Salix exigua
| Salix exigua | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Leaves and staminate flower | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Malpighiales |
| Family: | Salicaceae |
| Genus: | Salix |
| Species: | S. exigua |
| Binomial name | |
| Salix exigua | |
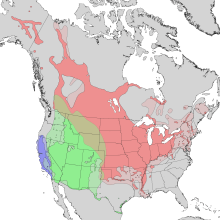 | |
| Natural range of Salix exigua S.e.exigua: green, S.e.hindsiana: blue, S.e.interior: red | |
Salix exigua (sandbar willow, narrowleaf willow, or coyote willow; syn. S. argophylla, S. hindsiana, S. interior, S. linearifolia, S. luteosericea, S. malacophylla, S. nevadensis, and S. parishiana) is a species of willow native to most of North America except for the southeast and far north, occurring from Alaska east to New Brunswick, and south to northern Mexico.[1] It is considered a threatened species in the eastern United States in Connecticut, Maryland, and Massachusetts.[2]
Description
It is a deciduous shrub reaching 4–7 m (13–23 ft) in height, spreading by basal shoots to form dense clonal colonies. The leaves are narrow lanceolate, 4–12 cm (1.6–4.7 in) long and 2–10 mm (0.079–0.394 in) broad, green, to grayish with silky white hairs at least when young; the margin is entire or with a few irregular, widely spaced small teeth. The flowers are produced in catkins in late spring, after the leaves appear. It is dioecious, with staminate and pistillate catkins on separate plants, the male catkins up to 10 cm (3.9 in) long, the female catkins up to 8 cm (3.1 in) long. The fruit is a cluster of capsules, each containing numerous minute seeds embedded in shiny white silk.[3][4]
Subspecies
The two subspecies, which meet in the western Great Plains, are:[1][3]
- S. exigua subsp. exigua – western North America, leaves grayish all summer with persistent silky hairs, seed capsules 3–6 mm (0.12–0.24 in) long
- S. exigua subsp. interior (Rowlee) Cronq. (syn. S. interior Rowlee) – eastern and central North America, leaves usually lose hairs and become green by summer, only rarely remaining pubescent, seed capsules 5–8 mm (0.20–0.31 in) long
Cultivation
Salix exigua is cultivated as an ornamental tree. In the UK it has gained the Royal Horticultural Society’s Award of Garden Merit.[5][6]
Uses
This willow had many uses for Native Americans; the branches were used as flexible poles and building materials, the smaller twigs were used to make baskets, the bark was made into cord and string, and the bark and leaves had several medicinal uses.[7] The Zuni people take an infusion of the bark for coughs and sore throats.[8]
References
- 1 2 "Salix exigua". Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN). Agricultural Research Service (ARS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Retrieved 22 December 2017.
- ↑ USDA Plants Profile: Salix exigua
- 1 2 Northern Prairie Wildlife Research Center: Salix exigua Archived 2008-03-28 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Jepson Flora: Salix exigua
- ↑ "RHS Plantfinder - Salix exigua". Retrieved 11 October 2018.
- ↑ "AGM Plants - Ornamental" (PDF). Royal Horticultural Society. July 2017. p. 93. Retrieved 11 October 2018.
- ↑ University of Michigan Native American Ethnobotany Index:Salix exigua
- ↑ Camazine, Scott and Robert A. Bye 1980 A Study Of The Medical Ethnobotany Of The Zuni Indians of New Mexico. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2:365–388 (p. 378)
External links
- Dominguez M. Collet (2004), Willows of Interior Alaska, US Fish and Wildlife Service
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Salix exigua. |