Stalag Luft III
| Stalag Luft III | |
|---|---|
| German: Stammlager Luft | |
| Part of Luftwaffe | |
|
Sagan, Lower Silesia, Germany (now Żagań, Poland) | |
 Model of the set used to film the movie The Great Escape. It depicts a smaller version of a single compound in Stalag Luft III. The model is now at the museum near where the prison camp was located. | |
 Stalag Luft III Sagan, Germany (pre-war borders, 1937) | |
| Coordinates | 51°35′55″N 15°18′27″E / 51.5986°N 15.3075°E |
| Type | Prisoner-of-war camp |
| Site information | |
| Controlled by |
|
| Site history | |
| In use | March 1942 – January 1945 |
| Events | The "Great Escape" |
| Garrison information | |
| Past commanders | Oberst Friedrich Wilhelm von Lindeiner-Wildau |
| Occupants | Allied air crews |
Stalag Luft III (German: Stammlager Luft III; literally "Main Camp, Air, III"; SL III) was a Luftwaffe-run prisoner of war (POW) camp during World War II, which held captured Western Allied air force personnel.
The Stalag was established in March 1942 in the German province of Lower Silesia near the town of Sagan (now Żagań, Poland), 160 kilometres (100 miles) south-east of Berlin. The site was selected because its sandy soil made it difficult for POWs to escape by tunnelling.
It is best known for two escape plots by Allied POWs.
- One in 1943 that became the basis of a fictionalised film, The Wooden Horse (1950), based on a book by escapee Eric Williams.
- The so-called Great Escape of March 1944, which was conceived by Royal Air Force Squadron Leader Roger Bushell, and was authorised by the senior British officer at Stalag Luft III, Herbert Massey. A heavily fictionalised version of the escape was depicted in a film, The Great Escape (1963), which was based on a book by former prisoner Paul Brickhill.
The camp was liberated by Soviet forces in January 1945.
Camp life 1942–44

The German military followed a practice whereby the different branches of the military were responsible for all POWs of equivalent branches. Hence the Luftwaffe was normally responsible for any Allied aircrew taken prisoner. This included captured naval aviators, such as members of the British Fleet Air Arm. In a few cases, other non-air force personnel were also held at Stalag Luft III.
Stammlager Luft (literally "Main Camp, Air") was Luftwaffe nomenclature for a POW camp. While the camp initially held only POWs who were officers, it was not known by the usual terms for such camps – Offizier Lager or Oflag. And later camp expansions added compounds for non-commissioned officers (NCOs).
The first compound (East Compound) of the camp was completed and opened on 21 March 1942. The first POWs, or kriegies, as they called themselves (from Kriegsgefangene), to be housed at Stalag Luft III were British and other Commonwealth officers, arriving in April 1942. The Centre compound was opened on 11 April 1942 and originally held British and other Commonwealth NCOs; by the end of 1942, however, they were replaced by USAAF personnel. The North Compound for British airmen, (where the "Great Escape" later occurred) opened on 29 March 1943. A South Compound for Americans was opened in September 1943 and USAAF prisoners began arriving at the camp in significant numbers the following month and the West Compound was opened in July 1944 for U.S. officers. Each compound consisted of fifteen single-story huts. Each 3.0-by-3.7-metre (10-by-12-foot) bunkroom slept fifteen men in five triple-deck bunks. Eventually the camp grew to approximately 24 hectares (60 acres) in size and housed about 2,500 Royal Air Force officers, about 7,500 U.S. Army Air Forces, and about 900 officers from other Allied air forces, for a total of 10,949 inmates, including some support officers.[1][2]
The prison camp had a number of design features that made escape extremely difficult. The digging of escape tunnels, in particular, was discouraged by several factors: the barracks housing the prisoners were raised approximately 60 centimetres (24 in) off the ground to make it easier for guards to detect tunnelling; the camp had been constructed on land that had a very sandy subsoil; the surface sand was bright yellow, so it could easily be detected if anyone dumped the darker, grey dirt found beneath it above ground, or even just had some of it on their clothing. The loose, collapsible sand meant the structural integrity of any tunnel would be very poor. A third defence against tunnelling was the placement of seismograph microphones around the perimeter of the camp, which were expected to detect any sounds of digging.
A substantial library with schooling facilities was available, where many POWs earned degrees such as languages, engineering or law. The exams were supplied by the Red Cross and supervised by academics such as a Master of King's College who was a POW in Luft III. The prisoners also built a theatre and put on high-quality bi-weekly performances featuring all the current West End shows.[3] The prisoners used the camp amplifier to broadcast a news and music radio station they named Station KRGY, short for Kriegsgefangener (POWs) and also published two newspapers, the Circuit and the Kriegie Times, which were issued four times a week.[4]
POWs operated a system whereby newcomers to the camp were vetted, to prevent German agents from infiltrating their ranks. Any POW who could not be vouched for by two POWs who knew the prisoner by sight was severely interrogated and afterwards escorted continually by other prisoners, until such time as he was deemed to be a genuine Allied POW. Several infiltrators were discovered by this method and none is known to have escaped detection in Luft III.
The German guards were referred to by POWs as "Goons" and, unaware of the Allied connotation, willingly accepted the nickname after being told it stood for "German Officer Or Non-Com".[5] German guards were followed everywhere they went by prisoners, who used an elaborate system of signals to warn others of their location. The guards' movements were then carefully recorded in a logbook kept by a rota of officers. Unable to stop what the prisoners called the "Duty Pilot" system, the Germans allowed it to continue and on one occasion the book was used by Kommandant von Lindeiner to bring charges against two guards who had slunk away from duty several hours early.[6]
The camp's 800 Luftwaffe guards were either too old for combat duty or young men convalescing after long tours of duty or from wounds. Because the guards were Luftwaffe personnel, the prisoners were accorded far better treatment than that granted to other POWs in Germany.[4] Deputy Commandant Major Gustav Simoleit, a professor of history, geography and ethnology before the war, spoke several languages, including English, Russian, Polish and Czech. Transferred to Sagan in early 1943, he proved sympathetic to allied airmen. Ignoring the ban against extending military courtesies to POWs, he provided full military honours for Luft III POW funerals, including one for a Jewish airman.[7]
Food was an ongoing matter of concern for the POWs. The recommended dietary intake for a normal healthy inactive adult male is 2,150 kilocalories (9,000 kilojoules).[8] Luft III issued "Non-working" German civilian rations which allowed 1,928 kcal (8,070 kJ) per day, with the balance made up from American, Canadian, and British Red Cross parcels and items sent to the POWs by their families.[4][9] As was customary at most camps, Red Cross and individual parcels were pooled and distributed to the men equally. The camp also had an official internal bartering system called a Foodacco – POWs marketed surplus goods for "points" that could be "spent" on other items.[10] The Germans paid captured officers the equivalent of their pay in internal camp currency (lagergeld), which was used to buy what goods were made available by the German administration. Every three months, weak beer was made available in the canteen for sale. As NCOs did not receive any "pay" it was the usual practice in camps for the officers to provide one-third for their use but at Luft III all lagergeld was pooled for communal purchases. As British government policy was to deduct camp pay from the prisoners' military pay, the communal pool avoided the practice in other camps whereby American officers contributed to British canteen purchases.[4]
Stalag Luft III had the best-organised recreational program of any POW camp in Germany. Each compound had athletic fields and volleyball courts. The prisoners participated in basketball, softball, boxing, touch football, volleyball, table tennis and fencing, with leagues organised for most. A 6.1 m × 6.7 m × 1.5 m (20 ft × 22 ft × 5 ft) pool used to store water for firefighting, was occasionally available for swimming.[4]
Many amenities were made possible by Swedish lawyer Henry Söderberg,[11] who was the YMCA representative to the area, and frequently brought to its camps not only sports equipment, and religious items supporting the work of chaplains, but also the wherewithal for each camp's band and orchestra, and well-equipped library.[12]
The first escape
The first escape occurred in October 1943 in the East Compound. Conjuring up a modern Trojan Horse, kriegies (prisoners) constructed a gymnastic vaulting horse largely from plywood from Red Cross parcels. The horse was designed to conceal men, tools and containers of soil. Each day the horse was carried out to the same spot near the perimeter fence and while prisoners conducted gymnastic exercises above, a tunnel was dug. At the end of each working day, a wooden board was placed over the tunnel entrance and covered with surface soil. The gymnastics disguised the real purpose of the vaulting horse and kept the sound of the digging from being detected by the microphones. For three months three prisoners, Lieutenant Michael Codner, Flight Lieutenant Eric Williams and Flight Lieutenant Oliver Philpot, in shifts of one or two diggers at a time, dug over 30 m (100 ft) of tunnel, using bowls as shovels and metal rods to poke through the surface of the ground to create air holes. No shoring was used except near the entrance. On the evening of 19 October 1943, Codner, Williams and Philpot made their escape.[13] Williams and Codner were able to reach the port of Stettin where they stowed away on a Danish ship and eventually returned to Britain. Philpot, posing as a Norwegian margarine manufacturer, was able to board a train to Danzig (now Gdańsk) and from there stowed away on a Swedish ship headed for Stockholm, from where he was repatriated to Britain. Accounts of this escape were recorded in the book Goon in the Block (later retitled The Wooden Horse) by Williams, the book Stolen Journey by Philpot and the 1950 film The Wooden Horse.[14]
The great escape
Background
There had been previous attempts at escaping from the camp (one of which inspired the film The Wooden Horse) and many tunnels had been started and discovered before completion.
In March 1943, Royal Air Force Squadron Leader Roger Bushell conceived a plan for a mass escape from the North Compound, which occurred on the night of 24/25 March 1944.[3][15] He was being held with the other British and Commonwealth airmen and he was in command of the Escape Committee that managed all escape opportunities from the north compound. Falling back on his legal background to represent his scheme, Bushell called a meeting of the Escape Committee to advocate for his plan. He said:
"Everyone here in this room is living on borrowed time. By rights we should all be dead! The only reason that God allowed us this extra ration of life is so we can make life hell for the Hun ... In North Compound we are concentrating our efforts on completing and escaping through one master tunnel. No private-enterprise tunnels allowed. Three bloody deep, bloody long tunnels will be dug – Tom, Dick, and Harry. One will succeed!"[16]
Herbert Massey, as senior British officer, authorised the escape attempt[17] which would have good chance of success; in fact, the simultaneous digging of three tunnels would become an advantage if any one of them was discovered, because the guards would scarcely imagine that another two were well underway. However, the most radical aspect of the plan was not the scale of the construction but the number of men intended to pass through the tunnels; in fact, while all previous attempts had involved up to 20 men, in this case Bushell was proposing to get over 200 out, all wearing civilian clothes and some with forged papers and escape equipment. As this escape attempt was unprecedented in size, it would require unparalleled organization; as the mastermind of the Great Escape, Roger Bushell inherited the codename of "Big X".[16] More than 600 prisoners were involved in the construction of the tunnels.[3]
The tunnels
Three tunnels were dug for the escape. They were named Tom, Dick, and Harry. The operation was so secretive that everyone was to refer to each tunnel by its name. Bushell took this so seriously that he threatened to court-martial anyone who even uttered the word "tunnel" aloud.[18]
Tom began in a darkened corner next to a stove chimney in hut 123 and extended west into the forest. It was found by the Germans and dynamited.
Dick's entrance was hidden in a drain sump in the washroom of hut 122 and had the most secure trap door. It was to go in the same direction as Tom and the prisoners decided that the hut would not be a suspected tunnel site as it was more inward than the others. Dick was abandoned for escape purposes because the area where it would have surfaced was cleared for camp expansion. Dick was then used to store dirt and supplies, and as a workshop.
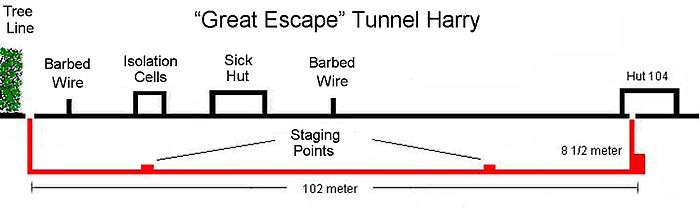
Harry, which began in hut 104, went under the Vorlager (which contained the German administration area), sick hut and the isolation cells to emerge at the woods on the northern edge of the camp.[19] The entrance to "Harry" was hidden under a stove. Ultimately used for the escape, it was discovered as the escape was in progress with only seventy-six of the planned two hundred twenty prisoners free. It was subsequently filled with sewage and sand, and sealed with cement by the Germans.
After the escape, the prisoners started digging another tunnel called George, but this was abandoned when the camp was evacuated.
Tunnel construction
The tunnels were very deep – about 9 m (30 ft) below the surface. They were very small, only 0.6 m (2 ft) square, though larger chambers were dug to house an air pump, a workshop, and staging posts along each tunnel. The sandy walls were shored up with pieces of wood scavenged from all over the camp, much from the prisoners' beds (of the twenty or so boards originally supporting each mattress, only about eight were left on each bed). Other wooden furniture was also scavenged.[20]




Other materials were also scavenged, such as Klim cans; tin cans that had originally held powdered milk supplied by the Red Cross for the prisoners. The metal in the cans could be fashioned into various tools and items, for example scoops and lamps, fueled by fat skimmed off soup served at the camp and collected in tiny tin vessels, with wicks made from old and worn clothing.[20] The main use of the Klim tins, however, was for the extensive ventilation ducting in all three tunnels.[21]
As the tunnels grew longer, a number of technical innovations made the job easier and safer. A pump was built to push fresh air along the ducting, invented by Squadron Leader Bob Nelson of 37 Squadron. The pumps were built of odd items including pieces from the beds, hockey sticks and knapsacks, as well as Klim tins.[20]
The usual method of disposing of sand from all the digging was to scatter it discreetly on the surface. Small pouches made of towels or long underpants were attached inside the prisoners' trousers; as they walked around, the sand could be scattered. Sometimes, they would dump sand into the small gardens they were allowed to tend. As one prisoner turned the soil, another would release sand while they both appeared to be in conversation.[20] The prisoners wore greatcoats to conceal the bulges from the sand, and were referred to as "penguins" because of their supposed resemblance. In sunny months, sand could be carried outside and scattered in blankets used for sun bathing; more than 200 were used to make an estimated 25,000 trips.[3] The Germans were aware that something was going on, but failed to discover any of the tunnels until much later. In an attempt to break up any escape attempt, nineteen of the top suspects were transferred without warning to Stalag VIIIC. Of those, only six had actually been involved with tunnel construction.
Eventually the prisoners felt they could no longer dump sand above ground because the Germans became too efficient at catching them doing it. After "Dick's" planned exit point was covered by a new camp expansion, the decision was made to start filling it up. As the tunnel's entrance was very well-hidden, "Dick" was also used as a storage room for items such as maps, postage stamps, forged travel permits, compasses and clothing.[22] Some guards cooperated by supplying railway timetables, maps, and many official papers so that they could be forged. Some genuine civilian clothes were obtained by bribing German staff with cigarettes, coffee or chocolate. These were used by escaping prisoners to travel away from the camp more easily, especially by train.[20]
The prisoners ran out of places to hide sand, and snow cover then made it impractical to scatter it undetected.[3] However, under the seats in the theatre there was a large empty space, but when it was built the prisoners had given their word not to misuse the materials; the parole system was regarded as inviolate. Internal "legal advice" was taken, and the SBOs decided that the completed building did not fall under the parole system. A seat in the back row was hinged and the sand dispersal problem thereby solved.[23]
As the war progressed, German prison camps began to receive larger numbers of American prisoners.[4] The Germans decided that new camps would be built specifically for U.S. airmen. To allow as many people to escape as possible, including the Americans, efforts on the remaining two tunnels increased. However, this drew attention from guards and in September 1943 the entrance to "Tom" became the 98th tunnel to be discovered in the camp; guards in the woods had seen sand being removed from the hut where it was located. Work on "Harry" ceased and did not resume until January 1944.[3][20]
Tunnel "Harry" completed
"Harry" was finally ready in March 1944. By then the Americans, some of whom had worked on "Tom", had been moved away; despite its portrayal in the Hollywood film, no American participated in the "Great Escape". Previously, the attempt had been planned for the summer for its good weather, but in early 1944 the Gestapo visited the camp and ordered increased effort to detect escapes. Rather than risk waiting and having their tunnel discovered, Bushell ordered the attempt be made as soon as it was ready.
In their plan, of the 600 who had worked on the tunnels only 200 would be able to escape. The prisoners were separated into two groups. The first group of 100, called "serial offenders," were guaranteed a place and included 30 who spoke German well or had a history of escapes, and an additional 70 considered to have put in the most work on the tunnels. The second group, considered to have much less chance of success, was chosen by drawing lots; called "hard-arsers", they would have to travel by night as they spoke little or no German and were only equipped with the most basic fake papers and equipment.[3]
The prisoners waited about a week for a moonless night, and on Friday 24 March the escape attempt began. As night fell, those allocated a place moved to Hut 104. Unfortunately for the prisoners, the exit trap door of Harry was frozen solid and freeing it delayed the escape for an hour and a half. Then it was discovered that the tunnel had come up short of the nearby forest; at 10.30 p.m. the first man out emerged just short of the tree line close to a guard tower. (According to Alan Burgess, in his book The Longest Tunnel, the tunnel reached the forest, as planned, but the first few trees were too sparse to provide adequate cover). As the temperature was below freezing and there was snow on the ground, a dark trail would be created by crawling to cover. To avoid being seen by the sentries, the escapes were reduced to about ten per hour, rather than the one every minute that had been planned. Word was eventually sent back that no-one issued with a number above 100 would be able to get away before daylight. As they would be shot if caught trying to return to their own barracks, these men changed back into their own uniforms and got some sleep. An air raid then caused the camp's (and the tunnel's) electric lighting to be shut down, slowing the escape even more. At around 1 a.m., the tunnel collapsed and had to be repaired.
Despite these problems, 76 men crawled through to freedom, until at 4:55 a.m. on 25 March, the 77th man was spotted emerging by one of the guards. Those already in the trees began running, while a New Zealand Squadron Leader Leonard Henry Trent VC who had just reached the tree line stood up and surrendered. The guards had no idea where the tunnel entrance was, so they began searching the huts, giving men time to burn their fake papers. Hut 104 was one of the last to be searched, and despite using dogs the guards were unable to find the entrance. Finally, German guard Charlie Pilz crawled back through the tunnel but found himself trapped at the camp end; he began calling for help and the prisoners opened the entrance to let him out, finally revealing its location.
An early problem for the escapees was that most were unable to find the way into the railway station, until daylight revealed it was in a recess of the side wall to an underground pedestrian tunnel. Consequently, many of them missed their night time trains, and decided either to walk across country or wait on the platform in daylight. Another unanticipated problem was that this was the coldest March for thirty years, with snow up to five feet deep, so the escapees had no option but to leave the cover of woods and fields and stay on the roads.[3]
Murders of escapees
| Nationalities of the 50 executed prisoners |
Following the escape, the Germans made an inventory of the camp and uncovered how extensive the operation had been. Four thousand bed boards had gone missing, as well as 90 complete double bunk beds, 635 mattresses, 192 bed covers, 161 pillow cases, 52 twenty-man tables, 10 single tables, 34 chairs, 76 benches, 1,212 bed bolsters, 1,370 beading battens, 1219 knives, 478 spoons, 582 forks, 69 lamps, 246 water cans, 30 shovels, 300 m (1,000 ft) of electric wire, 180 m (600 ft) of rope, and 3424 towels. 1,700 blankets had been used, along with more than 1,400 Klim cans.[20] Electric cable had been stolen after being left unattended by German workers; because they had not reported the theft, they were executed by the Gestapo.[25] Thereafter each bed was supplied with only nine bed boards, which were counted regularly by the guards.
Of 76 escapees, 73 were captured. Adolf Hitler initially wanted them to be shot as an example to other prisoners, along with Commandant von Lindeiner, the architect who designed the camp, the camp's security officer and all the guards on duty at the time. Hermann Göring, Field Marshal Keitel, Major-General Westhoff and Major-General Hans von Graevenitz (inspector in charge of war prisoners)[26] all argued against the executions as a violation of the Geneva Conventions. Hitler eventually ordered SS head Himmler to execute more than half of the escapees. Himmler passed the selection on to General Arthur Nebe, and fifty were executed singly or in pairs.[3][27] Roger Bushell, the leader of the escape, was shot by Gestapo official Emil Schulz just outside Saarbrucken, Germany.[15] Bob Nelson is said to have been spared by the Gestapo because they may have believed he was related to his namesake Admiral Nelson. His friend Dick Churchill was probably spared because of his surname, shared with the British Prime Minister.[28] Seventeen were returned to Stalag Luft III, two were sent to Colditz Castle, and four were sent to Sachsenhausen concentration camp, where one quipped "the only way out of here is up the chimney."[29] They managed to tunnel out and escape three months later, although they were recaptured and returned;[3][27] two were subsequently sent to Oflag IV-C Colditz.
There were three successful escapees:
- Per Bergsland, Norwegian pilot of No. 332 Squadron RAF, escapee #44
- Jens Müller, Norwegian pilot of No. 331 Squadron RAF, escapee #43
- Bram van der Stok, Dutch pilot of No. 41 Squadron RAF, escapee #18
Bergsland and Müller escaped together, and made it to neutral Sweden by train and boat with the help of friendly Swedish sailors.[30] Van der Stok, granted one of the first slots by the Escape Committee due to his language and escape skills, traveled through much of occupied Europe with the help of the French Resistance before finding safety at a British consulate in Spain.[27]
Aftermath

The Gestapo investigated the escape and, whilst this uncovered no significant new information, the camp Kommandant, von Lindeiner-Wildau, was removed and threatened with court martial. Having feigned mental illness to avoid imprisonment, he was later wounded by Soviet troops advancing toward Berlin, while acting as second in command of an infantry unit. He surrendered to British forces as the war ended, and was a prisoner of war for two years at the prisoner of war camp known as the "London Cage". He testified during the British SIB investigation concerning the Stalag Luft III murders. Originally one of Hermann Göring's personal staff, after being refused retirement, von Lindeiner had been posted as Sagan kommandant. He had followed the Geneva Accords concerning the treatment of POWs and had won the respect of the senior prisoners.[7] He was repatriated in 1947 and died in 1963 aged 82.
On April 6, 1944 the new camp Kommandant Oberstleutnant Erich Cordes informed Massey that he had received official communication from the German High Command that 41 of the escapees had been shot while resisting arrest. Massey was himself repatriated on health grounds a few days later.
Over subsequent days, prisoners collated the names of 47 prisoners they considered to be unaccounted for. On 15 April (17 April in some sources) the new senior British officer, Group Captain Douglas Wilson RAAF, surreptitiously passed a list of these names to an official visitor from the Swiss Red Cross.[31]
Cordes was replaced soon afterwards by Oberst Werner Braune. Braune was appalled that so many escapees had been killed, and allowed the prisoners who remained there to build a memorial, to which he also contributed. (The memorial still stands at its original site.)
The British government learned of the deaths from a routine visit to the camp by Swiss authorities as the protecting power in May; the Foreign Secretary Anthony Eden announced the news to the House of Commons on 19 May 1944.[32][33] Shortly afterwards the repatriated Massey arrived in Britain and briefed the Government regarding the fate of the escapees. Eden updated Parliament on 23 June, promising that, at the end of the war, those responsible would be brought to exemplary justice.[34]
Post-war investigation and prosecutions
General Arthur Nebe, who is believed to have selected the airmen to be shot, was involved in the 20 July plot to kill Hitler and executed by Nazi authorities in 1945.
After the war ended, the Royal Air Force Police (RAFP) investigative branch began to research the Great Escape and launched a manhunt for German personnel considered responsible for killing escapees.[35]
Colonel Telford Taylor was the US prosecutor in the High Command case at the Nuremberg Trials. The indictment called for the General Staff of the Army and the High Command of the German Armed Forces to be considered criminal organisations; the witnesses were several of the surviving German field marshals and their staff officers.[36] One of the crimes charged was of the murder of the fifty.[37] Colonel of the Luftwaffe Bernd von Brauchitsch, who served on the staff of Reich Marshal Hermann Göring, was interrogated by Captain Horace Hahn about the murders.[38] Several Gestapo officers responsible for the murders were executed or imprisoned.
Survivors
By September 2014, Gordon King of Edmonton, Alberta, Canada,[39] was the only prisoner still alive who had worked directly on the Great Escape, but was not one of the escapees. He had been number 141 to escape and operated the pump to send air into the tunnel. Speaking candidly of his low number and resulting inability to get out of the tunnel that night, he said he considered himself fortunate. King had been shot down over Germany in 1943 and spent the rest of the war as a prisoner. He participated in the Battle Scars TV series in his home town of Edmonton.[39]
Jack Harrison, who was one of the 200 men of the Great Escape, died on 4 June 2010, at the age of 97.[40][41] Les Broderick, who kept watch over the entry of the "Dick" tunnel, died on 8 April 2013 aged 91. He was in a group of three who had escaped out of the "Harry" tunnel but were recaptured when a cottage they had hoped to rest in turned out to be full of soldiers.[42] Ken Rees, a digger, was in the tunnel when the escape was discovered. He later lived in North Wales and died at age 93 on 30 August 2014. His book is called Lie in the Dark and Listen.[43][44] A reunion of Stalag Luft III survivors was held in 1983 in Chicago. Illinois. The reunion included a mock interrogation between Hanns Scharf and Col. Frances Gabreski. The reunion, including the mock interrrogation, is available on DVD from RDR Productions in Glenview, IL
Dick Churchill is the last of the 76 escapees still living as of March 2017; then an RAF Squadron Leader, he was among the 23 not executed by the Nazis.[45][46] Churchill, a Handley Page Hampden bomber pilot, was discovered after the escape hiding in a hay loft. In a 2014 interview at the age of 94, he said he was fairly certain that he had been spared execution because his captors thought he might be related to British Prime Minister Winston Churchill.[45]
Paul Royle, a Bristol Blenheim pilot, was interviewed in March 2014 as part of the 70th anniversary of the escape, living in Perth, Australia at the age of 100. He downplayed the significance of the escape and did not claim that he did anything extraordinary, saying: "While we all hoped for the future we were lucky to get the future. We eventually defeated the Germans and that was that." Royle died, aged 101, in August 2015.[46]
Legacy
In 2014, the 70th anniversary of the escape, the RAF staged a commemoration of the escape attempt, with 50 serving personnel carrying a photograph of one of the men shot.[47]
Liberation in 1945
Just before midnight on 27 January 1945, with Soviet troops only 26 km (16 mi) away, the remaining 11,000 POWs were marched out of camp with the eventual destination of Spremberg. In below-freezing temperatures and 15 cm (6 in) of snow, 2,000 prisoners were assigned to clear the road ahead of the main group. After a 55 km (34 mi) march, the POWs arrived in Bad Muskau where they rested for thirty hours, before marching the remaining 26 km (16 mi) to Spremberg. On 31 January, the South Compound prisoners plus 200 men from the West Compound were sent by train to Stalag VII-A at Moosburg followed by the Centre compound prisoners on 7 February. 32 prisoners escaped during the march to Moosburg but all were recaptured.[48] The North, East and remaining West compound prisoners at Spremberg were sent to Stalag XIII-D at Nürnberg on 2 February.
With the approach of US forces on 13 April, the American prisoners at XIII-D were marched to Stalag VII-A. While the majority reached VII-A on 20 April, many had dropped out on the way with the German guards making no attempt to stop them. Built to hold 14,000 POWs, Stalag VII-A now held 130,000 from evacuated stalags with 500 living in barracks built for 200. Some chose to live in tents while others slept in air raid slit trenches.[49] The U.S. 14th Armored Division liberated the prisoners of VII-A on 29 April.[4]
Kenneth W. Simmons' book Kriegie (1960) vividly describes the life of POWs in the American section of Stalag Luft III in the final months of the war, ending with the winter forced-march away from the camp, escaping the advancing Soviet troops and eventually being liberated.
In popular culture
The POW camp was actually referred to as Stalag Luft 3 by the Germans, and Paul Brickhill, in his early writings about the escape, also wrote it that way. For his book The Great Escape, his English editors changed it to Stalag Luft III, and such has been its influence on popular culture that Stalag Luft III it has remained.[50]
Eric Williams was a navigator on a downed bomber who was held at Stalag Luft III. After the war, on the long sea voyage home, Williams wrote Goon in the Block, a short book based on his experience. Four years later, in 1949, he rewrote it as a longer third-person narrative under the title The Wooden Horse,[51] which was filmed as The Wooden Horse in 1950. He included many details omitted in his first book, but changed his name to "Peter Howard", Michael Codner to "John Clinton" and Oliver Philpot to "Philip Rowe". Williams also wrote a prequel, The Tunnel, an extended study of the mentalities of life as a prisoner of war. Although not an escape novel, it shows the profound urge to escape, and explores the ways that camp life affected men's emotions.
Paul Brickhill was an Australian-born Spitfire pilot, shot down in 1943 over Tunisia to become a prisoner of war. While imprisoned at Stalag Luft III, he was involved in the escape attempt. He did not take part in tunnelling but was in charge of "stooges", the relay teams who would alert prisoners that German search teams had entered the camp. He was originally scheduled to be an early escapee but when it was discovered he suffered from claustrophobia, he was dropped down to the bottom of the list. He later said he figured this probably saved his life. After the war, Brickhill co-wrote Escape to Danger (with Conrad Norton, and original artwork: London: Faber and Faber, 1946). Later Brickhill wrote a larger study and the first major account of the escape in The Great Escape (1950), bringing the incident to a wide public attention. This book became the basis of the film (1963).
The film was based on the real events but with numerous compromises for its commercial appeal, such as including Americans among the escapees (none of whom were actually American). While some characters were fictitious, many were amalgams of and some based on real people. There were no actual escapes by motorcycle or aircraft nor were the recaptured prisoners executed in one place at the same time. The film has resulted in the story and the memory of the fifty executed airmen remaining widely known, if in a distorted form.[52]
The search for those responsible for the murder of the Allied officers, and the subsequent trials, was depicted in a 1988 television film named The Great Escape II: The Untold Story starring Christopher Reeve.[53] Donald Pleasence in a supporting role plays a member of the SS (in the 1963 original Pleasence had played Flight-Lieutenant Colin Blythe, 'The Forger'). The murder of the prisoners in this film is more accurate than in the 1963 original, with the POWs being shot individually or in pairs, but other portions of the film are fictional.
The camp was the basis for a single-player mission and multi-player map in the first Call of Duty video game. Most of the buildings and guard towers were identical to the camp and the single-player mission involved rescuing a British officer from a prison cell that closely resembled the camp's solitary confinement building. Stalag Luft is also a playable POW camp in the computer and Xbox game The Escapists, but with a slightly different name of "Stalag Flucht".
The Great Escape is a video game which shares a title and similar plot to the movie. for the Sinclair ZX Spectrum computer published by Ocean Software in 1986,[54] and later ported for the Commodore 64, Amstrad CPC, and DOS computers. The game surroundings were similar to the actual camp but the supposed location was in Northern Germany, and one side of the camp overlooked the North Sea. The ZX Spectrum version of The Great Escape was placed at number 23 in the Your Sinclair official top 100,[55]
The Great Escape also was a game for Xbox and PlayStation 2 released in 2003. The plot-line follows that of the film of the same name, except there are also levels featuring some of the characters first captures and early escape attempts, as well as a changed ending.
Notable prisoners
Notable military personnel held at Stalag Luft III included:
- Fighter and test pilot Roland Beamont, later to test fly the English Electric Canberra and Lightning, arrived at Stalag Luft III just after the "Great Escape", having been shot down in his Tempest by ground fire, while attacking a troop train near Bocholt while on his 492nd operational sortie.
- Australian journalist Paul Brickhill was an inmate at Stalag Luft III from 1943 until release. In 1950 he wrote the first comprehensive account about The Great Escape, which was later adapted into the film and went on to chronicle the life of Douglas Bader in Reach for the Sky and the efforts of 617 "Dam Busters" Squadron.
- Josef Bryks, Czechoslovak RAFVR fighter pilot and serial escaper, was held at Stalag Luft III from August 1943 to July 1944.[56]
- Col. Darr Alkire, Commander of the 449th Bombardment Group. The senior officer in charge of the West Compound from April 1944 to release in April 1945. Future Brigadier General and Silver Star recipient.
- Flying Officer Ray Grayston, RAF, one of the "Dam Busters" who had bombed the Eder Dam, was an inmate at Stalag Luft III from 1943 to 1945.[57]
- Flight Lieutenant George Harsh RCAF was a member of the Great Escape's executive committee and the camp "security officer". He was one of the 19 "suspects" transferred to Belaria compound shortly before the escape. Born in 1910 to a wealthy and prominent Georgia family, Harsh, a medical student, was sentenced to life imprisonment in 1929 for the self-confessed thrill killing of a grocer. He saved the life of a fellow prisoner by performing an emergency appendectomy, for which Georgia governor Eugene Talmadge released him on parole in November 1940 and finally granted him a full pardon. He then joined the RCAF as a tail gunner and after being shot down in 1942 was sent to Stalag Luft III. In 1971 he published his autobiography which has since been translated into German and Russian.[58]
- David M. Jones, Commander of the 319th Bombardment Group in North Africa, was an inmate at Stalag Luft III for two and a half years. According to his biography he led the digging team on Harry. In early 1942 Jones took part in the Doolittle Raid undertaken in retaliation for the December 1941 attack on Pearl Harbor.
- Squadron Leader Phil Lamason RNZAF, who was also the senior officer in charge of 168 Allied airmen initially held at Buchenwald concentration camp.
- P. P. Kumaramangalam DSO, MBE of the then British Indian Army, a future Chief of the Indian Army.
- Flight Lieutenant Gordon "Moose" Miller RCAF, helped carry the Wooden Horse in and out each day under the German guns without faltering with the weight of two concealed diggers and a day's worth of earth. He was awarded the Distinguished Flying Cross for repairing a damaged Wellington in flight and allowing the crew to parachute to safety.[59]
- Robert M. Polich, Sr., also of the United States Army Air Forces, who received the Distinguished Flying Cross, later featured in the short film Red Leader on Fire which was submitted for the Minnesota's Greatest Generation short film festival in 2008.[60]
- Col. Delmar T. Spivey, who was, for a time, the Senior American Officer (SAO), was captured on 12 August 1943, while flying as an observer on a Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress of the 407th Bomb Squadron, 92d Bomb Group.[61][62][63] As the USAAF expert on aerial gunnery, Spivey was on the mission to evaluate possible improvements to gun turrets.[64][65] (MACR 655)[66] Spivey assumed command as SAO, in Centre Compound, in August 1943. Amazed by the prisoners' ingenuity, he had a carefully coded history of the camp created, so that future POWs would not have to "re-invent the wheel." This carefully hidden record was retrieved and carried at no little risk when the camp was hastily evacuated in late January 1945, as the Germans marched the prisoners away from the rapidly advancing Russian armies. The documents served as the basis and initial impetus for "Stalag Luft III – The Secret Story", a definitive history of the camp, by Col. Arthur A. Durand, USAF (Ret.).[67]
- Wing Commander Robert Stanford Tuck, a British flying ace with 29 victories, was imprisoned at Sagan until shortly before the Great Escape; suspected of being a ringleader, he was transferred to Belaria, which Tuck credited with saving his life. (His mentor, Roger Bushell, was among those shot after the Great Escape). Tuck eventually managed to escape on 1 February 1945, during the evacuation of the camp, with the help of Polish RAF pilot Zbigniew Kustrzyński. Both made it to the Russian lines.[68]
- Brigadier-General Arthur W. Vanaman, the highest-ranking USAAF officer captured in the European Theatre of Operations. Vanaman, an intelligence officer, succeeded Spivey as SAO in mid-1944. He had (like Spivey) been captured after flying as an observer on a bombing mission. The crew had advised Vanaman to bail out after his aircraft had been hit by flak and filled with smoke. This, ironically, had been caused by the ignition of a harmless smoke marker and the bomber had returned to base safely.
Some held at Stalag Luft III went on to notable careers in the entertainment industry:
- British actor Peter Butterworth and English writer Talbot Rothwell were both inmates of Stalag Luft III; they became friends and later worked together on the Carry On films. Butterworth was one of the vaulters covering for the escapees during the escape portrayed by the book and film The Wooden Horse.[69] After the war and as an established actor, Butterworth auditioned for the film but "didn't look convincingly heroic or athletic enough" according to the makers of the film.[70]
- British actor Rupert Davies had many roles in productions at the theatre in the camp; his most famous roles on film and TV may have been Inspector Maigret in the BBC series Maigret that aired over 52 episodes from 1960 to 1963 and George Smiley in the movie The Spy Who Came in from the Cold.
- English writer and broadcaster Hugh Falkus was an inmate at Stalag Luft III from around 1943, after his Spitfire was shot down over France. Falkus reportedly worked on 13 escape tunnels during his time as a POW, although never officially listed as an escapee.[71]
- American novelist and screenwriter Len Giovannitti was held in Stalag Luft III's Center Compound. A navigator with the 742nd Bomb Squadron, 455th Bomb Group of the Fifteenth Air Force, he was on his 50th mission when his B-24 Liberator was shot down over Austria on 26 June 1944. A POW for nearly a year, he incorporated his experiences, including the winter march to Germany and liberation in Bavaria, in a novel he wrote between April 1953 and May 1957, The Prisoners of Combine D, published by Henry Holt and Company (ASIN: B0007E6KMG).
- Singer Cy Grant, born in British Guiana, served as a Flight Lieutenant in the RAF and spent two years as a prisoner of war, including time at Stalag Luft III. After the war he qualified as a barrister but went on to be a singer, actor and author. His was the first black face to be regularly seen on British television, singing the news as "topical calypsos" (punning on "tropical") on the BBC Tonight programme.[72][73]
- Wally Kinnan, one of the first well known U.S. television broadcast meteorologists, was also in the camp.
Stalag Luft III inmates also became involved in politics.
- Justin O'Byrne, who spent more than three years as a POW, represented Tasmania in the Australian Senate for 34 years and served as President of the Senate.[74]
- Professor Basil Chubb, author and political science lecturer, spent 15 months there after being shot down over Germany.[75]
- Frederick Irving, later a US diplomat and civil servant.
- Charles W. Sandman, Jr., a navigator in the USAAF, spent over seven months in Stalag Luft III. Sandman entered the camp weighing approximately 86 kg (190 lb) and left weighing 57 kg (125 lb). In his diary, Sandman describes the harsh winters and struggles to secure rations sent by the American Red Cross. After the war, he was elected to the US Senate from New Jersey and criticized for supporting President Nixon during the Watergate scandal.
- Peter Thomas, later Lord Thomas after a political career as a Welsh Conservative politician and cabinet minister under Edward Heath, spent four years as a prisoner of war including being imprisoned at Stalag Luft III.
See also
- Christopher Hutton
- Cowra breakout—at least 545 Japanese POWs escaped
- Hogan's Heroes, television WW II-setting sitcom (partly set near Hammelburg)
- Island Farm and "The German Great Escape"
- MI9
- MIS-X
- Stalag 17, 1953 film
- Stalag Luft I
- Stalag VIII-B, a notorious camp
- Oflag
Notes
- ↑ Petersen, Quentin Richard. "Stalag Luft III". Selected Recollections Chosen from a Fortunate Life, a continuing memoir. World War II Living Memorial, Memories Gallery. SeniorNet.org. Retrieved 28 June 2009.
- ↑ "Museum of Allied Prisoners of War Martyrdom". Żagań, Poland: Serwis Museum. Archived from the original on 20 July 2011. Retrieved 28 June 2009.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "Pilot Officer Bertram A. "Jimmy" James". Retrieved 21 October 2009.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "American Prisoners Of War In Germany: Stalag Luft 3". War Department Intelligence Service. 15 July 1944. Archived from the original on 28 July 2007. Retrieved 21 October 2009.
- ↑ Ives, Raymond (2008). Fickle Finger of Fate: The Memoir of a Bombardier with the 96th Bomb Group. Merriam Press. p. 77.
- ↑ Dickens, Monica (1974). Great Escape. Pan Books. ISBN 0-330-24065-X.
- 1 2 Davis, Rob. "The Great Escape, Stalag Luft III, Sagan". Retrieved 28 June 2009.
- ↑ "Daily Calorie Requirements ARCHIVE". Webstation.com.au. Archived from the original on 1 March 2015. Retrieved 18 May 2017.
- ↑ The German guards were not much better fed than the prisoners and also used the Red Cross parcels to supplement their diet.
- ↑ AIR40/2645 Official Camp History – Part I Para 2(e)
- ↑ www.comstation.com
- ↑ www.amazon.com
- ↑ AIR40/2645 Part I – Official Camp History – SLIII(E)
- ↑ "The Geneva Convention Relative to the Treatment of Prisoners of War". Archived from the original on 29 June 2009. Retrieved 28 June 2009.
The Convention requires that a Detaining Power may discipline, but not punish, escapees (Articles 42, 91–93), help the POW keep and maintain his or her uniform (Art. 27) and provide official documentation of POW status and identity (Art. 17), but makes no provision for a POW's willful abandonment of these markers. As any enemy agent out of uniform may be executed as a spy, evidence of one's POW status was essential. All escapees kept their German-issued POW identity disc and uniform badges and brevets hidden in their civilian clothing though these items could expose their cover during a routine search.
- 1 2 Craig, Phil (24 October 2009). "He shot the hero of the Great Escape in cold blood. But was this one Nazi who DIDN'T deserve to hang?". Daily Mail. Daily Mail and General Trust. Retrieved 10 January 2011.
- 1 2 "Squadron Leader Roger Bushell". Pegasusarchive.org. Retrieved 26 August 2014.
- ↑ "Wartime Great Escape hero Herbert Martin Massey honoured at Hilton birthplace". Derby Telegraph. 5 December 2016.
- ↑ Brickhill, Paul: The Great Escape, p. 38
- ↑ Dando-Collins. p.97
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Great Escape". Nova. Season 31. Episode 582. 16 November 2004.
- ↑ "Inside Tunnel "Harry"" (Interactive diagram with 16 annotated points of interest). Documentary film interactive guide. PBS/NOVA. October 2004. Retrieved 27 September 2009.
- ↑ Compasses were made from melted fragments of broken Bakelite gramophone records, incorporating a tiny needle made from slivers of magnetised razor blades. On the underside of each the prisoners stamped "Made in Stalag Luft III – Patent Pending".
- ↑ Brickhill, Paul (1950). "13". The Great Escape.
- ↑ John Gifford Stower, Pilot Officer, Royal Air Force Voluntary Reserve. He was born on the 09-15-1916 in Jujuy, Argentina, and died on the 03-31-1944 in Zagan, Poland (Germany at the time). He was part of 142 Squadron when his Stirling was shot down and was one of the 50 POWs executed by the Gestapo under Hitler’s direct orders on 31 March 1944. His name is on the Memorial to "The Fifty" down the road toward Żagań. "Nacidos con Honor", Claudio Meunier, Ed. Grupo Abierto, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2008; and "Alas de Trueno", Claudio Meunier & Carlos García, n/a, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2005.
- ↑ Brickhill 1950, p. 268.
- ↑ "Hans von Graevenitz". World War II Gravestones. Retrieved 15 July 2018.
- 1 2 3 Carroll 2004
- ↑ Churchill, Dick. "Last British 'Great Escaper' tells how he escaped execution". Retrieved 24 March 2014.
- ↑ "Great Escape: The Untold Story (WW2 POW Documentary) - Timeline". BBC.
- ↑ The Great Escape - The Three That Got Away(Nova)
- ↑ Simon Read, Human Game: Hunting the Great Escape Murderers, London, Constable & Robinson, p. 21
- ↑ Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). House of Commons. 19 May 1944. col. 437–439.
- ↑ "47 British and Allied airmen shot by Germans". The Manchester Guardian. 20 May 1944. p. 6.
- ↑ Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). House of Commons. 23 June 1944. col. 477–482.
- ↑ Andrews, Allen (1976). Exemplary Justice. London: Harrap. ISBN 978-0-245-52775-3.
- ↑ Guilt, Responsibility and the Third Reich. Cambridge: Heffer. 1970. ISBN 0-85270-044-X.
- ↑ "Nuremberg Trial Proceedings Vol. 1 Indictment: Count Three C.2". Avalon Project. Yale University. Retrieved 28 June 2009.
- ↑ "Seventy-Ninth Day: Tuesday, 12 March 1946: Morning Session". Nuremberg Trial Proceedings. 9. Avalon Project, Yale Law School. Retrieved 1 March 2010.
- 1 2 "Stanley C. Gordon "Gord" King, Air Force". The Memory Project. Retrieved 7 September 2014.
- ↑ Smith, Lewis (8 June 2010). "Jack Harrison, last of the Great Escapers dies, aged 97". The Independent. London: Independent Print Limited. Retrieved 25 June 2010.
- ↑ "Jack Harrison: wartime bomber pilot and Stalag Luft III PoW". The Times. London. 9 June 2010. Retrieved 25 June 2010.
- ↑ "Obituaries: Flight Lieutenant Les Brodrick". The Telegraph. 12 April 2013. Retrieved 13 April 2013.
- ↑ Rees & Arrandale 2004.
- ↑ "Wing Commander Ken Rees – obituary". The Daily Telegraph. Telegraph Media Group. 1 September 2014. Retrieved 2 September 2014.
- 1 2 "Last British 'Great Escaper' tells how he escaped execution". The Daily Telegraph. Telegraph Media Group. Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- 1 2 "The Great Escape: Perth survivor Paul Royle marks 70th anniversary". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 27 March 2014.
- ↑ Hall, Robert (March 24, 2014). "'The Great Escape' commemorated in Poland". BBC News. Retrieved March 15, 2015.
- ↑ "The Story of Stalag Luft III, Part IX – The March". AFHI Virtual Museum. Stalag Luft III Former Prisoners of War Association.
- ↑ "The Story of Stalag Luft III, Part X – Moosburg". AFHI Virtual Museum. Stalag Luft III Former Prisoners of War Association.
- ↑ Dando-Collins 2016
- ↑ Williams, Eric (1949). The Wooden Horse. London: Collins. ISBN 978-1783462414.
- ↑ Warren, Jane. "The Truth About The Great Escape | Express Yourself | Comment |". The Daily Express. Northern andShell Media. Retrieved 17 November 2016.
- ↑ The Great Escape II: The Untold Story on IMDb
- ↑ The Great Escape at SpectrumComputing.co.uk
- ↑ The YS Official Top 100 Part 4 Archived 2006-08-16 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Josef Bryks". Free Czechoslovak Air Force. 20 February 2011. Retrieved 27 October 2017.
- ↑ "Flying Officer Ray Grayston". The Daily Telegraph. Telegraph Media Group. 28 April 2010.
- ↑ Harsh, George (1971). Lonesome Road. W. W. Norton. ISBN 978-0-393-07456-7.
- ↑ Jacobson, Ray. 426 Squadron History. Toronto. ISBN 0-9693381-0-4.
- ↑ "Moving Pictures 2008 Film Competition". Minnesota Historical Society. Retrieved 28 June 2009.
- ↑ Hatch, Gardner N., W. Curtis Musten, and John S. Edwards, American Ex-Prisoners of War: Non Solum Armis, Volume 4, Paducah, Kentucky: Turner Publishing Company, 2000, Library of Congress card number 00-110967, ISBN 1-56311-624-3, p. 150.
- ↑ Bowman, Martin W., Home by Christmas?: The Story of US Airmen at War, Patrick Stephens, 1987, ISBN 0-85059-834-6, p. 23.
- ↑ Gilbert, Adrian, POW: Allied prisoners in Europe, 1939–1945, John Murray Publishers, 2007, p. 31.
- ↑ Katsaros, John, "CODE BURGUNDY: The Long Escape", 2009, ISBN 1-57256-108-4, Chapter 8, "Emergency Orders", p. 39.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 August 2014. Retrieved 9 October 2014.
- ↑ mission_date=1943-08-12
- ↑ Durand, Arthur A., Col., USAF (Ret.), "Stalag Luft III – The Secret Story", Louisiana State University Press, New Ed edition, October 1999, Introduction.
- ↑ Forrester, Larry. Fly for Your Life: The Story of RR Stanford Tuck, DSO, DFC (Fortunes of War). London: Cerberus Publishing Ltd., 1981. ISBN 1-84145-025-1. Page 334, 339, 347.
- ↑ "Lt Peter Butterworth (Carry On Star)". Forum.keypublishing.com. Retrieved 26 August 2014.
- ↑ Biography for Peter Butterworth on IMDb
- ↑ Hugh Falkus – A Life on the Edge, published by The Medlar Press Ltd, Ellesmere, Shropshire, UK.
- ↑ "Cy Grant" (obituary), Daily Telegraph (London), 15 February 2010.
- ↑ "GRANT – Cy", Caribbean Aircrew in the RAF during WW2.
- ↑ Ray, Robert (16 Nov 1993). "Condolences: Hon. Justin Hilary O'Byrne AO". Hansard. Retrieved 24 June 2008.
- ↑ "Father of political science in Ireland" (PDF). The Irish Times. Trinity College Dublin. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 July 2009. Retrieved 24 June 2008.
References
- Ash, William (2005). Under the Wire. ISBN 0-593-05408-3.
- Barris, Ted (2013). The Great Escape: A Canadian Story. Thomas Allen. ISBN 978-1-77102-272-9.
- Brickhill, Paul (1950). The Great Escape. New York: Norton. ISBN 9780393325799.
- Burgess, Alan (1990). The Longest Tunnel. New York: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 1591140978.
- Carroll, Tim (2004). The Great Escapers. Mainstream Publishers. ISBN 1-84018-904-5.
- Clark, Albert Patton (2005). 33 Months as a POW in Stalag Luft III: A World War II Airman Tells His Story. Golden, CO: Fulcrum. ISBN 978-1-55591-536-0.
- Cockroft, Steph (18 November 2014). "Incredible tale of the British soldier who survived WWI, signed up aged 52 to fight the Nazis as an air gunner, was shot down and emerged unscathed from reprisals in aftermath of the Great Escape". Daily Mail. Daily Mail and General Trust.
- Dando-Collins, Stephen (2016). The Hero Maker,A Biography of Paul Brickhill. Sydney: Penguin Random House. ISBN 978-0-85798-812-6.
- Durand, Arthur A (1989). Stalag Luft III. Patrick Stephens Ltd. ISBN 1-85260-248-1.
- Foot, MRD; Langley, James (1979). MI9: Escape and Evasion 1939–1945. London: The Bodley Head. ISBN 978-0-316-28840-8.
- James, BA "Jimmy" (1983). Moonless Night. London: William Kimber. Available in a later ed. OCLC 19469692
- Kozak-Holland, Mark. Project Lessons from the Great Escape (Stalag Luft III). Archived from the original on 1 January 2008. The prisoners formally structured their work as a project. This book analyzes their efforts using modern project management methods.
- Millar, George (1947). Horned Pigeon. London: Heinemann. Available in a later ed. OCLC 51108963
- Nichol, John; Rennell, Tony (2002). The Last Escape. London: Penguin. Archived from the original on 20 February 2014.
- Rees, Ken; Arrandale, Karen (2004). Lie in the Dark and Listen: The Remarkable Exploits of a WWII Bomber Pilot and Great Escaper. Grub Street. ISBN 978-1-904010-77-7.
- Walther, Guy (2013). The Real Great Escape. London: Bantam Press. ISBN 978-0-593-07190-8.
- Younger, Calton (1956). No Flight from the Cage. Frederick Muller. ISBN 0-352-30828-1.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Stalag Luft III. |
- Żagań Museum web site
- StalagLuft3.com - Major resource for information on Stalag Luft III, The Great Escape and The Long March
- "The Great Escape From Stalag Luft 3". 392nd Bomber Group Association.
- Wooden horse escape kit presented to Imperial War Museum
- Interactive Map of the Tunnel "Harry" from website accompanying Nova documentary "Great Escape" first airing on PBS, 5 June 2007
- B24.net
- StalagLuftIII.net
- The Story of Cy Eaton
- Oral history interview with Richard Andrews, a private in the U.S. Army that was held at Stalag Luft III from the Veterans History Project at Central Connecticut State University
- First hand account of Stalag Luft III by Wing Commander Ken Rees
- Great Escape (PBS Nova)
- "Shot After Escape"; the names of those executed as reported in a May 1944 issue of Flight
- New publication with private photos of the shooting of the film "The Great Escape" & documents of 2nd unit cameraman Walter Riml