Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk
| Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk Южно-Сахалинск (Russian) | |
|---|---|
| - City[1] - | |
 View over a residential area of Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk | |
.svg.png) Location of Sakhalin Oblast in Russia | |
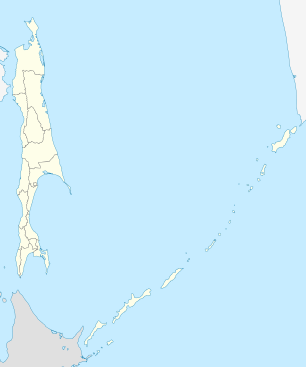 Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk | |
 |
.png) |
Coat of arms |
Flag |
| Administrative status (as of December 2011) | |
| Country | Russia |
| Federal subject | Sakhalin Oblast[1] |
| Administratively subordinated to | city of oblast significance of Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk[1] |
| Administrative center of | Sakhalin Oblast,[1] city of oblast significance of Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk[1] |
| Municipal status (as of May 2010) | |
| Urban okrug | Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk Urban Okrug[2] |
| Administrative center of | Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk Urban Okrug[2] |
| Head | Sergey Nadsadin[3] |
| Statistics | |
| Population (2010 Census) | 181,728 inhabitants[4] |
| - Rank in 2010 | 99th |
| Time zone | MAGT (UTC+11:00)[5] |
| Founded | 1882 |
| City status since | 1946[6] |
| Previous names |
Vladimirovka (until 1882), Toyohara (until 1946) |
| Postal code(s)[7] | 693000 |
| Dialing code(s) | +7 4242; +7 424[8] |
| Website |
www |
| Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk on Wikimedia Commons | |
Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk (Russian: Ю́жно-Сахали́нск, literally "Southern Sakhalin") is a city in Sakhalin island, and the administrative center of Sakhalin Oblast, Russia. It is located in the Far East part of Russia, situated above Japan. [9] Gas and oil extraction as well as processing are amongst the main industrial manufactures on an island. It is also a place of working of main US oil companies such as ExxonMobile etc. It was called Vladimirovka (Влади́мировка) from 1882 to 1905, then Toyohara (Japanese: 豊原市 Hepburn: Toyohara-shi) from 1905 to 1946. Population: Template:Ru census
History
Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk began as a small Russian settlement called Vladimirovka, founded by convicts in 1882.[6] The Treaty of Portsmouth in 1905, which brought an end to the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905, awarded the southern half of the Sakhalin Island to Japan. Vladimirovka was renamed Toyohara (meaning "bountiful plain"), and was the prefect capital of the Japanese Karafuto Prefecture.
After the end of World War II, the Japanese portion of Sakhalin island was occupied by Soviet troops. Ownership of the city was transferred to the Soviet Union and it was renamed Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk ("Southern Sakhalin"). Town status was granted to it in 1946.[6]
 Early days of Vladimirovka
Early days of Vladimirovka This Japanese D51 steam locomotive stands outside the Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk Railway Station
This Japanese D51 steam locomotive stands outside the Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk Railway Station Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk's Museum
Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk's Museum
Administrative and municipal status
Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk is the administrative center of the oblast.[1] Within the framework of administrative divisions, it is, together with ten rural localities, incorporated as the city of oblast significance of Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk—an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts.[1] As a municipal division, the city of oblast significance of Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk is incorporated as Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk Urban Okrug.
Economy and infrastructure
Due to significant investment from oil companies like ExxonMobil and Shell, Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk has experienced substantial economic growth. Although this growth has primarily occurred in the northern part of the island, both companies maintain headquarters and residential complexes in the city of Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk itself. The demand for natural resources by the Japanese, Chinese, and South Koreans has ensured continued prosperity in the foreseeable future for the entire island.
There has been significant criticism, including from Presidential Envoy Kamil Iskhakov, that Sakhalin is not caring for its citizens. Despite sizable gas deposits and incoming investments from gas companies, the regional administration does not yet have plans for the installation of gas services on the island. The oblast also continues to have the highest rate of juvenile crime in all of Russia, and more than 40% of its businesses are unprofitable.
Out of the very few remaining Japanese buildings in Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, one now functions as the local museum. The building was designed in the Emperor's Crown Style by Japanese architect Yoshio Kaizuka, and completed in 1937.[10]
 Central part of Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk
Central part of Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk- Central part of Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk
 Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk museum in Japanese days
Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk museum in Japanese days Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk museum in 2012
Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk museum in 2012
Transportation
The city is served by the Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk Airport. The city is also the hub for the island's narrow gauge railway network, the Sakhalin Railway, built under the Japanese administration in the early 20th century. In addition to railways, the town is also a hub for roadways, such as the A-391 (which travels east to Korsakov) and the A-392 (which travels west to Kholmsk).
Education
Institutes of elementary and middle education include: Sakhalin International School
Institutes of higher education in the city include Sakhalin State University and Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk institute of economics, law and informatics. Also there are some branches of other high schools:
- Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk institute (branch) of Russian State trade-economics university
- Branch of Far East State university of railways
- Branch of Modern Academy of the humanities
- Branch of The Pacific State economics university
- Branch of Russian economics academy named after G.V. Plekhanov
- Branch of Far East law institute
Mass media
Television
- 3 - 1TV Russia
- 5 - Rossiya-24 (Russia-24)
- 10- Rossiya-1 (Russia-1)
- 12 - ASTV (Alternative Sakhalin Television)
- 21 - The first multplex digital TV DVB T2
- 23 - Che
- 27 - Domashny / OTV (Sakhalin Regional Television)
- 30 - NTV Russia
- 33 - STS
- 35 - Ren-TV / Echo of Sakhalin
- 43 - Match TV Russia (ex. Russia-2)
- 46 - Petersburg–Channel_5
- 49 - Rossiya-K (Russia-K)
- 51 - The second multiplex of digital TV DVB T2
Radio
- 87,9 Autoradio (plan)
- 88,3 Retro FM
- 88,9 Radio Record
- 89,9 Russian Radio
- 101,7 Radio Chanson
- 102,5 Europa Plus
- 102,9 Humor FM
- 103,5 Mayak
- 104,4 Love Radio
- 105,1 Radio Dacha (plan)
- 105,5 Radio ASTV
- 106,0 Radio Rossii
- 106,5 Dorognoe Radio
- 107,2 Vesti FM
Population
Demographics
Most residents are ethnic Russians, but there also exists a sizable population of Koreans. Of the 43,000 Sakhalin Koreans, half are estimated to live in Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, comprising roughly 12% of the city's population. Also smaller numbers of indigenous minorities, such as Ainu, Nivkhs and Oroks can be found.
Religion
The Latin Catholic Church of St James in Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk is the cathedral episcopal see of the missionary (exempt, pre-diocesan) Apostolic Prefecture of Yuzhno Sakhalinsk (Karafuto until 2002, missio sui iuris until 1938).
Geography and climate
The city is located on the Susuya River. It is the largest city on the island, and the only one with more than 100,000 inhabitants. The straight-line distance to Moscow is 10,417 kilometers (6,473 mi).
Due to restrictions, foreigners wishing to leave Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk in order to travel to any other part of the Sakhalin Oblast and its internal and territorial waters are required to seek permission from the Federal Security Service (FSB) and the Border Guard. Scuba diving and recreating on the seacoast is permitted only in places defined by the Border Guard.[11]
The climate is humid continental (Köppen Dfb) with mild summers and cold winters. Maritime influences can be seen in that precipitation is much higher than in interior Russia and that summers are distinctly cooler than in Khabarovsk or Irkutsk, while winters are much milder. Summers are frequently foggy, reducing the amount of sunshine. Considering its southerly marine position winters are very cold, albeit warmer than expected for surrounding inland areas affected by the Siberian High.
| Climate data for Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 4.3 (39.7) |
6.4 (43.5) |
12.5 (54.5) |
22.9 (73.2) |
28.5 (83.3) |
30.8 (87.4) |
34.4 (93.9) |
34.7 (94.5) |
29.0 (84.2) |
23.5 (74.3) |
18.1 (64.6) |
8.4 (47.1) |
34.7 (94.5) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −6.7 (19.9) |
−5.3 (22.5) |
−0.3 (31.5) |
6.9 (44.4) |
13.4 (56.1) |
17.7 (63.9) |
20.8 (69.4) |
22.4 (72.3) |
19.0 (66.2) |
12.3 (54.1) |
3.2 (37.8) |
−3.7 (25.3) |
8.3 (46.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −12.2 (10) |
−11.7 (10.9) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
1.7 (35.1) |
7.2 (45) |
11.7 (53.1) |
15.5 (59.9) |
17.3 (63.1) |
13.2 (55.8) |
6.5 (43.7) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
−8.6 (16.5) |
2.8 (37) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −17.3 (0.9) |
−17.6 (0.3) |
−10.8 (12.6) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
2.5 (36.5) |
7.4 (45.3) |
12.0 (53.6) |
13.6 (56.5) |
8.4 (47.1) |
1.7 (35.1) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−13.3 (8.1) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −36.2 (−33.2) |
−34.8 (−30.6) |
−30.5 (−22.9) |
−25.2 (−13.4) |
−6.2 (20.8) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
1.3 (34.3) |
3.6 (38.5) |
−4.2 (24.4) |
−11.8 (10.8) |
−25.7 (−14.3) |
−33.5 (−28.3) |
−36.2 (−33.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 50 (1.97) |
35 (1.38) |
49 (1.93) |
59 (2.32) |
66 (2.6) |
51 (2.01) |
82 (3.23) |
111 (4.37) |
115 (4.53) |
101 (3.98) |
81 (3.19) |
64 (2.52) |
864 (34.02) |
| Average rainy days | 0.3 | 0.4 | 2 | 10 | 17 | 17 | 20 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 9 | 2 | 135 |
| Average snowy days | 25 | 24 | 24 | 13 | 3 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 20 | 27 | 140 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 83 | 81 | 78 | 76 | 77 | 83 | 86 | 87 | 83 | 80 | 81 | 83 | 82 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 129 | 153 | 181 | 191 | 197 | 198 | 165 | 149 | 187 | 160 | 116 | 102 | 1,928 |
| Source #1: Pogoda.ru.net[12] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: NOAA (sun 1961–1990)[13] | |||||||||||||
Twin towns and sister cities
Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk is twinned with:





References
Notes
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Law #25-ZO
- 1 2 Law #524
- ↑ "Сергей Надсадин вступил в должность мэра Южно-Сахалинска". astv.ru (in Russian).
- ↑ Russian Federal State Statistics Service (2011). "Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года. Том 1" [2010 All-Russian Population Census, vol. 1]. Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года (2010 All-Russia Population Census) (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved June 29, 2012.
- ↑ Правительство Российской Федерации. Федеральный закон №107-ФЗ от 3 июня 2011 г. «Об исчислении времени», в ред. Федерального закона №271-ФЗ от 03 июля 2016 г. «О внесении изменений в Федеральный закон "Об исчислении времени"». Вступил в силу по истечении шестидесяти дней после дня официального опубликования (6 августа 2011 г.). Опубликован: "Российская газета", №120, 6 июня 2011 г. (Government of the Russian Federation. Federal Law #107-FZ of June 31, 2011 On Calculating Time, as amended by the Federal Law #271-FZ of July 03, 2016 On Amending Federal Law "On Calculating Time". Effective as of after sixty days following the day of the official publication.).
- 1 2 3 Южно-сахалинск - Исторический словарь - Словари и Энциклопедии
- ↑ Почта России. Информационно-вычислительный центр ОАСУ РПО. (Russian Post). Поиск объектов почтовой связи (Postal Objects Search) (in Russian)
- ↑ Телефонные коды Сахалина - Dialing codes of Sakhalin (in Russian)
- ↑ "Where is Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, Russia?". WorldAtlas. Retrieved 2018-09-25.
- ↑ http://www.russianmuseums.info/M1096
- ↑ Freedom of movement for foreigners on Sakhalin restricted
- ↑ "Weather and Climate-The Climate of Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk" (in Russian). Weather and Climate (Погода и климат). Retrieved 29 November 2015.
- ↑ "Juzno–Sahalinsk (Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk) Climate Normals 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 29 November 2015.
Sources
- Сахалинская областная Дума. Закон №25-ЗО от 23 марта 2011 г. «Об административно-территориальном устройстве Сахалинской области», в ред. Закона №62-ЗО от 27 июня 2013 г. «О внесении изменения в статью 10 Закона Сахалинской области "Об административно-территориальном устройстве Сахалинской области"». Вступил в силу 9 апреля 2011 г.. Опубликован: "Губернские ведомости", №55(3742), 29 марта 2011 г. (Sakhalin Oblast Duma. Law #25-ZO of March 23, 2011 On the Administrative-Territorial Structure of Sakhalin Oblast, as amended by the Law #62-ZO of June 27, 2013 On Amending Article 10 of the Law of Sakhalin Oblast "On the Administrative-Territorial Structure of Sakhalin Oblast". Effective as of April 9, 2011.).
- Сахалинская областная Дума. Закон №524 от 21 июля 2004 г. «О границах и статусе муниципальных образований в Сахалинской области», в ред. Закона №45-ЗО от 27 мая 2013 г. «О внесении изменения в Закон Сахалинской области "О границах и статусе муниципальных образований в Сахалинской области"». Вступил в силу 1 января 2005 г. Опубликован: "Губернские ведомости", №175–176(2111–2112), 31 июля 2004 г. (Sakhalin Oblast Duma. Law #524 of July 21, 2004 On the Borders and Status of the Municipal Formations in Sakhalin Oblast, as amended by the Law #45-ZO of May 27, 2013 On Amending the Law of Sakhalin Oblast "On the Borders and Status of the Municipal Formations in Sakhalin Oblast". Effective as of January 1, 2005.).
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk. |