |
| Water | Emotion, empathy, sensitivity | Cancer, Scorpio, Pisces | ||
Classification according to element has gained such importance, that some astrologers start their interpretation of a natal chart, by studying the balance of elements shown by the position of planets and angles[14] (especially the Sun, the Moon and the Ascendant signs).
The three modalities
Each of the four elements manifests in three modalities: Cardinal, Fixed and Mutable.[15] As each modality comprehends four signs, these are also known as Quadruplicities.[8][9]
| Modality | Symbol[16] | Keywords[17][18] | Signs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cardinal | Action, dynamic, initiative, great force | Aries, Cancer, Libra, Capricorn | |
| Fixed | Resistance to change, great willpower, inflexible | Taurus, Leo, Scorpio, Aquarius | |
| Mutable | Adaptability, flexibility, resourcefulness | Gemini, Virgo, Sagittarius, Pisces | |
The combination of element and modality provides a basic sign characterization. For instance, Capricorn is a cardinal earth sign, meaning that it is associated with action (cardinal modality) in the material world (earth element).[19] The next table displays the twelve combinations of elements and modalities.
| Element | Fire | Earth | Air | Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardinal | Aries | Capricorn | Libra | Cancer |
| Fixed | Leo | Taurus | Aquarius | Scorpio |
| Mutable | Sagittarius | Virgo | Gemini | Pisces |
Planetary rulerships

Rulership is the connection between planet and correlated sign and house.[20] The traditional rulerships are as follows: Aries (Mars), Taurus (Venus), Gemini (Mercury), Cancer (Moon), Leo (Sun), Virgo (Mercury), Libra (Venus), Scorpio (Pluto), Sagittarius (Jupiter), Capricorn (Saturn), Aquarius (Uranus), and Pisces (Neptune).[21][22]
Psychologically-oriented astrologers often believe that Saturn is the ruler or co-ruler of Aquarius instead of Uranus; Neptune is the ruler or co-ruler of Pisces instead of Jupiter, and that Pluto is the ruler or co-ruler of Scorpio instead of Mars. Some astrologers[23] believe that the planetoid Chiron may be the ruler of Virgo, while other group of modern astrologers claim that Ceres is the ruler of Taurus instead.
Dates table
The following table shows both traditional[21] and modern[24] rulerships.
| Symbol | Unicode Char |
Sign names | Dates | Ruling celestial body Modern |
Ruling celestial body Classical |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ♈ | Aries | March 21 – April 20 | Mars | Mars | |
| ♉ | Taurus | April 21 – May 20 | Venus | Venus | |
| ♊ | Gemini | May 21 – June 21 | Mercury | Mercury | |
| ♋ | Cancer | June 22 – July 22 | Moon | Moon | |
| ♌ | Leo | July 23 – August 23 | Sun | Sun | |
| ♍ | Virgo | August 23 – September 21 | Mercury | Earth | |
| ♎ | Libra | September 22 – October 22 | Venus | Venus | |
| ♏ | Scorpio | October 23 – November 21 | Pluto | Mars | |
| ♐ | Sagittarius | November 22 – December 21 | Jupiter | Jupiter | |
| ♑ | Capricorn | December 22 – January 20 | Saturn | Saturn | |
| ♒ | Aquarius | January 21 – February 19 | Uranus | Saturn | |
| ♓ | Pisces | February 20 – March 20 | Neptune | Jupiter | |
The twelves signs each have opposites, resulting in six opposite couples. Fire and Air elements are opposites and Earth and Water elements are opposites.[25] Spring signs are opposite to autumn ones, and winter signs are opposite to summer ones.[26][27][28][29]
- Aries is opposite to Libra
- Cancer is opposite to Capricorn
- Gemini is opposite to Sagittarius
- Pisces is opposite to Virgo
- Taurus is opposite to Scorpio
- Leo is opposite to Aquarius
Dignity and detriment, exaltation and fall
A traditional belief of astrology, known as essential dignity, is the idea that the Sun, Moon and planets are more powerful and effective in some signs than others, because the basic nature of both is held to be in harmony. By contrast, they are held to find some signs to be weak or difficult to operate in because their natures are thought to be in conflict. These categories are Dignity, Detriment, Exaltation and Fall.
- Dignity and Detriment: A planet is strengthened or dignified if it falls within the sign that it rules. In other words, it is said to exercise Rulership of the sign. For example, the Moon in Cancer is considered "strong" (well-dignified). If a planet is in the sign opposite which it rules (or is dignified in), it is said to be weakened or in Detriment (for example, the Moon in Capricorn).[30]
In traditional astrology, other levels of Dignity are recognised in addition to Rulership. These are known as Exaltation, Triplicity, Terms or bounds, and Face or Decan, which together are known as describing a planet's Essential dignity, the quality or ability of one's true nature.[30]
- Exaltation and Fall: In addition, a planet is also strengthened when it is in its sign of Exaltation. In traditional horary astrology, Exaltation denotes a level of dignity somewhat exaggerated compared to rulership. Exaltation was considered to give the planet (or what it signified in a horary chart) dignity, with the metaphor of an honoured guest – who is the centre of attention but the extent of their ability to act is limited. Examples of planets in their Exaltation are: Saturn (Libra), Sun (Aries), Venus (Pisces), Moon (Taurus), Mercury (Virgo, although some disagree to this classification), Mars (Capricorn), Jupiter (Cancer). A planet in the opposite sign of its Exaltation is said to be in its Fall, and thus weakened, perhaps seemingly more so than Detriment.[30] There is no agreement as to the signs in which the three extra-Saturnian planets may be considered to be exalted.[31]
The following table summarizes the positions described above:
| Planet (Symbol) | Dignity | Detriment | Exaltation | Fall |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sun ( | Leo | Aquarius | Aries | Libra |
| Moon ( | Cancer | Capricorn | Taurus | Scorpio |
| Mercury ( | Gemini and Virgo | Sagittarius and Pisces | Virgo | Pisces |
| Venus ( | Libra and Taurus | Aries and Scorpio | Pisces | Virgo |
| Mars ( | Aries and Scorpio | Libra and Taurus | Capricorn | Cancer |
| Jupiter ( | Sagittarius and Pisces | Gemini and Virgo | Cancer | Capricorn |
| Saturn ( | Capricorn and Aquarius | Cancer and Leo | Libra | Aries |
| Earth | Virgo | Scorpio | Leo | Cancer |
In addition to essential dignity, the traditional astrologer considers Accidental dignity of planets. This is placement by house in the chart under examination. Accidental dignity is the planet's "ability to act." So we might have, for example, Moon in Cancer, dignified by rulership, is placed in the 12th house it would have little scope to express its good nature.[32] The 12th is a cadent house as are the 3rd, 6th and 9th and planets in these houses are considered weak or afflicted. On the other hand, Moon in the 1st, 4th, 7th or 10th would be more able to act as these are Angular houses. Planets in Succedent houses of the chart (2nd, 5th, 8th, 11th) are generally considered to be of medium ability to act. Besides Accidental Dignity, there are a range of Accidental Debilities, such as retrogradation, Under the Sun's Beams, Combust, and so forth.
Additional classifications
Each sign can be divided into three 10° sectors known as decans or decanates, though these have fallen into disuse. The first decanate is said to be most emphatically of its own nature and is ruled by the sign ruler.[33] The next decanate is sub-ruled by the planet ruling the next sign in the same triplicity. The last decanate is sub-ruled by the next in order in the same triplicity.[34]
While the element and modality of a sign are together sufficient to define it, they can be grouped to indicate their symbolism. The first four signs, Aries, Taurus, Gemini and Cancer, form the group of personal signs. The next four signs, Leo, Virgo, Libra and Scorpio form the group of interpersonal signs. The last four signs of the zodiac, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius and Pisces, form the group of transpersonal signs.[35]
Dane Rudhyar presented the tropical zodiac primary factors,[36] used in the curriculum of the RASA School of Astrology. The tropical zodiac is the zodiac of seasonal factors as opposed to the sidereal zodiac (constellation factors). The primary seasonal factors are based on the changing ratio of sunlight and darkness across the year. The first factor is whether the chosen time falls in the half of the year when daylight is increasing, or the half of the year when darkness is increasing. The second factor is whether the chosen time falls in the half of the year when there is more daylight than darkness, or the half when there is more darkness than daylight. The third factor is which of the four seasons the chosen time falls in, defined by the first two factors. Thus[37][38]
- The winter season is when daylight is increasing and there is more darkness than daylight.
- The spring season is when daylight is increasing and there is more daylight than darkness.
- The summer season is when darkness is increasing and there is more daylight than darkness.
- The autumn season is when darkness is increasing and there is more darkness than daylight.
Indian astrology
In Indian astrology, there are five elements: fire, earth, air, water, and ether. The master of fire is Mars, while Mercury is of earth, Saturn of air, Venus of water, and Jupiter of ether.
Jyotish astrology recognises twelve zodiac signs (Rāśi),[39] that correspond to those in Western astrology. The relation of the signs to the elements is the same in the two systems.
Nakshatras
A nakshatra (Devanagari: नक्षत्र, Sanskrit nakshatra, from naksha- 'map', and tra- 'guard'), or lunar mansion, is one of the 27 divisions of the sky identified by the prominent star(s), as used in Hindu astronomy and astrology (Jyotisha).[40] "Nakshatra" in Sanskrit and Tamil means a "star."
Chinese zodiac signs
Chinese astrological signs operate on cycles of years, lunar months, and two-hour periods of the day (also known as shichen). A particular feature of the Chinese zodiac is its operation in a 60-year cycle in combination with the Five Phases of Chinese astrology (Wood, Fire, Metal, Water and Earth).[41] Nevertheless, some researches say that there is an obvious relationship between the Chinese 12-year cycle and zodiac constellations: each year of the cycle corresponds to a certain disposal of Jupiter. For example, in the year of Snake Jupiter is in the Sign of Gemini, in the year of Horse Jupiter is in the Sign of Cancer and so on. So the Chinese 12-year calendar is a solar-lunar-jovian calendar.
Zodiac symbolism
The following table shows the twelve signs and their attributes.
| Sign | Yin/Yang | Direction | Season | Fixed Element | Trine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rat | Yang | North | Mid-Winter | Water | 1st |
| Ox | Yin | North | Late Winter | Earth | 2nd |
| Tiger | Yang | East | Early Spring | Wood | 3rd |
| Rabbit | Yin | East | Mid-Spring | Wood | 4th |
| Dragon | Yang | East | Late Spring | Earth | 1st |
| Snake | Yin | South | Early Summer | Fire | 2nd |
| Horse | Yang | South | Mid-Summer | Fire | 3rd |
| Sheep | Yin | South | Late Summer | Earth | 4th |
| Monkey | Yang | West | Early Autumn | Metal | 1st |
| Rooster | Yin | West | Mid-Autumn | Metal | 2nd |
| Dog | Yang | West | Late Autumn | Earth | 3rd |
| Pig | Yin | North | Early Winter | Water | 4th |
The twelve signs
In Chinese astrology, the zodiac of twelve animal sign represents twelve different types of personality. The zodiac traditionally begins with the sign of the Rat, and there are many stories about the Origins of the Chinese Zodiac which explain why this is so. When the twelve zodiac signs are part of the 60-year calendar in combination with the four elements, they are traditionally called the twelve Earthly Branches. The Chinese zodiac follows the lunisolar Chinese calendar[42] and thus the "changeover" days in a month (when one sign changes to another sign) vary each year. The following are the twelve zodiac signs in order.[43]
- 子 Rat (Yang, 1st Trine, Fixed Element Water): Rat years include 1900, 1912, 1924, 1936, 1948, 1960, 1972, 1984, 1996, 2008, 2020, 2032. The Rat also corresponds to a particular month in the year. The hours of the Rat are 11pm – 1am.
- 丑 Ox (Yin, 2nd Trine, Fixed Element Earth:[44] Ox years include 1901, 1913, 1925, 1937, 1949, 1961, 1973, 1985, 1997, 2009, 2021, 2033. The Ox also corresponds to a particular month in the year. The hours of the Ox are 1am – 3am.
- 寅 Tiger (Yang, 3rd Trine, Fixed Element Wood): Tiger years include 1902, 1914, 1926, 1938, 1950, 1962, 1974, 1986, 1998, 2010, 2022, 2034. The Tiger also corresponds to a particular month in the year. The hours of the Tiger are 3am – 5am.
- 卯 Rabbit (Yin, 4th Trine, Fixed Element Wood): Rabbit Years include 1903, 1915, 1927, 1939, 1951, 1963, 1975, 1987, 1999, 2011, 2023, 2035. The Rabbit also corresponds to a particular month in the year. The hours of the Rabbit are 5am – 7am.
- 辰 Dragon (Yang, 1st Trine, Fixed Element Earth[44]): Dragon years include 1904, 1916, 1928, 1940, 1952, 1964, 1976, 1988, 2000, 2012, 2024, 2036. The Dragon also corresponds to a particular month in the year. The hours of the Dragon are 7am – 9am.
- 巳 Snake (Yin, 2nd Trine, Fixed Element Fire): Snake years include 1905, 1917, 1929, 1941, 1953, 1965, 1977, 1989, 2001, 2013, 2025, 2037. The Snake also corresponds to a particular month in the year. The hours of the Snake are 9am – 11am.
- 午 Horse (Yang, 3rd Trine, Fixed Element Fire): Horse years include 1906, 1918, 1930, 1942, 1954, 1966, 1978, 1990, 2002, 2014, 2026, 2038. The Horse also corresponds to a particular month in the year. The hours of the Horse are 11am – 1pm.
- 未 Goat (Yin, 4th Trine, Fixed Element Earth[44]): Goat years include 1907, 1919, 1931, 1943, 1955, 1967, 1979, 1991, 2003, 2015, 2027, 2039. The Goat also corresponds to a particular month in the year. The hours of the Goat are 1pm – 3pm.
- 申 Monkey (Yang, 1st Trine, Fixed Element Metal): Monkey years include 1908, 1920, 1932, 1944, 1956, 1968, 1980, 1992, 2004, 2016, 2028, 2040. The Monkey also corresponds to a particular month in the year. The hours of the Monkey are 3pm – 5pm.
- 酉 Rooster (Yin, 2nd Trine, Fixed Element Metal): Rooster years include 1909, 1921, 1933, 1945, 1957, 1969, 1981, 1993, 2005, 2017, 2029, 2041. The Rooster also corresponds to a particular month in the year. The hours of the Rooster are 5pm – 7pm.
- 戌 Dog (Yang, 3rd Trine, Fixed Element Earth[44]): Dog years include 1910, 1922, 1934, 1946, 1958, 1970, 1982, 1994, 2006, 2018, 2030, 2042. The Dog also corresponds to a particular month in the year. The hours of the Dog are 7pm – 9pm.
- 亥 Pig (Yin, 4th Trine, Fixed Element Water): Pig years include 1911, 1923, 1935, 1947, 1959, 1971, 1983, 1995, 2007, 2019, 2031, 2043. The Pig also corresponds to a particular month in the year. The hours of the Pig are 9pm – 11pm.
The five elements
- Wood: The wood person has high morals, is self-confident, expansive and co-operative, with wide and varied interests and idealistic goals. The direction associated with Wood is East, and the season is spring, which makes it the fixed element for the animal signs Tiger and Rabbit.[44]
- Fire: The fire person has leadership qualities, dynamic passion, and is decisive, self-confident, positive and assertive. The direction associated with Fire is South, and the season is summer, which makes it the fixed element for the animal signs Snake and Horse.[44]
- Earth: The earth person is serious, logical and methodical, intelligent, objective and good at planning. The direction associated with Earth is Center. The season for Earth is the changeover point of the four seasons. It is the fixed element for the animal signs Ox, Dragon, Goat and Dog.[44]
- Metal: The metal person is sincere, has fixed values and opinions, is strong of will, and has eloquence of speech. The direction associated with Metal is West. The season for Metal is Autumn. It is the fixed element for the animal signs Monkey and Rooster.[44]
- Water: The water person is persuasive, intuitive, and empathetic. The water person is objective and often sought out for their counsel. The direction associated with water is North. The season for Water is Winter. It is the fixed element for the animal signs Rat and Pig.[44]
The five elements operate together with the twelve animal signs in a 60-year calendar. The five elements appear in the calendar in both their yin and yang forms and are known as the ten Celestial stems. When trying to calculate the relevant year of the cycle in relation to the Gregorian calendar, an easy rule to follow is that years that end in an even number are Yang (representing masculine, active and light), those that end with an odd number are Yin (representing feminine, passive and darkness).[44]
Notes
- Mayo (1979), p. 35.
- Jeffrey Bennett; Megan Donohue; Nicholas Schneider; Mark Voit (2007). The cosmic perspective (4th ed.). San Francisco, CA: Pearson/Addison-Wesley. pp. 82–84. ISBN 0-8053-9283-1.
- Zarka, Philippe (2011). "Astronomy and astrology" (PDF). Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union. 5 (S260): 420–425. doi:10.1017/S1743921311002602.
- Bobrick (2005), pp. 10, 23.
- Johnsen (2004).
- Sachs (1948), p. 289. Isolated references to celestial "signs" in Sumerian sources are insufficient to speak of a Sumerian zodiac, see Rochberg (1998), p. ix.
- Charlie Higgins (1997). "Astrology and The Four Elements". Archived from the original on 2010-01-03. Retrieved 2009-12-27.
- Pelletier, Robert, and Leonard Cataldo (1984). Be Your Own Astrologer. London: Pan Books. pp. 43–44
- Pottenger, Maritha (1991). Astro Essentials. San Diego: ACS Publications. pp. 31–36.
- Arroyo (1989), p. 27.
- Arroyo (1989), pp. 30–34
- Hone (1978), p. 42
- Glyphs from the alchemical symbology.
- Arroyo (1975). pp. 131–140.
- Arroyo (1989), p. 29.
- As used in Sepharial's "The Manual of Astrology"-Brazilian edition (1988) by Editora Nova Fronteira S/A, Rio de Janeiro
- Hone (1978), p. 40
- Arroyo (1989), p. 30
- Hone (1978), p. 75
- Hone (1978), p. 22
- Carol Wills (2007). "Rulerships". astrologynow.com. Archived from the original on 2007-01-27. Retrieved 2007-11-29.
- Shamos, Geoffery (2013). "Astrology as a Social Framework: The 'Children of Planets', 1400–1600". Journal for the Study of Religion, Nature and Culture. 7 (4): 434–460. doi:10.1558/jsrnc.v7i4.434.
- "Chiron as True Ruler of Virgo?". Retrieved July 18, 2014.
- Hone (1978), p. 21.
- "Opposition". dichesegnosei.it (in Italian).
- "The element of Air". dichesegnosei.it (in Italian).
- "The element of Fire". dichesegnosei.it (in Italian).
- "The element of Water". dichesegnosei.it (in Italian).
- "The element of Earth". dichesegnosei.it (in Italian).
- "Glossary of Astrological Terms". Logos, Asaa 1998–2004. 26 Nov 2007. "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2008-01-22. Retrieved 2007-11-29.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Hone (1978), p. 144
- "Accidental Dignity". www.gotohoroscope.com. Astrological Dictionary 1998–2007. 26 November 2007.
- Hone (1978), p. 87
- Hone (1978), p. 88
- "An Introduction to Astrology." Spiritsingles.com 25 Nov.2007. "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2007-12-09. Retrieved 2007-11-29.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Rudhyar (1943)
- Armstrong, Robin (2009). "The Signs and the Houses". RASA School of Astrology.
- Armstrong, Robin (2009). "I Ching: The Sequence of Change". RA Publications.
- Sutton (1999) pp. 74–92.
- Sutton (1999), p. 168.
- "'Almanac' 'lunar' zodiac beginning of spring as the boundary dislocation? – China Network". 16 February 2009. Retrieved 5 January 2011.
- Novak, Sarah. "The Chinese Zodiac". Faces. 34: 42.
- Theodora Lau, Ibid, pp. 2–8, 30–5, 60–4, 88–94, 118–24, 148–53, 178–84, 208–13, 238–44, 270–78, 306–12, 338–44, 2005
- Chinese Astrology: Exploring the Eastern Zodiac by Shelly Wu
References
- Arroyo, Stephen (1975). Astrology, Psychology and The Four Elements. California: CCRS Publications
- Arroyo, Stephen (1989). Chart Interpretation Handbook. California: CCRS Publications. ISBN 0-916360-49-0
- Bobrick, Benson (2005). The Fated Sky: Astrology in History. Simon & Schuster. 369 pp.
- Caiozzo, Anna (2003). Images of the Sky. Paris-Sorbonne. Signs and Constellations.
- Eric Francis (2016). "Why Your Zodiac Sign is Not Wrong"
- Hone, Margaret (1978). The Modern Text-Book of Astrology. Revised edition. England: L. N. Fowler & Co. Ltd. ISBN 085243-357-3
- Johnsen, Linda (2004 March). A Thousand Suns: Designing Your Future with Vedic Astrology. Yes International Publishers.
- Mayo, Jeff (1979). Teach Yourself Astrology. London: Hodder and Stoughton.
- Rochberg, Francesca (1998), "Babylonian Horoscopes", American Philosophical Society, New Series, Vol. 88, No. 1, pp. i–164. doi:10.2307/1006632. JSTOR 1006632.
- Rudhyar, Dane (1943). Astrological Signs – The Pulse of Life.
- Sachs, Abraham (1948), "A Classification of the Babylonian Astronomical Tablets of the Seleucid Period", Journal of Cuneiform Studies, Vol. 2, No. 4, pp. 271–290. doi:10.2307/3515929. JSTOR 3515929.
- Sutton, Komilla (1999). The Essentials of Vedic Astrology. England: The Wessex Astrologer Ltd.