Southern Liang (Sixteen Kingdoms)
| Southern Liang (南涼) 西平 (397), 武威 (397-401), 河西 (401-408), 涼 (408-414) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 397–414 | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
| Status | Vassal of Later Qin | ||||||||||
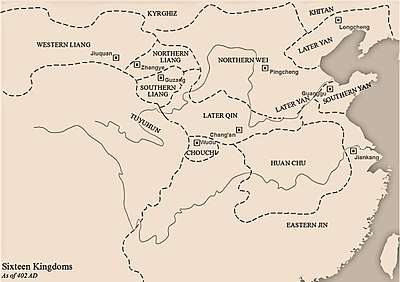
| Capital |
Lianchuan (397-399) Ledu (399, 402-406, 410-414) Xiping (399-402) Guzang (406-410) | ||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||
| Prince | |||||||||||
• 397-399 | Tufa Wugu | ||||||||||
• 399-402 | Tufa Lilugu | ||||||||||
• 402-414 | Tufa Rutan | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Established | 397 | ||||||||||
| 404 | |||||||||||
• Tufa Rutan's entry into Guzang | 406 | ||||||||||
• Tufa Rutan's defeat by Liu Bobo at Yangwu | 407 | ||||||||||
• Tufa Rutan's reassertion of own era name | 408 | ||||||||||
• Disestablished | 414 | ||||||||||
• Tufa Rutan's death | 415 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
The Southern Liang (Chinese: 南凉; pinyin: Nánliáng, 397-414) was a state of the Sixteen Kingdoms during the Jin Dynasty (265-420) in China. The founding family Tufa was of Xianbei ethnicity and distant relative of the Tuoba imperial house of Northern Wei. According to the Jin Shu, the name was changed from Tuoba to Tufa because one of the Tufa ancestors was born on a blanket, and in the Xianbei language, "Tufa" meant "blanket."[1]
All rulers of the Southern Liang proclaimed themselves "Wang".
In 414 Southern Liang was conquered by the Western Qin state of the Xianbei ethnicity.
Rulers of the Southern Liang
| Temple names | Posthumous names | Family names and given name | Durations of reigns | Era names and their according durations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liezu (烈祖 Lièzǔ) | Wu (武 Wǔ) | Tufa Wugu (禿髮烏孤 Tūfǎ Wūgū) | 397-399 | Taichu (太初 Tàichū) 397-399 |
| Did not exist | Kang (康 Kāng) | Tufa Lilugu (禿髮利鹿孤 Tūfǎ Lìlùgū) | 399-402 | Jianhe (建和 Jiànhé) 399-402 |
| Did not exist | Jing (景 Jǐng) | Tufa Rutan (禿髮傉檀 Tūfǎ Rǔtán) | 402-414 | Hongchang (弘昌 Hóngchāng) 402-404 Jiaping (嘉平 Jiāpíng) 409-414 |
The family tree of Southern Liang rulers
| Southern Liang | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
References
- ↑ Cui Hong. "南涼錄" [Record of Southern Liang]. Shiliuguo Chunqiu. Volume 12. Retrieved 21 September 2011.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.