Sphenopalatine artery
| Sphenopalatine artery | |
|---|---|
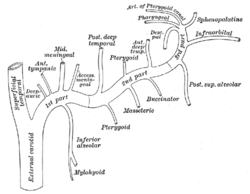 Plan of branches of internal maxillary artery. (Sphenopalatine visible in upper right.) | |
| Details | |
| Source | maxillary artery |
| Branches |
posterior lateral nasal branches posterior septal branches |
| Supplies | frontal, maxillary, ethmoidal, and sphenoidal sinuses |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria sphenopalatina |
| TA | A12.2.05.088 |
| FMA | 49804 |
|
Anatomical terminology | |
The sphenopalatine artery (nasopalatine artery) is an artery of the head, commonly known as the artery of epistaxis.[1]
Course
The sphenopalatine artery is a branch of the maxillary artery which passes through the sphenopalatine foramen into the cavity of the nose, at the back part of the superior meatus. Here it gives off its posterior lateral nasal branches.
Crossing the under surface of the sphenoid, the sphenopalatine artery ends on the nasal septum as the posterior septal branches. Here it will anastomose with the branches of the greater palatine artery.
Clinical significance
The sphenopalatine artery is the artery responsible for the most serious, posterior nosebleeds (also known as epistaxis). It can be ligated surgically to control such nosebleeds.
See also
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 562 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- lesson4 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (infratempfossaart)
- lesson9 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (nasalseptumart)