Navy Command (Royal Navy)
| Navy Command Headquarters | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Active | 2008 - present |
| Country |
|
| Allegiance | Queen Elizabeth II |
| Branch | Royal Navy |
| Type | Navy Command |
| Part of | Ministry of Defence, Naval Service |
| Garrison/HQ |
HQ HMS Excellent, Whale Island, Hampshire 50°48′53.7″N 1°5′59.1″W / 50.814917°N 1.099750°W |
| Commanders | |
| Current commander | Admiral Sir Philip Jones |
| Ceremonial chief | Queen Elizabeth II |
Navy Command Headquarters is the senior command organisation of the British Royal Navy. It was formed in 2008 from the merging of Fleet Command and Naval Home Command. Navy Command Headquarters oversees all aspects of maritime activities including operations, administration, personnel and logistics.[1] The Royal Navy's surface fleet and submarine service, the Fleet Air Arm, the Royal Marines and the Royal Fleet Auxiliary all report to officers within this building and site.
History
Prior to 1964 responsibility for control and direction of the British Naval Affairs lay with Admiralty, naval command lay with the Admiralty Naval Staff. Following the merger of the Admiralty in 1964 into the new Ministry of Defence it became known as the Navy Department.[2][3] The Royal Navy was historically divided into a number of fleets and ashore commands, prominent examples being the Home Fleet and Portsmouth Command. By the 1960s a system was introduced to change the previous, globally dispersed assets, the fleet system was replaced at first by a Western Fleet and Eastern Fleet. However these were also eventually abolished and their units amalgamated into CINCFLEET.[4] At the same time, the commands established to manage individuals naval bases were replaced in 1969 after the post of Commander-in-Chief, Plymouth was merged with that of Commander-in-Chief, Portsmouth to form Naval Home Command. As overseas bases continued to be reduced, the Navy's shore establishments became more concentrated in the UK, under Naval Home Command.
Navy Command Headquarters
 Henry Leach Building, Whale Island
Henry Leach Building, Whale Island West Battery, Whale Island
West Battery, Whale Island
The Navy Command Headquarters is based at Whale Island, Portsmouth, it also includes the Command Centre in Northwood, and also has support staff in Portsmouth Naval Base.[5]
- Henry Leach Building and West Battery Building, HMS Excellent, Portsmouth - Senior Naval staff
- Moore Building, HMS Excellent - Fleet Battle Staff.
- Command Centre, Northwood - Maritime operations staff.
- HMNB Portsmouth: - Support Staff
- Maritime Warfare Centre: - Operational Knowledge-Centered support service.
- Royal Navy Chaplaincy Service - Pastoral support.
- Office of the Flag Officer Sea Training - Training support.
The Purpose built Headquarters at Whale Island was opened in 2002 was named after Admiral of the Fleet Sir Henry Leach, the First Sea Lord during the Falklands War. The purpose of the NCHQ, as the higher echelon of Navy Command, is the carry out three main tasks: Force Generation, Planning for the future and Advice, Assurance and Accountability.[6]
The equivalent in the British Army is Army Headquarters at Andover and the equivalent in the Royal Air Force is Headquarters Air Command at High Wycombe.
Structure of the Navy Command
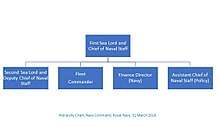



The First Sea Lord and Chief of Naval Staff, is the Royal Navy's professional head and Chairman of the Navy Board. He is responsible to the Secretary of State for the fighting effectiveness, efficiency and morale of the Naval Service, and supports the Secretary of State for Defence in the management and direction of the Armed Forces.
Office of the First Sea Lord and Chief of Naval Staff
- Office of the First Sea Lord and Chief of Naval Staff - based at the Ministry of Defence - as part of the Chiefs of the Defence Staff.
- Office of the Second Sea Lord and Deputy Chief of Naval Staff
- Office of the Fleet Commander
- Assistant Chief of the Naval Staff (Policy)
- Office of the Finance Director (Navy)
Senior Naval Staff
- First Sea Lord and Chief of Naval Staff [11]
- Second Sea Lord and Deputy Chief of Naval Staff [11]
- Fleet Commander [11]
- Chief of Material (Fleet) and Chief Naval Engineer Officer [11] - based at Defence Equipment and Support H.Q. formerly Chief of Fleet Support, now split between Chief of Materiel (Submarines) and Chief of Materiel (Ships)[12]
Office of the Second Sea Lord and Deputy Chief of Naval Staff
Office of the Assistant Chief of the Naval Staff (Aviation & Carriers)
- Assistant Chief of the Naval Staff, Aviation and Carriers, (ACNS A&C) [11]
Office of the Assistant Chief of the Naval Staff (Capability)
- Assistant Chief of the Naval Staff (Capability), (ACNS Cap) [11] - also Controller of the Navy and Chief of Staff, Navy Command Headquarters.
Office of the Assistant Chief of the Naval Staff (Personnel)
- Assistant Chief of the Naval Staff (Personnel), (ACNS Pers) [11]
Office of the Assistant Chief of the Naval Staff (Ships)
Office of the Assistant Chief of the Naval Staff (Submarines)
- Assistant Chief of the Naval Staff (Submarines), (ACNS Sub) [11] - also (FO S&NI)
Office of the Assistant Chief of the Naval Staff (Support)
- Assistant Chief of the Naval Staff (Support), (ACNS Sup) [11]
- Assistant Chief of Staff Logistics and Infrastructure, (COS Logs & Infra) [11]
- Assistant Chief of Staff Engineering Support, (COS Eng Sup) [11]
- Commander, Portsmouth, Naval Base, (NBC (P) [11]
- Commander, Clyde, Naval Base, (NBC (C) [11]
- Commander, Devonport, Naval Base, (NBC (D) [11]
Office of the Flag Officer Scotland and Northern Ireland
The Flag Officer Scotland and Northern Ireland, (FO S&NI) [11] - also (ACNS Submarines) is the senior Royal Navy Representative within Scotland and Northern Ireland liaising with the Scottish government and NI Assembly on Naval issues.
- Flag Officer Scotland and Northern Ireland
Office of the Chaplain of the Fleet
Office of the Naval Secretary
Flag Officer, Maritime Reserves
- Commander Maritime Reserves (COMMARRES) [11] - also (ACNS Pers & NAV SEC)
Office of the Fleet Commander
As of 31 March 2016:[9][13][10]
Office of the Assistant Chief of the Naval Staff (Training)
Office of the Commander Operations
- Commander Operations, (COMOP) [11]
- Commander Portsmouth Flotilla, (COMPORFLOT) [11]
- Commander Devonport Flotilla, (COMDEVFLOT) [11]
- Commander Faslane Flotilla, (COMFASFLOT) [11]
- Commander 3 Commando Brigade Royal Marines, (Comd 3CDO BDE RM) [11]
Office of the Commander UK Maritime Forces
- Commander Commander United Kingdom Maritime Forces (COMUKMARFOR)
- Commander Amphibious Task Group, (COMATG) [11]
- Commander Carrier Strike Group, (COMCSG) [11]
Office of the Commander UK Amphibious Forces/Commandant General Royal Marines
- Commander UK Amphibious Forces/Commandant General Royal Marines, (COMAMPHIBFOR CGRM) [11]
Office of the Assistant Chief of the Naval Staff (Policy)
As of 31 March 2016:[9]
- Assistant Chief of the Naval Staff, (Policy), (ACNS Pol) [11] directs and develops naval strategic policy and strategy for the Royal Navy.
Office of the Assistant Chief of Staff (Policy)
- Assistant Chief of Staff (Policy), (ACOS Policy) [11] (ACNS Pol) manages the department and staff of (ACNS Pol).
Office of the Commodore, Naval Staff
- Commodore, Naval Staff, (Cdre NS) [11] superintends the Naval Staff Directorate provides administrative support to Admiralty Board and the Navy Board.
- Naval Staff Directorate [14]
Office of the Commodore, Regional Forces
- Commodore, Regional Forces, (Cdre REGFOR) & Naval Regional [11] superintends the 4 UK geographical naval regional commands.
Office of the Head of Royal Navy Communications
- Head of Royal Navy Communications, (COMMS Hd) [11] Principal Navy Command advisor on RN communications and communications strategy.
Office of the Finance Director Navy
As of 31 March 2016:[9]
- Finance Director (Navy) [11] is the Chief Financial Officer of Navy Command's delegated budget and superintends the Command Secretariat.
Office of the Assistant Chief of Staff Resources and Plans
- Assistant Chief of Staff Resources and Plans [11] supports the Director of Navy Finance in delivering the Naval financial objectives and adhering to the framework of legal, political, financial and regulatory authorities.
Office of the Command Secretary
- Command Secretary [11] is the senior civilian in Navy Command Headquarters responsible for civilian personnel, external accountability, resource management and certain aspects of planning.
Office of the Deputy Finance Director, Navy
- Deputy Finance Director [11] is responsible overall financially managing Navy Command and the Head of the Navy Command Finance department.
Office of the Head of Navy Effectiveness and Strategy
- Head of Navy Effectiveness and Strategy [11] superintends multidisciplinary project teams, specializing in policy, commercial and financial expertise he reports back to both the (FD(N) and ACNS(Pol).
Navy Command supporting organisations
Command Centre Northwood
Northwood is the UK’s principal military headquarters site is home to 5 operational HQs. The Joint Forces Command HQ, including Permanent Joint Headquarters and the Joint Forces Headquarters, the Commander Operations for the Royal Navy.[15]
Defence Equipment and Support
Formed in April 2007 from the amalgamation of both the Defence Logistics Organisation (DLO) and the Defence Procurement Agency (DPA) to form Defence Equipment and Support (DE&S). It provides naval equipment and also responsible for sustaining the Fleet and ensuring that the required vessels and units are available for operations according to the command plan. Superintended by the Chief of Staff, who administers the Maritime Warfare Centre, communications systems, engineering and certain functions of Fleet Air Arm support.[16] [17][16]
Flag Officer Sea Training
Is the organisation responsible for training on all Royal Navy and Royal Fleet Auxiliary vessels.[18]
Fleet Battle Staff
Based in two locations (Portsmouth and Plymouth) the Fleet Battle Staff is the operational planning department, that plans exercises and operations for large multinational naval and marine task groups across the globe. The actual conduct of naval operations is generally the responsibility of the Joint Forces Command.[19]
Maritime Warfare Centre
The Maritime Warfare Centre is an Operational Knowledge-Centered Support service allows the Royal Navy the ability to observe and process all aspects of operational experience to learn lessons from previous operations and enhance fighting power.[20]
Royal Naval Chaplaincy Service
The Royal Naval Chaplaincy Service is responsible to the First Sea Lord for provision of pastoral support, ensuring the spiritual and pastoral needs of all Service personnel the service is superintended by the Chaplain of the Fleet.[21]
References
- ↑ http://www.armedforces.co.uk/navy/listings/l0006.html Royal Navy Command and Organisation: Fleet Headquarters
- ↑ Stationary Office, H.M. (31 October 1967). The Navy List. Spink and Sons Ltd, London, England. pp. 524–532.
- ↑ Lagassé, ed. by Paul (2000). "Admiralty". The Columbia encyclopedia (6. ed.). [New York]: Columbia Univ. Press u.a. ISBN 978-0787650155.
- ↑ "Royal Navy - Fleet Command and Organisation - Naval Home Command - Defence Equipment and Support - n2a2 - Armed Forces". armedforces.co.uk. R & F Defence Publications, 2017. Retrieved 8 August 2017.
- ↑ "Navy Command HQ, Royal Navy". royalnavy.mod.uk. Royal Navy, MOD, UK. Retrieved 7 August 2017.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2013-12-26. Retrieved 2013-12-25. Navy Matters - Headquarters organisation
- ↑ "Ministry of Defence, Organogram". data.gov.uk. Ministry of Defence, 2016. Retrieved 7 August 2017.
- ↑ "MOD roles and salaries: Navy Command Senior, as of April 2017". www.gov.uk. Ministry of Defence, April 2016. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 MOD, Organogram, 31 March 2016
- ↑ "Defence Equipment & Support organisation chart: May 2017 (updated 18 May 2018)" (PDF). Defence Equipment and Support. Retrieved 10 August 2018.
- ↑ "Royal Marines". royalnavy.mod.uk. Royal Navy, MOD, 2017. Retrieved 7 August 2017.
- ↑ Speller, Ian (2004). The Royal Navy and Maritime Power in the Twentieth Century. Routledge. p. 126. ISBN 9781134269822.
- ↑ Government, H.M. "Northwood Headquarters - GOV.UK". gov.uk. MOD. UK. 2017. Retrieved 8 August 2017.
- 1 2 Government, H.M. "Defence Equipment and Support - GOV.UK". www.gov.uk. MOD, 2017. Retrieved 8 August 2017.
- ↑ DE&S Organisation Chart retrieved August 2017
- ↑ "FOST, Royal Navy". royalnavy.mod.uk. Royal Navy, MOD, 2017. Retrieved 8 August 2017.
- ↑ Government, H.M. "Fleet Battle Staff". webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk. National Archives, 17 April 2009. Retrieved 8 August 2017.
- ↑ "Supporting the Maritime Warfare Centre". BAE Systems International. BAE Systems, 2017. Retrieved 8 August 2017.
- ↑ Government, H.M. "Chaplains, Royal Navy". www.royalnavy.mod.uk. Royal Navy, MOD, 2017. Retrieved 8 August 2017.
Sources
- Government, H.M. "The Navy List" (PDF). royalnavy.mod.uk. H.M. Stationery Office, January, 2017.
- "Ministry of Defence, Organogram". data.gov.uk. Ministry of Defence, 2016. Retrieved 7 August 2017.
- "MOD roles and salaries: Navy Command Senior, as of April 2016". www.gov.uk. Ministry of Defence, April 2016. Retrieved 7 August 2017.
- "Navy Command HQ, Royal Navy". royalnavy.mod.uk. Royal Navy, MOD, UK. Retrieved 7 August 2017.
- Speller, Ian (2004). The Royal Navy and Maritime Power in the Twentieth Century. Routledge. ISBN 9781134269822.
- Stationary Office, H.M. (1967). The Navy List. Spink and Sons Ltd, London, England.
Further reading
- Grove. D. Philip and Redford. Duncan. (2014). "The Royal Navy: A History Since 1900". I.B.Tauris. IBAN: 9780857735072.