Janata Dal (Secular)
Janata Dal (Secular) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Abbreviation | JD(S) |
| Leader | H. D. Deve Gowda |
| Lok Sabha leader | H. D. Deve Gowda |
| Rajya Sabha leader | D. Kupendra Reddy |
| Founder | H. D. Deve Gowda |
| Founded | July 1999 |
| Preceded by | Janata Dal |
| Headquarters | JP Bhavan, 19/1, Platform Road, Sheshadripura, Bengaluru, Karnataka-560020 |
| Student wing | Student Janata Dal |
| Youth wing | Yuva Janata Dal |
| Women's wing | Mahila Janata Dal |
| Labour wing | Karmikara Janata Dal |
| Ideology |
Social democracy Social liberalism Secularism[1] |
| Political position | Centre |
| Colours | Green |
| ECI Status | State Party[2] |
| Alliance |
Third Front (2009-2015) Janata Parivar (2015-2018) National Democratic Alliance (2006-2007) Left Democratic Front (2006-present) United Progressive Alliance (2018-present) |
| National convener | H. D. Deve Gowda |
| Seats in Lok Sabha |
1 / 545 [3](currently 531 members + 1 Speaker) |
| Seats in Rajya Sabha |
1 / 245
|
| Seats in Karnataka Legislative Assembly |
36 / 224
|
| Seats in Kerala Legislative Assembly |
3 / 140
|
| Number of states and union territories in government |
2 / 31
|
| Election symbol | |
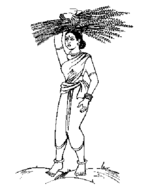 | |
| Website | |
| Source:[5] | |
The Janata Dal (Secular) is an Indian political party[6] led by former Prime Minister of India, H. D. Deve Gowda. The party is recognized as a State Party in the states of Karnataka and Kerala. It was formed in July 1999 by the split of Janata Dal party.[7][8] It has a political presence mainly in Karnataka. In Kerala, the party is part of the Left Democratic Front.
History

The Janata Dal (Secular), formed in 1999, had its origins in the Janata Party, founded in 1977 as a coalition of several smaller parties that combined forces to oppose the Indian National Congress.[9] In 1988 the Janata Party and other smaller parties merged to form the Janata Dal.[10][11][12] In 1996, Janata Dal reached its pinnacle when H. D. Deve Gowda became Prime Minister of India, heading the United Front (UF) coalition government.[13][14]
The Janata Dal split in 1999, when a faction led by Chief Minister J. H. Patel lent support to the BJP-led National Democratic Alliance leading to the formation of Janata Dal (Secular) under H. D. Deve Gowda. The Sharad Yadav faction of the Janata Dal, the Lok Shakti and the Samata Party merged as the Janata Dal (United).[15][16] Even though the premise for the split was its opposition to allying with the National Democratic Alliance, H. D. Deve Gowda stayed equally away from the Indian National Congress from the outset.[17]
JD(S) in Karnataka state for a time governed in a coalition with the Indian National Congress (INC) party, the first coalition government in Karnataka. There was much controversy over the JD(S) allying with the INC in Bangalore as the INC formerly had an outright majority and was diminished to second place with the BJP having a plurality. However, the JD(S) considered INC to be the lesser of the two evils on account of its erstwhile secular and center left credentials.
The 2004 Karnataka Assembly election witnessed the revival of the party's fortunes with JD(S) becoming part of the ruling coalition in the state. Subsequently, party leader H. D. Kumaraswamy headed a popular coalition government in the state for 20 months with support from the BJP.[18][14]
On 14 April 2015, the JD(S), Janata Dal (United), Rashtriya Janata Dal, the Indian National Lok Dal, Samajwadi Party, and Samajwadi Janata Party (Rashtriya) announced that they would merge into a new national Janata Parivar alliance in order to oppose the BJP, thus leaving the UPA.[19]
Prominent Members
- H. D. Deve Gowda, President of Janata Dal (Secular), former Prime Minister of India and Former Chief Minister of Karnataka.
- H. D. Kumaraswamy, Chief Minister of Karnataka, son of former Prime Minister of India H. D. Deve Gowda and Karnataka State President of Janata Dal (Secular).[20]
- Sarekoppa Bangarappa, Former Chief Minister of Karnataka.[21]
- N. M. Joseph, Vice President of Janata Dal (Secular).
- H. D. Revanna, Cabinet Minister, Present MLA, Karnataka (Son of H. D. Deve Gowda).
- Mathew T. Thomas, former Kerala State President of Janata Dal (Secular) and current Kerala State Minister for Water Resources.
- Madhu Bangarappa, former MLA of Karnataka Legislative Assembly.
- Jose Thettayil, Vice President of Janata Dal (Secular), former minister Govt. of Kerala.
- C. K. Nanu, former minister Govt of Kerala and MLA.
- Neelalohithadasan Nadar, Former Kerala State President of Janata Dal (Secular) (Former Minister Govt. of Kerala; Former Member of Parliament, Govt. of India).
- K. Krishnankutty, Kerala State President and MLA.
Chief Ministers
- H. D. Kumaraswamy - 3 February 2006 to 9 October 2007, 23 May 2018 to present.
Assembly election history in Karnataka
| Year | Assembly Election | Seats Contested | Seats Won | Votes Secured | Percentage Of Votes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1999 | 11th Assembly | 203 | 10 | 23,16,885 | 10.42[22] |
| 2004 | 12th Assembly | 220 | 59 | 52,20,121 | 20.77%[23] |
| 2008 | 13th Assembly | 219 | 28 | 49,59,252 | 18.96%[24] |
| 2013 | 14th Assembly | 222 | 40 | 63,29,864 | 20.09% |
| 2018 | 15th Assembly | 202 | 37 | 66,66,307 | 18.30% |
Lok Sabha election history in Karnataka
| Year | Lok Sabha Election | Seats Contested | Seats Won | Votes Secured | Percentage Of Votes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 14th Lok Sabha | 28 | 2 | 51,35,205 | 20.45%[25] |
| 2009 | 15th Lok Sabha | 21 | 3 | 33,35,530 | 13.58% |
| 2014 | 16th Lok Sabha | 25 | 2 | 34,06,465 | 11.00%[26] |
See also
References
- ↑ "Official website ideology section". Jds.ind.in. 2014-10-26. Retrieved 2017-03-12.
- ↑ "List of Political Parties and Election Symbols main Notification Dated 18.01.2013" (PDF). India: Election Commission of India. 2013. Retrieved 9 May 2013.
- ↑ "Members: Lok Sabha". loksabha.nic.in. Lok Sabha Secretariat. Retrieved 28 September 2018.
- ↑ Karnataka polls: JDS finally takes net to catch voters - News Oneindia. News.oneindia.in (2013-02-13). Retrieved on 2014-05-21.
- ↑ http://eci.nic.in/eci_main/mis-Political_Parties/Constitution_of_Political_Parties%5CConstitution_of_The%20Janata%20Dal%20Secular.pdf
- ↑ "History of Janata Dal (Secular) according to its website". Retrieved 2007-09-30.
- ↑ "EC to hear Janata Dal symbol dispute". Archived from the original on 1 February 2009. Retrieved 2007-09-30.
- ↑ "The Nation:Janata Dal:Divided Gains (India Today article)". Retrieved 2007-09-30.
- ↑ "britannica.com : Janata Dal (Secular)".
- ↑ "article on Chandrashekar". Retrieved 2007-09-30.
- ↑ "Bouquet of ideologies - article in the Hindu". Retrieved 2007-09-30.
- ↑ "Janata Dal". Retrieved 2007-09-30.
- ↑ "Profile of Deve Gowda on PMO website". Archived from the original on 10 October 2007. Retrieved 30 September 2007.
- 1 2 History « Welcome to Janata Dal (Secular) Official Website. Jds.ind.in. Retrieved on 2014-05-21.
- ↑ "Janata.in". www.janata.in.
- ↑ Archived 3 January 2008 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ ""Gowda rules out tieup with Congress " - Tribune India article". Retrieved 2007-09-30.
- ↑
- ↑ "'Janata Parivar' formalised, Mulayam Singh named chief of new party | Zee News". Zeenews.india.com. 2015-04-15. Retrieved 2017-03-12.
- ↑ "Kumaraswamy takes reins of JD(S) in Karnataka". The Hindu. Retrieved 2017-03-12.
- ↑ D A I J I W O R L D. D A I J I W O R L D (2011-08-10). Retrieved on 2014-05-21.
- ↑ %http://eci.nic.in/eci_main/StatisticalReports/SE_1999/StatisticalReport-KT99.pdf
- ↑ List Of Political Parties. (PDF) . Retrieved on 2014-05-21.
- ↑ http://eci.nic.in/eci_main/StatisticalReports/AE2008/stats_report_KT2008.pdf
- ↑ http://eci.nic.in/eci_main/StatisticalReports/LS_2004/Vol_I_LS_2004.pdf
- ↑ "Partywise Trends & Result". 21 May 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Janata Dal (Secular). |