Lithium amide
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Lithium amide | |
| Other names
Lithamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.062 |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| LiNH 2 | |
| Molar mass | 22.96 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.178 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 375 °C (707 °F; 648 K) |
| Boiling point | 430 °C (806 °F; 703 K) decomposes |
| reacts | |
| Solubility | slightly soluble in ethanol insoluble in ammonia |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
-182 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Lithium amide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li+NH2−, i.e. it is composed of a lithium cation, and the conjugate base of ammonia. It is a white solid with a tetragonal crystal structure.
Lithium amides
The anionic conjugate bases of amines are known as amides. Thus a lithium amide may also refer to any compound in the class of the lithium salt of an amine. These chemicals have the general form Li+NR2−, with the chemical lithium amide itself as the parent structure. Common lithium amides include lithium diisopropylamide (LDA), Lithium tetramethylpiperidide (LiTMP), and lithium hexamethyldisilazide (LiHMDS).
Lithium amide can be made by adding lithium metal to liquid ammonia:
- 2Li + 2NH3 → 2LiNH2 + H2
Lithium amides in general can be similarly formed, substituting ammonia with the appropriate amine:
- 2Li + 2R2NH → 2LiNR2 + H2
Lithium amides are very reactive compounds and can act as strong bases. Unless the nitrogen atom is hindered, they can also act as nucleophiles.
Examples
Lithium tetramethylpiperidide has been crystallised as a tetramer.[1] On the other hand, the lithium derivative of bis(1-phenylethyl)amine crystallises as a trimer:[2]
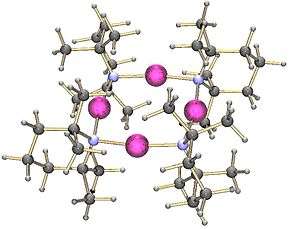 Tetrameric lithium tetramethylpiperidide |
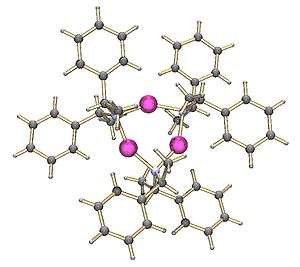 Trimeric lithium bis(1-phenylethyl)amide |
It is also possible to make mixed oligomers of metal alkoxides and amides.[3] These are related to the superbases which are mixtures of metal alkoxides and alkyls. The cyclic oligomers form when the nitrogen of the amide forms a sigma bond to a lithium while the nitrogen lone pair binds to another metal centre.
Other organolithium compounds (such as BuLi) are generally considered to exist in and function via high-order, aggregated species.
See also
References
- ↑ M.F. Lappert; M.J. Slade; A. Singh; J.L. Atwood; R.D. Rogers; R. Shakir (1983). "Structure and reactivity of sterically hindered lithium amides and their diethyl etherates: crystal and molecular structures of [Li{N(SiMe3)2}(OEt2)]2 and tetrakis(2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinatolithium)". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 105 (2): 302–304. doi:10.1021/ja00340a031.
- ↑ D.R. Armstrong; K.W. Henderson; A.R. Kennedy; W.J. Kerr; F.S. Mair; J.H. Moir; P.H. Moran; R. Snaith (1999). "Structural studies of the chiral lithium amides [{PhC(H)Me}2NLi] and [PhCH2{PhC(H)Me}NLi·THF] derived from α-methylbenzylamine". Dalton Transactions: 4063–4068. doi:10.1039/A904725E.
- ↑ K.W. Henderson, D.S. Walther & P.G. Williard (1995). "Identification of a Unimetal Complex of Bases by 6Li NMR Spectroscopy and Single-Crystal Analysis". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 117 (33): 8680–8681. doi:10.1021/ja00138a030.
- Merck Index, 11th Edition, 5398.
