7-simplex
In 7-dimensional geometry, a 7-simplex is a self-dual regular 7-polytope. It has 8 vertices, 28 edges, 56 triangle faces, 70 tetrahedral cells, 56 5-cell 5-faces, 28 5-simplex 6-faces, and 8 6-simplex 7-faces. Its dihedral angle is cos−1(1/7), or approximately 81.79°.
| Regular octaexon (7-simplex) | |
|---|---|
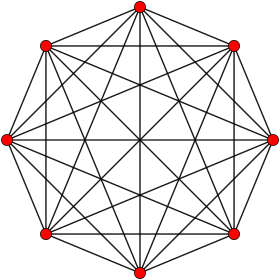 Orthogonal projection inside Petrie polygon | |
| Type | Regular 7-polytope |
| Family | simplex |
| Schläfli symbol | {3,3,3,3,3,3} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram | |
| 6-faces | 8 6-simplex |
| 5-faces | 28 5-simplex |
| 4-faces | 56 5-cell |
| Cells | 70 tetrahedron |
| Faces | 56 triangle |
| Edges | 28 |
| Vertices | 8 |
| Vertex figure | 6-simplex |
| Petrie polygon | octagon |
| Coxeter group | A7 [3,3,3,3,3,3] |
| Dual | Self-dual |
| Properties | convex |
Alternate names
It can also be called an octaexon, or octa-7-tope, as an 8-facetted polytope in 7-dimensions. The name octaexon is derived from octa for eight facets in Greek and -ex for having six-dimensional facets, and -on. Jonathan Bowers gives an octaexon the acronym oca.[1]
As a configuration
This configuration matrix represents the 7-simplex. The rows and columns correspond to vertices, edges, faces, cells, 4-faces, 5-faces and 6-faces. The diagonal numbers say how many of each element occur in the whole 7-simplex. The nondiagonal numbers say how many of the column's element occur in or at the row's element. This self-dual simplex's matrix is identical to its 180 degree rotation.[2][3]
Coordinates
The Cartesian coordinates of the vertices of an origin-centered regular octaexon having edge length 2 are:
More simply, the vertices of the 7-simplex can be positioned in 8-space as permutations of (0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1). This construction is based on facets of the 8-orthoplex.
Images
| 7-Simplex in 3D | ||||||
 Ball and stick model in triakis tetrahedral envelope |
 7-Simplex as an Amplituhedron Surface |
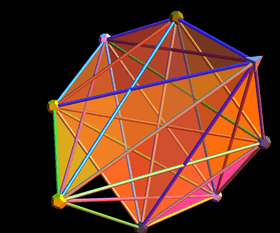 7-simplex to 3D with camera perspective showing hints of its 2D Petrie projection | ||||
| Ak Coxeter plane | A7 | A6 | A5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graph |  |
 |
 |
| Dihedral symmetry | [8] | [7] | [6] |
| Ak Coxeter plane | A4 | A3 | A2 |
| Graph |  |
 |
 |
| Dihedral symmetry | [5] | [4] | [3] |
Related polytopes
This polytope is a facet in the uniform tessellation 331 with Coxeter-Dynkin diagram:
This polytope is one of 71 uniform 7-polytopes with A7 symmetry.
| A7 polytopes | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 t0 |
 t1 |
 t2 |
 t3 |
 t0,1 |
 t0,2 |
 t1,2 |
 t0,3 | ||||
 t1,3 |
 t2,3 |
 t0,4 |
 t1,4 |
 t2,4 |
 t0,5 |
 t1,5 |
 t0,6 | ||||
 t0,1,2 |
 t0,1,3 |
 t0,2,3 |
 t1,2,3 |
 t0,1,4 |
 t0,2,4 |
 t1,2,4 |
 t0,3,4 | ||||
 t1,3,4 |
 t2,3,4 |
 t0,1,5 |
 t0,2,5 |
 t1,2,5 |
 t0,3,5 |
 t1,3,5 |
 t0,4,5 | ||||
 t0,1,6 |
 t0,2,6 |
 t0,3,6 |
 t0,1,2,3 |
 t0,1,2,4 |
 t0,1,3,4 |
 t0,2,3,4 |
 t1,2,3,4 | ||||
 t0,1,2,5 |
 t0,1,3,5 |
 t0,2,3,5 |
 t1,2,3,5 |
 t0,1,4,5 |
 t0,2,4,5 |
 t1,2,4,5 |
 t0,3,4,5 | ||||
 t0,1,2,6 |
 t0,1,3,6 |
 t0,2,3,6 |
 t0,1,4,6 |
 t0,2,4,6 |
 t0,1,5,6 |
 t0,1,2,3,4 |
 t0,1,2,3,5 | ||||
 t0,1,2,4,5 |
 t0,1,3,4,5 |
 t0,2,3,4,5 |
 t1,2,3,4,5 |
 t0,1,2,3,6 |
 t0,1,2,4,6 |
 t0,1,3,4,6 |
 t0,2,3,4,6 | ||||
 t0,1,2,5,6 |
 t0,1,3,5,6 |
 t0,1,2,3,4,5 |
 t0,1,2,3,4,6 |
 t0,1,2,3,5,6 |
 t0,1,2,4,5,6 |
 t0,1,2,3,4,5,6 | |||||
Notes
- Klitzing, Richard. "7D uniform polytopes (polyexa) x3o3o3o3o3o — oca".
- Coxeter, H.S.M. (1973). "§1.8 Configurations". Regular Polytopes (3rd ed.). Dover. ISBN 0-486-61480-8.
- Coxeter, H.S.M. (1991). Regular Complex Polytopes (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 117. ISBN 9780521394901.
External links
- Glossary for hyperspace, George Olshevsky.
- Polytopes of Various Dimensions
- Multi-dimensional Glossary
Fundamental convex regular and uniform polytopes in dimensions 2–10 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family | An | Bn | I2(p) / Dn | E6 / E7 / E8 / F4 / G2 | Hn | |||||||
| Regular polygon | Triangle | Square | p-gon | Hexagon | Pentagon | |||||||
| Uniform polyhedron | Tetrahedron | Octahedron • Cube | Demicube | Dodecahedron • Icosahedron | ||||||||
| Uniform 4-polytope | 5-cell | 16-cell • Tesseract | Demitesseract | 24-cell | 120-cell • 600-cell | |||||||
| Uniform 5-polytope | 5-simplex | 5-orthoplex • 5-cube | 5-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform 6-polytope | 6-simplex | 6-orthoplex • 6-cube | 6-demicube | 122 • 221 | ||||||||
| Uniform 7-polytope | 7-simplex | 7-orthoplex • 7-cube | 7-demicube | 132 • 231 • 321 | ||||||||
| Uniform 8-polytope | 8-simplex | 8-orthoplex • 8-cube | 8-demicube | 142 • 241 • 421 | ||||||||
| Uniform 9-polytope | 9-simplex | 9-orthoplex • 9-cube | 9-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform 10-polytope | 10-simplex | 10-orthoplex • 10-cube | 10-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform n-polytope | n-simplex | n-orthoplex • n-cube | n-demicube | 1k2 • 2k1 • k21 | n-pentagonal polytope | |||||||
| Topics: Polytope families • Regular polytope • List of regular polytopes and compounds | ||||||||||||