Griqua people
| Total population | |
|---|---|
|
Unknown c. 2 to 5 million | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| South Africa, Namibia | |
| Languages | |
| Afrikaans, English, Korana | |
| Religion | |
| various Protestant denominations, especially Dutch Calvinist ones | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Coloureds, Khoikhoi, Basters, Oorlam, Afrikaners |
The Griqua (/ˈɡriːkwə/; Afrikaans: Griekwa, sometimes incorrectly referred to as Korana or Koranna) are a subgroup of Southern Africa's heterogeneous and multiracial Coloured people, who have a unique origin in the early history of the Cape Colony.
Similar to the Trekboers, another Afrikaans-speaking group at the time, they originally populated the frontiers of the nascent Cape Colony. The men of their semi-nomadic society were mobilised into commando units of mounted gunmen, but chose to leave Dutch society. Also like the Boers, they migrated inland from the Cape, and established several states in what are now South Africa and Namibia.
During apartheid, the Griqua people were classified as Coloureds, as they were mostly descended from mixed-race unions between Dutch male colonists and Khoikhoi women, in addition to some Tswana and San women. They have since mostly integrated with other mixed-race populations in South Africa and Namibia.
Name
The Griqua are a racially and culturally mixed people who are primarily descended from the intermarriages and sexual relations (sometimes rape) between European colonist men and primarily Khoikhoi women. Genetic studies of the 21st century have shown these people also had Tswana, San, and Xhosa ancestry. Later the Europeans chose mixed-race women of the Khoikhoi, who were living in the Cape during the 17th and 18th centuries. As time went on, mixed-race people began to marry among themselves, establishing a distinct ethnic group that tended to be more assimilated to Dutch and European ways than tribal peoples in separated villages.
The mixed-race groups that developed in the early Cape Colony adopted different names for themselves, including Bastaards, Basters, Korana, Oorlam, and Griqua. Like the Afrikaners, many of these groups migrated inland to escape British colonial rule.
According to the 18th-century Dutch historian Isaak Tirion, the Khoi name Griqua (or Grigriqua) is first recorded in 1730 in reference to a group of people living in the northeastern section of the Cape Colony.[1] In 1813, Reverend John Campbell of the London Missionary Society (LMS) used the term Griqua to describe a mixed-race group of Chariguriqua (a Cape Khoikhoi group), Bastaards, Korana, and Tswana living at the site of present-day Griekwastad (then known as Klaarwater).[2] The British found their "proud name", Bastaards, offensive, so the LMS called them Griqua.
Because of a common ancestor named Griqua and shared links to the Chariguriqua (Grigriqua), the people officially changed their name to the Griqua.[3]
History
Origin and early history


The Dutch East India Company (VOC) did not intend for its Cape Colony possessions at the southern tip of Africa to develop into a political entity. As the colony expanded and became more successful, its leadership did not worry about its frontiers. As a result, the frontier of the colony was indeterminate and ebbed and flowed at the whim of individuals. While the VOC undoubtedly benefited from the trading and pastoral endeavours of the Trekboers, it did little to control or support them in their quest for land. The high proportion of single Dutch men led to many taking indigenous women as wives and companions, producing mixed-race children. These multiracial offspring gradually developed as a sizable population who spoke Dutch and were instrumental in developing the colony.
These children did not attain the social or legal status accorded their fathers, mostly because colonial laws recognised only Christian forms of marriage. This group became known as Basters, derived from bastaard, the Dutch word for "bastard" (or "crossbreed"). As part of the European colonists' paramilitary response to insurgent resistance from Khoi and San peoples, they conscripted Basters men into commando units. This allowed the men to become skilled in lightly armed and mounted skirmish tactics. But many recruited to war chose to abandon Dutch society and strike out to pursue a way of life more in keeping with their maternal culture. The resulting stream of disgruntled Dutch-speaking marksmen leaving the Cape hobbled the primarily Dutch colonists' ability to crew commando units. It also created belligerent, skilled groups of opportunists who harassed indigenous populations along the Orange River. Once free of colonial rule, these groups referred to themselves as Oorlam. In particular, the group led by Klaas Afrikaner became notorious for its exploits. They attracted enough attention from the Dutch authorities that Afrikaner was eventually rendered to the colony and banished to Robben Island in 1761.[4]
Griqua migrations

One of the most influential of these Oorlam groups was the Griqua. In the 19th century, the Griqua controlled several political entities which were governed by Kapteins (Dutch for "Captain") and their councils, with their own written constitutions.[5] The first Griqua Kaptein was Adam Kok I, a former slave who had bought his own freedom. Kok led his people north from the interior of the Cape Colony, likely to escape discrimination, before moving north again. He eventually led them beyond the Cape Colony, near the Orange River just west and south of what would eventually become the Boer Republics of the Orange Free State and Transvaal, respectively.[6] This area is where most of the tribe settled; although some remained nomadic. Prior to beginning their migrations, the Griqua had largely adopted what would be known as the Afrikaans language.
Kok's successor, Andries Waterboer, founded Griqualand West, and controlled it until the influx of Europeans after the discovery of diamonds. In 1834, the Cape Colony recognised Waterboer's rights to his land and people. It signed a treaty with him to ensure payment by Europeans for the use of the land for mining. Soon after 1843, the competition between the Cape Colony, Orange Free State, and the Transvaal became too much for the Griqua. Led by Adam Kok III, they migrated east and established Griqualand East. Griqualand East existed for only a few months before it was annexed by the Cape Colony in 1874.[7]
Both Griqualand East and Griqualand West were incorporated into the Cape Colony by the British. In the mid-20th century, the Griqua were classified as Coloureds under apartheid's racial classification system.
Current situation

Despite similarly mixed-race origins, those Coloured peoples identifying as Basters are considered to be a separate ethnic group and live primarily in south-central Namibia, while those who consider themselves Griqua are mostly located around Campbell and Griquatown in the historic territory of Griqualand West in the Northern Cape; around the small Le Fleur Griqua settlement at Kranshoek in the Western Cape; and at Kokstad in KwaZulu-Natal.
Due primarily to the racial policies of South Africa during the apartheid era, many Griqua people accepted classification in the larger "Coloured" group for fear that their Griqua roots might place them at a lower level than other groups. As a result, estimates of the size of the Griqua population are difficult to determine and remain largely unknown.
Genetic evidence indicates that the majority of the present-day Griqua population is descended from a combination of European, Khoikhoi and Tswana ancestors, with a small percentage of San, or Bushmen, ancestry.[8]
Griqua people are represented by the National Khoisan Consultative Conference (Afrikaans: Nasionale Khoe-San Oorlegplegende Konferensie), which was established in Oudtshoorn in 2001 to represent the interests of South Africa's Khoisanid peoples. The conference participates in cooperative research and development projects with the provincial government of the Western Cape and the University of the Free State in Bloemfontein. Members of the influential Le Fleur clan of Griqua are especially represented in this body.
The Griqua have also established their own church, known as the Griqua Church, which is Protestant. The Church has a strong focus on maintaining Griqua cultural and ethnic identity.
One of several disputed theories as to the origin of Bloemfontein's name connects it to the Griqua leader Jan Bloem (1775–1858). However, this may be a coincidence as Bloemfontein is Dutch for "fountain of flowers", or "blooming fountain", and the area could have been named for its local vegetation.
Griqualand
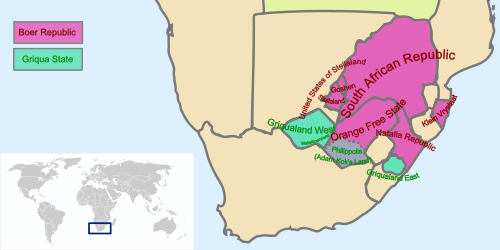
Several areas of South Africa became known as Griqualand when the group migrated inland from the Cape and established separate communities.
- Griqualand East is the area around Kokstad on KwaZulu-Natal's frontier with the Eastern Cape. This area was settled by, and subsequently named after, Adam Kok III, who led more than 2,000 Griqua over the Drakensberg in 1861. Griqua descendants are now largely concentrated in Kokstad, where the Griqua Church is a center of the community.
- Griqualand West is the area around Kimberley, which became an important mining town in the decades following the first local discovery of diamonds in 1866. Kimberley is also known for its sports teams, including the Griquas rugby team, which competes in South Africa's annual Currie Cup tournament and contests its home matches at Griqua Park.
See also
References
- ↑ Landkaart Kaap de Goede Hoop
- ↑ Griekwastad
- ↑ Monica Wilson and Leonard Thompson, The Oxford History of South Africa: Volume I (Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1969); 70.
- ↑ Nigel Penn. 2005. The Forgotten Frontier. ISBN 0-8214-1682-0.
- ↑ Jeroen G. Zandberg. 2005. Rehoboth Griqua Atlas. ISBN 90-808768-2-8.
- ↑ Christopher Saunders, Historical Dictionary of South Africa (London: The Scarecrow Press, 1983); 74.
- ↑ Martin Meredith, Diamonds, Gold, and War (New York: Public Affairs, 2007); 22.
- ↑ Alan G. Morris. 1997. "The Griqua and the Khoikhoi: Biology, Ethnicity and the Construction of Identity", in: Kronos Journal of Cape History, No. 24, page 106 – 118
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Griqua. |
- History of the Griquas
- "Children of the Mist – the lost tribe of South Africa"
- Kokstad with historical Griqua images
- Kranshoek – meeting with Griqua Paramount Chief le Fleur
- Griquatown and Campbell with historical Griqua images
- Griquatown – 1812 and today
- The History of Kokstad & East Griqualand
- History of the Rehoboth Basters and the Griqua in Maps and Pictures
- Griqua coinage