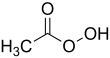
Peracetic acid
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethaneperoxoic acid[1] | |||
| Other names
Peroxyacetic acid Acetic peroxide Acetyl hydroperoxide Proxitane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| Abbreviations | PAA | ||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.079 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number | SD8750000 | ||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H4O3 | |||
| Molar mass | 76.05 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 1.0375 g/mL | ||
| Melting point | 0 °C (32 °F; 273 K)[2] | ||
| Boiling point | 105 °C (221 °F; 378 K) 25 C @ (1.6 kPa)[2] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 8.2 | ||
Refractive index (nD) |
1.3974 (589 nm, 20 °C)[2] | ||
| Viscosity | 3.280 cP | ||
| Pharmacology | |||
| QG51AD03 (WHO) | |||
| Hazards | |||
EU classification (DSD) (outdated) |
Oxidant (O) Corrosive (C) Dangerous for the environment (N) | ||
| R-phrases (outdated) | R8 R5 R11 R25 R34 | ||
| S-phrases (outdated) | (S1/2) S3/7 S14 S36/37/39 S45 S61 | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | 40.5 °C (104.9 °F; 313.6 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Peracetic acid (also known as peroxyacetic acid, or PAA), is an organic compound with the formula CH3CO3H. This organic peroxide is a colorless liquid with a characteristic acrid odor reminiscent of acetic acid. It can be highly corrosive.
Peracetic acid is a weaker acid than the parent acetic acid, with a pKa of 8.2.[2]
Production
Peracetic acid is produced industrially by the autoxidation of acetaldehyde:[2]
- O2 + CH3CHO → CH3CO3H
It forms upon treatment of acetic acid with hydrogen peroxide with a strong acid catalyst:[3]
- H2O2 + CH3CO2H ⇌ CH3CO3H + H2O
As an alternative, acetyl chloride and acetic anhydride can be used to generate a solution of the acid with lower water content.
Peracetic acid is generated in situ by some laundry detergents. This route involves the reaction of tetraacetylethylenediamine (TAED) in the presence of an alkaline hydrogen peroxide solution. The peracetic acid is a more effective bleaching agent than hydrogen peroxide itself.[4][5] PAA is also formed naturally in the environment through a series of photochemical reactions involving formaldehyde and photo-oxidant radicals.[6]
Peracetic acid is always sold in solution as a mixture with acetic acid and hydrogen peroxide to maintain its stability. The concentration of the acid as the active ingredient can vary.
Uses
The United States Environmental Protection Agency first registered peracetic acid as an antimicrobial in 1985 for indoor use on hard surfaces. Use sites include agricultural premises, food establishments, medical facilities, and home bathrooms. Peracetic acid is also registered for use in dairy and cheese processing plants, on food processing equipment, and in pasteurizers in breweries, wineries, and beverage plants.[7] It is also applied for the disinfection of medical supplies, to prevent biofilm formation in pulp industries, and as a water purifier and disinfectant. Peracetic acid can be used as a cooling tower water disinfectant, where it prevents biofilm formation and effectively controls Legionella bacteria. A trade name for peracetic acid as an antimicrobial is Nu-Cidex.[8]
Epoxidation
Although less active than more acidic peracids (e.g., m-CPBA), peracetic acid in various forms is used for the epoxidation of various alkenes. Useful application are for unsaturated fats, synthetic and natural rubbers, and some natural products such as pinene. A variety of factors affect the amount of free acid or sulfuric acid (used to prepare the peracid in the first place).[9]
Safety
Peracetic acid is a strong oxidizing agent and severe irritant to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency published the following Acute Exposure Guidelines (AEGL):[10]
| eight-hour TWA AEGL | Definition | mg/m3 | ppm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | The concentration at which the general population will experience transient and reversible problems, such as notable discomfort, irritation, or certain asymptomatic non-sensory effects. | 0.52 | 0.17 |
| 2 | The concentration that results in irreversible or other serious, long-lasting adverse health effects or an impaired ability to escape. | 1.6 | 0.52 |
| 3 | The concentration that results in life-threatening health effects or death | 4.1 | 1.3 |
See also
References
- ↑ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 749. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Klenk, Herbert; Götz, Peter H.; Siegmeier, Rainer; Mayr, Wilfried, "Peroxy Compounds, Organic", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_199
- ↑ Rangarajan, B.; Havey, A.; Grulke, E.; Culnan, P. D. (1995). "Kinetic parameters of a two-phase model for in situ epoxidation of soybean oil". J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 72: 1161–1169.
- ↑ Smulders, Eduard; Von Rybinski, Wolfgang; Sung, Eric; Rähse, Wilfried; Steber, Josef; Wiebel, Frederike; Nordskog, Anette (2007), "Laundry Detergents", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a08_315.pub2
- ↑ "Peracetic acid" (PDF). Agriculture Marketing Service. United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 2006-11-11.
- ↑ "Hazardous Substances Data Bank". ToxNet. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 2006-11-11.
- ↑ "Hydrogen Peroxide and Peroxyacetic Acid". U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved 2006-11-11.
- ↑ Lynam, P. A.; Babb, J. R.; Fraise, A. P. (1995). "Comparison of the mycobactericidal activity of 2% alkaline glutaraldehyde and 'Nu-Cidex' (0.35% peracetic acid)". J. Hosp. Infect. 30 (3): 237–240. PMID 8522783.
- ↑ Sienel, Guenter; Rieth, Robert; Rowbottom, Kenneth T. (2000), "Epoxides", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a09_531
- ↑ peracetic acid