8-simplex
In geometry, an 8-simplex is a self-dual regular 8-polytope. It has 9 vertices, 36 edges, 84 triangle faces, 126 tetrahedral cells, 126 5-cell 4-faces, 84 5-simplex 5-faces, 36 6-simplex 6-faces, and 9 7-simplex 7-faces. Its dihedral angle is cos−1(1/8), or approximately 82.82°.
| Regular enneazetton (8-simplex) | |
|---|---|
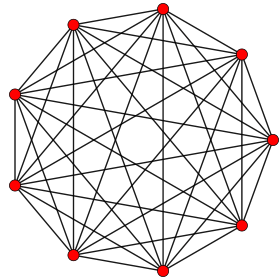 Orthogonal projection inside Petrie polygon | |
| Type | Regular 8-polytope |
| Family | simplex |
| Schläfli symbol | {3,3,3,3,3,3,3} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram | |
| 7-faces | 9 7-simplex |
| 6-faces | 36 6-simplex |
| 5-faces | 84 5-simplex |
| 4-faces | 126 5-cell |
| Cells | 126 tetrahedron |
| Faces | 84 triangle |
| Edges | 36 |
| Vertices | 9 |
| Vertex figure | 7-simplex |
| Petrie polygon | enneagon |
| Coxeter group | A8 [3,3,3,3,3,3,3] |
| Dual | Self-dual |
| Properties | convex |
It can also be called an enneazetton, or ennea-8-tope, as a 9-facetted polytope in eight-dimensions. The name enneazetton is derived from ennea for nine facets in Greek and -zetta for having seven-dimensional facets, and -on.
As a configuration
This configuration matrix represents the 8-simplex. The rows and columns correspond to vertices, edges, faces, cells, 4-faces, 5-faces, 6-faces and 7-faces. The diagonal numbers say how many of each element occur in the whole 8-simplex. The nondiagonal numbers say how many of the column's element occur in or at the row's element. This self-dual simplex's matrix is identical to its 180 degree rotation.[1][2]
Coordinates
The Cartesian coordinates of the vertices of an origin-centered regular enneazetton having edge length 2 are:
More simply, the vertices of the 8-simplex can be positioned in 9-space as permutations of (0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1). This construction is based on facets of the 9-orthoplex.
Another origin-centered construction uses (1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1)/3 and permutations of (1,1,1,1,1,1,1,-11)/12 for edge length √2.
Images
| Ak Coxeter plane | A8 | A7 | A6 | A5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graph |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Dihedral symmetry | [9] | [8] | [7] | [6] |
| Ak Coxeter plane | A4 | A3 | A2 | |
| Graph |  |
 |
 | |
| Dihedral symmetry | [5] | [4] | [3] |
Related polytopes and honeycombs
This polytope is a facet in the uniform tessellations: 251, and 521 with respective Coxeter-Dynkin diagrams:






























This polytope is one of 135 uniform 8-polytopes with A8 symmetry.
| A8 polytopes | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
t0 |
t1 |
t2 |
t3 |
t01 |
t02 |
t12 |
t03 |
t13 |
t23 |
t04 |
t14 |
t24 |
t34 |
t05 |
t15 |
t25 |
t06 |
t16 |
t07 |
t012 |
t013 |
t023 |
t123 |
t014 |
t024 |
t124 |
t034 |
t134 |
t234 |
t015 |
t025 |
t125 |
t035 |
t135 |
t235 |
t045 |
t145 |
t016 |
t026 |
t126 |
t036 |
t136 |
t046 |
t056 |
t017 |
t027 |
t037 |
t0123 |
t0124 |
t0134 |
t0234 |
t1234 |
t0125 |
t0135 |
t0235 |
t1235 |
t0145 |
t0245 |
t1245 |
t0345 |
t1345 |
t2345 |
t0126 |
t0136 |
t0236 |
t1236 |
t0146 |
t0246 |
t1246 |
t0346 |
t1346 |
t0156 |
t0256 |
t1256 |
t0356 |
t0456 |
t0127 |
t0137 |
t0237 |
t0147 |
t0247 |
t0347 |
t0157 |
t0257 |
t0167 |
t01234 |
t01235 |
t01245 |
t01345 |
t02345 |
t12345 |
t01236 |
t01246 |
t01346 |
t02346 |
t12346 |
t01256 |
t01356 |
t02356 |
t12356 |
t01456 |
t02456 |
t03456 |
t01237 |
t01247 |
t01347 |
t02347 |
t01257 |
t01357 |
t02357 |
t01457 |
t01267 |
t01367 |
t012345 |
t012346 |
t012356 |
t012456 |
t013456 |
t023456 |
t123456 |
t012347 |
t012357 |
t012457 |
t013457 |
t023457 |
t012367 |
t012467 |
t013467 |
t012567 |
t0123456 |
t0123457 |
t0123467 |
t0123567 |
t01234567 |
References
- Coxeter 1973, §1.8 Configurations
- Coxeter, H.S.M. (1991). Regular Complex Polytopes (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 117. ISBN 9780521394901.
- Coxeter, H.S.M.:
- — (1973). "Table I (iii): Regular Polytopes, three regular polytopes in n-dimensions (n≥5)". Regular Polytopes (3rd ed.). Dover. pp. 296. ISBN 0-486-61480-8.
- Sherk, F. Arthur; McMullen, Peter; Thompson, Anthony C.; Weiss, Asia Ivic, eds. (1995). Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-01003-6.
- (Paper 22) — (1940). "Regular and Semi Regular Polytopes I". Math. Zeit. 46: 380–407. doi:10.1007/BF01181449.
- (Paper 23) — (1985). "Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes II". Math. Zeit. 188: 559–591. doi:10.1007/BF01161657.
- (Paper 24) — (1988). "Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes III". Math. Zeit. 200: 3–45. doi:10.1007/BF01161745.
- Conway, John H.; Burgiel, Heidi; Goodman-Strass, Chaim (2008). "26. Hemicubes: 1n1". The Symmetries of Things. p. 409. ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5.
- Johnson, Norman (1991). "Uniform Polytopes" (Manuscript). Cite journal requires
|journal=(help)- Johnson, N.W. (1966). The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs (PhD). University of Toronto. OCLC 258527038.
- Klitzing, Richard. "8D uniform polytopes (polyzetta) x3o3o3o3o3o3o3o — ene".
External links
- Glossary for hyperspace, George Olshevsky.
- Polytopes of Various Dimensions
- Multi-dimensional Glossary
Fundamental convex regular and uniform polytopes in dimensions 2–10 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family | An | Bn | I2(p) / Dn | E6 / E7 / E8 / F4 / G2 | Hn | |||||||
| Regular polygon | Triangle | Square | p-gon | Hexagon | Pentagon | |||||||
| Uniform polyhedron | Tetrahedron | Octahedron • Cube | Demicube | Dodecahedron • Icosahedron | ||||||||
| Uniform 4-polytope | 5-cell | 16-cell • Tesseract | Demitesseract | 24-cell | 120-cell • 600-cell | |||||||
| Uniform 5-polytope | 5-simplex | 5-orthoplex • 5-cube | 5-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform 6-polytope | 6-simplex | 6-orthoplex • 6-cube | 6-demicube | 122 • 221 | ||||||||
| Uniform 7-polytope | 7-simplex | 7-orthoplex • 7-cube | 7-demicube | 132 • 231 • 321 | ||||||||
| Uniform 8-polytope | 8-simplex | 8-orthoplex • 8-cube | 8-demicube | 142 • 241 • 421 | ||||||||
| Uniform 9-polytope | 9-simplex | 9-orthoplex • 9-cube | 9-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform 10-polytope | 10-simplex | 10-orthoplex • 10-cube | 10-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform n-polytope | n-simplex | n-orthoplex • n-cube | n-demicube | 1k2 • 2k1 • k21 | n-pentagonal polytope | |||||||
| Topics: Polytope families • Regular polytope • List of regular polytopes and compounds | ||||||||||||