Truncated icosidodecahedron
| Truncated icosidodecahedron | |
|---|---|
 (Click here for rotating model) | |
| Type | Archimedean solid Uniform polyhedron |
| Elements | F = 62, E = 180, V = 120 (χ = 2) |
| Faces by sides | 30{4}+20{6}+12{10} |
| Conway notation | bD or taD |
| Schläfli symbols | tr{5,3} or |
| t0,1,2{5,3} | |
| Wythoff symbol | 2 3 5 | |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | Ih, H3, [5,3], (*532), order 120 |
| Rotation group | I, [5,3]+, (532), order 60 |
| Dihedral angle | 6-10: 142.62° 4-10: 148.28° 4-6: 159.095° |
| References | U28, C31, W16 |
| Properties | Semiregular convex zonohedron |
 Colored faces |
 4.6.10 (Vertex figure) |
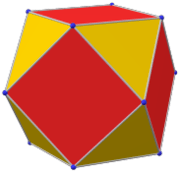
 Disdyakis triacontahedron (dual polyhedron) |
 Net |
In geometry, the truncated icosidodecahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces.
It has 62 faces: 30 squares, 20 regular hexagons, and 12 regular decagons. It has more vertices (120) and edges (180) than any other convex nonprismatic uniform polyhedron. Since each of its faces has point symmetry (equivalently, 180° rotational symmetry), the truncated icosidodecahedron is a zonohedron.
Names
|
The name truncated icosidodecahedron, given originally by Johannes Kepler, is misleading. An actual truncation of a icosidodecahedron has rectangles instead of squares. This nonuniform polyhedron is topologically equivalent to the Archimedean solid. Alternate interchangeable names are:
|
  Icosidodecahedron and its truncation |
The name great rhombicosidodecahedron refers to the relationship with the (small) rhombicosidodecahedron (compare section Dissection).
There is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron with a similar name, the nonconvex great rhombicosidodecahedron.
Area and volume
The surface area A and the volume V of the truncated icosidodecahedron of edge length a are:
If a set of all 13 Archimedean solids were constructed with all edge lengths equal, the truncated icosidodecahedron would be the largest.
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a truncated icosidodecahedron with edge length 2φ − 2, centered at the origin, are all the even permutations of:[4]
- (±1/φ, ±1/φ, ±(3 + φ)),
- (±2/φ, ±φ, ±(1 + 2φ)),
- (±1/φ, ±φ2, ±(−1 + 3φ)),
- (±(2φ − 1), ±2, ±(2 + φ)) and
- (±φ, ±3, ±2φ),
where φ = 1 + √5/2 is the golden ratio.
Dissection
The truncated icosidodecahedron is the convex hull of a rhombicosidodecahedron with cuboids above its 30 squares whose height to base ratio is the golden ratio. The rest of its space can be dissected into 12 nonuniform pentagonal cupolas below the decagons and 20 nonuniform triangular cupolas below the hexagons.
Orthogonal projections
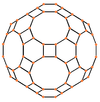
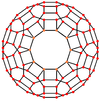
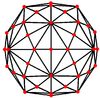
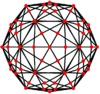
The truncated icosidodecahedron has seven special orthogonal projections, centered on a vertex, on three types of edges, and three types of faces: square, hexagonal and decagonal. The last two correspond to the A2 and H2 Coxeter planes.
| Centered by | Vertex | Edge 4-6 |
Edge 4-10 |
Edge 6-10 |
Face square |
Face hexagon |
Face decagon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid |  |
 |
 | ||||
| Wireframe |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Projective symmetry |
[2]+ | [2] | [2] | [2] | [2] | [6] | [10] |
| Dual image |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Spherical tilings and Schlegel diagrams
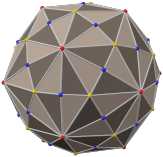
The truncated icosidodecahedron can also be represented as a spherical tiling, and projected onto the plane via a stereographic projection. This projection is conformal, preserving angles but not areas or lengths. Straight lines on the sphere are projected as circular arcs on the plane.
Schlegel diagrams are similar, with a perspective projection and straight edges.
| Orthographic projection | Stereographic projections | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Decagon-centered | Hexagon-centered | Square-centered | |
 |
 |
 |
 |
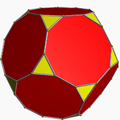
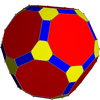
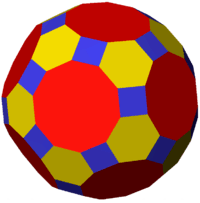
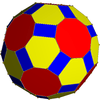
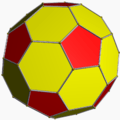
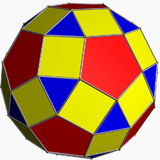
Geometric variations
Within Icosahedral symmetry there are unlimited geometric variations of the truncated icosidodecahedron with isogonal faces. The truncated dodecahedron, rhombicosidodecahedron, and truncated icosahedron as degenerate limiting cases.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Truncated icosidodecahedral graph
| Truncated icosidodecahedral graph | |
|---|---|
 5-fold symmetry | |
| Vertices | 120 |
| Edges | 180 |
| Radius | 15 |
| Diameter | 15 |
| Girth | 4 |
| Automorphisms | 120 (A5×2) |
| Chromatic number | 2 |
| Properties | Cubic, Hamiltonian, regular, zero-symmetric |
| Table of graphs and parameters | |
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a truncated icosidodecahedral graph (or great rhombicosidodecahedral graph) is the graph of vertices and edges of the truncated icosidodecahedron, one of the Archimedean solids. It has 120 vertices and 180 edges, and is a zero-symmetric and cubic Archimedean graph.[5]
 3-fold symmetry |
 2-fold symmetry |
Related polyhedra and tilings
 |
 |
| Bowtie icosahedron and dodecahedron contain two trapezoidal faces in place of the square.[6] | |
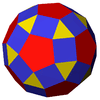
| Family of uniform icosahedral polyhedra | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry: [5,3], (*532) | [5,3]+, (532) | ||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
| {5,3} | t{5,3} | r{5,3} | t{3,5} | {3,5} | rr{5,3} | tr{5,3} | sr{5,3} |
| Duals to uniform polyhedra | |||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||
| V5.5.5 | V3.10.10 | V3.5.3.5 | V5.6.6 | V3.3.3.3.3 | V3.4.5.4 | V4.6.10 | V3.3.3.3.5 |
This polyhedron can be considered a member of a sequence of uniform patterns with vertex figure (4.6.2p) and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
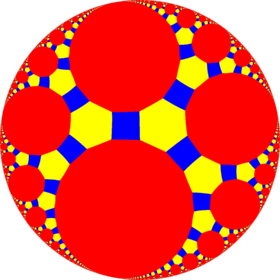
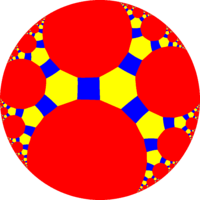
| *n32 symmetry mutations of omnitruncated tilings: 4.6.2n | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sym. *n32 [n,3] |
Spherical | Euclid. | Compact hyperb. | Paraco. | Noncompact hyperbolic | |||||||
| *232 [2,3] |
*332 [3,3] |
*432 [4,3] |
*532 [5,3] |
*632 [6,3] |
*732 [7,3] |
*832 [8,3] |
*∞32 [∞,3] |
[12i,3] |
[9i,3] |
[6i,3] |
[3i,3] | |
| Figures |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
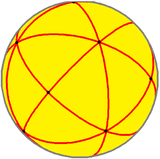
| Config. | 4.6.4 | 4.6.6 | 4.6.8 | 4.6.10 | 4.6.12 | 4.6.14 | 4.6.16 | 4.6.∞ | 4.6.24i | 4.6.18i | 4.6.12i | 4.6.6i |
| Duals | 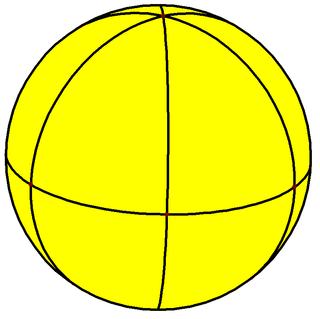 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Config. | V4.6.4 | V4.6.6 | V4.6.8 | V4.6.10 | V4.6.12 | V4.6.14 | V4.6.16 | V4.6.∞ | V4.6.24i | V4.6.18i | V4.6.12i | V4.6.6i |
Notes
- ↑ Wenninger, (Model 16, p. 30)
- ↑ Williamson (Section 3-9, p. 94)
- ↑ Cromwell (p. 82)
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W. "Icosahedral group". MathWorld.
- ↑ Read, R. C.; Wilson, R. J. (1998), An Atlas of Graphs, Oxford University Press, p. 269
- ↑ Symmetrohedra: Polyhedra from Symmetric Placement of Regular Polygons Craig S. Kaplan
References
- Wenninger, Magnus (1974), Polyhedron Models, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-09859-5, MR 0467493
- Cromwell, P. (1997). Polyhedra. United Kingdom: Cambridge. pp. 79–86 Archimedean solids. ISBN 0-521-55432-2.
- Williams, Robert (1979). The Geometrical Foundation of Natural Structure: A Source Book of Design. Dover Publications, Inc. ISBN 0-486-23729-X.
- Cromwell, P.; Polyhedra, CUP hbk (1997), pbk. (1999).
- Eric W. Weisstein, GreatRhombicosidodecahedron (Archimedean solid) at MathWorld.
- Klitzing, Richard. "3D convex uniform polyhedra x3x5x - grid".
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Great rhombicosidodecahedron". MathWorld.
- * Weisstein, Eric W. "Great rhombicosidodecahedral graph". MathWorld.
- Editable printable net of a truncated icosidodecahedron with interactive 3D view
- The Uniform Polyhedra
- Virtual Reality Polyhedra The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra