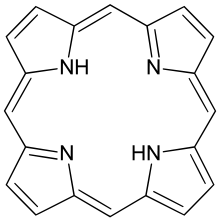
Porphine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Porphine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.690 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H14N4 | |
| Molar mass | 310.35196 g/mol |
| Appearance | Dark red, shiny leaflets |
| Melting point | N/A |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
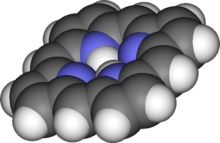
Porphine is the parent chemical compound for types of biochemically significant compounds called porphyrins. The chemical formula of porphin is C20H14N4. Porphin is an organic compound that is aromatic and heterocyclic. It consists of four pyrrole-like rings joined by four methine (=CH−) groups to form a larger macrocycle ring. The compound itself is a solid.[1] Porphine is almost only of theoretical interest; however, substituted derivatives are pervasive in biochemistry, with the dominant example being protoporphyrin IX.[2] Many synthetic analogues are also known, including octaethylporphyrin.[3] and tetraphenylporphyrin.[4]
Structural characteristics of porphine and its derivatives
- Common porphyrins
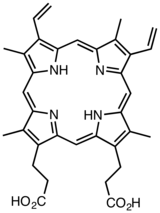 Derivatives of protoporphyrin IX are common in nature, the precursor to hemes.
Derivatives of protoporphyrin IX are common in nature, the precursor to hemes.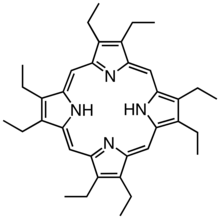 Octaethylporphyrin (H2OEP) is a synthetic analogue of protoporphyrin IX. Unlike the natural porphyrin ligands, OEP2− is highly symmetrical.
Octaethylporphyrin (H2OEP) is a synthetic analogue of protoporphyrin IX. Unlike the natural porphyrin ligands, OEP2− is highly symmetrical.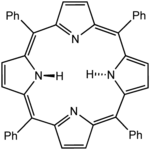 Tetraphenylporphyrin (H2TPP)is another synthetic analogue of protoporphyrin IX. Unlike the natural porphyrin ligands, TPP2− is highly symmetrical. Another difference is that its methyne centers are occupied by phenyl groups.
Tetraphenylporphyrin (H2TPP)is another synthetic analogue of protoporphyrin IX. Unlike the natural porphyrin ligands, TPP2− is highly symmetrical. Another difference is that its methyne centers are occupied by phenyl groups.
Porphine is planar. The two NH centers are trans.
Complex with metal in the center
Concomitant with the displacement of two N-H protons, porphine binds metal ions at its center. The insertion of the metal center is slow in the absence of catalysts. In nature, these catalysts (enzymes) are called chelatases. When there is no metal ion (or atom) bound to the nitrogens in the center, then the compounds are called free porphine or free porphyrin. If they are bonded to a metal in the center, then they are bound. A porphyrin with an iron atom of the type found in myoglobin, hemoglobin, or certain cytochromes is called heme. See the Porphyrin article for further details.
Compounds similar to porphine are the parent compounds for similar ring systems with other central metal atoms in biochemistry. These include chlorin, which has a magnesium ion in several types of chlorophyll; bacteriochlorin, found in bacteriochlorophyll; and corrin, which has a cobalt center in cobalamin or vitamin B12.
See also
References
- ↑ "Porphyrin". Encyclopedia of Inorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry. Wiley-VCH. 2011. doi:10.1002/9781119951438.eibd0638.
- ↑ Paul R. Ortiz de Montellano (2008). "Hemes in Biology". Wiley Encyclopedia of Chemical Biology. John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/9780470048672.wecb221.
- ↑ Jonathan L. Sessler; Azadeh Mozaffari; Martin R. Johnson (1992). "3,4-Diethylpyrrole and 2,3,7,8,12,13,17,18-Octaethylporphyrin". Org. Synth. 70: 68. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.070.0068.
- ↑ Lindsey, Jonathan S. (2000). "Synthesis of meso-substituted porphyrins". In Kadish, Karl M.; Smith, Kevin M.; Guilard, Roger. Porphyrin Handbook. 1. pp. 45–118. ISBN 0-12-393200-9.