List of fjords in Canada
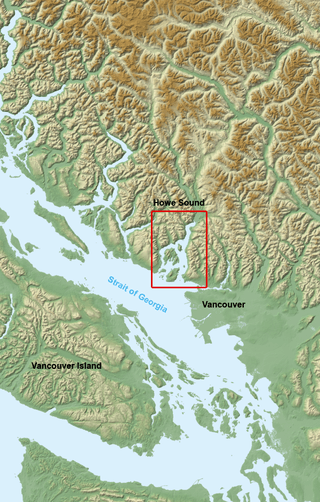
Fjords in Canada are long, narrow inlets characterized by steep sides, created in a valley carved by glacial activity. A fjord can have two or more basins separated by sills. The bowls can have a depth of 20 to 500 m (66 to 1,640 ft) and the dividing sills can raise up to a few metres below the water surface. Mountainous glaciated areas in Canada are along the British Columbia Coast: from the Alaskan border along the Portland Canal to Indian Arm. Kingcome Inlet is a typical West Coast fjord.
Saglek Fjord,[1] Nachvak Fjord,[1] Anaktalâk Bay,[1] Western Brook Pond, Hebron Fjord, Bonne Bay and Trout River Pond in Gros Morne National Park are located along the coastline of Newfoundland and Labrador.[2]
Quebec's Saguenay River valley contains a fjord. The Saguenay Fjord is 100 km (62 mi) long and 275 m (902 ft) deep.[2]
The Canadian Arctic Archipelago features fjords such as those around Ellesmere and Baffin Island, including Alexandra Fjord, Ellesmere Island,[3] and Sam Ford Fiord,[4] Baffin Island.
When a portion of the high cliff wall falls off, it may cause a tsunami. This occurred in the early 20th century at Western Brook Pond of Gros Morne National Park when a 30 m (98 ft) tsunami was created after Broke Off Cliff fell.[5]
Fjords listed here may consist of several complex waterways. These waterways may contribute to the length of the fjord. For more information on these please see the main fjord source or Wikipedia article. Some examples are Dean Channel and Douglas Channel. The locality of Hagensborg in the Bella Coola Valley in the Dean Channel fjord was settled by Norwegian immigrants in 1894 as it reminded them of home.[6] The total length of the fjord from the head of Dean Channel to the mouth of Fitz Hugh Sound is about 170 km (110 mi) rivalling Hardangerfjord in Norway for length. The Hardangerfjord, the Queen of fjords, at a length of 179 km (111 mi) is claimed to be fourth largest fjord in the world and second largest of Norway.[7][8]
Anaktalak Fjord, Saglek Fjord and Nachvak Fjord off the coast of Newfoundland and Labrador are being studied for environmental changes due to global warming. Increased tourism and marine traffic, contaminants from air, water or industrial pollution, changing weather patterns are affecting what once had been pristine water basins of the fjords protected by sills.[1]
The use of the word canal to name fjords or inlets on the British Columbian and Southeast Alaskan coast is a legacy of the Spanish exploration of the area in the 18th century. For example, Haro Strait between Victoria and the San Juan Islands was originally Canal de Haro. The English cognate to the Spanish canal is "channel", which is found throughout the coast, cf. Dean Channel.
Some fjords on the British Columbian coast have rapids, termed skookumchucks which means strong waters in Chinook Jargon). Skookumchucks are caused by the shallows and narrows near the mouth of a fjord as the water inside the fjord's depths is drawn through, to or from, the more open waters beyond.[9][10][11]
The phenomenon of Mountain-gap wind or squamish or outflow affects the fjords of Canada and Norway. The outflow winds at the Salt and Bols fjords of Norway and the Howe Sound and Portland Inlet of Canada have been compared. European winds may be termed Bora. The cold dry air of the continental interior seeks out the easier passage through the fjord valley creating hurricane-force winds.[12]

According to the definition, fjord, Western Brook Pond and Trout River Pond in Newfoundland's Gros Morne National Park, are also often described as a fjords, but are actually freshwater lakes cut off from the sea, so is not a fjord in the English sense of the term. Such lakes are sometimes called "fjord lakes".[13] It is of interest to note that Pissing Mare Falls at 350 m (1,150 ft) high, is one of several waterfalls to drain into Western Brook Pond, Along the British Columbia Coast, a notable fjord-lake is Owikeno Lake, which is a freshwater extension of Rivers Inlet.
List of fjords
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Three fjords under scientists' microscope". The Gazette. Canwest Digital Media, a division of Canwest Publishing Inc.. Saturday, October 18. Retrieved 2008-11-10. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - 1 2 Pickard, G. L. (2008). "Fjord". The Canadian Encyclopedia > Geography > Oceanography > Fjord. Historica Foundation of Canada.
- ↑ Noton / Minden. "Alexandra Fjord, Ellesmere Island". Webshots Tour. Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ "The amusingly named Sam Ford Fjord, Baffin Island, far northeastern Canada". Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ Ruffman, Alan; P.Geo (2002). "Atlantic Tsunamis: "Like a River Returning"". IXBN=0-674-00884-7. Maritime Museum of the Atlantic. Archived from the original on 2008-11-18. Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ "Regions & Towns - Bella Coola". Web Design by Sage Internet Solutions. Shangaan Webservices Inc. 1998–2008. Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ "Hardangerfjord". Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ "Eidfjord Cruiseport – Hardangerfjord" (PDF). Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ Cassidy, Frederic Gomes; Joan Houston Hall (2002-12-31). Dictionary of American Regional English - Google Books Result. originally by Harvard University Press then by Google books online. ISBN 978-0-674-00884-7. Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ Dawson, Dr. W. Bell (1996 2000). "Reply to Observations by Vice-Admiral Sir Frederick C. Learmonth regarding Lake Melville and the narrows". Memorial University of Newfoundland. Retrieved 2008-11-10. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ "Skookumchuck". Web Design by Sage Internet Solutions. Shangaan Webservices Inc. 1998–2008. Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ Jackson, PL (1994). "AMS Online Journals - Gap Winds in a Fjord. Part I: Observations on Howe Sound British Columbia" (pdf). THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA. Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ Nasmith, Hugh (1962). Late glacial history and surficial deposits of the Okanagan Valley, British Columbia. Victoria, BC, Canada: BC Ministry of Energy, Mines and Petroleum Resources.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 "Water Features - Nunavut". The Atlas of Canada. Archived from the original on 2012-09-26. Retrieved 2008-11-11.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 "Fjords". World's Rim. 1998–2008. Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ "BCGNIS Query Results". Government of British Columbia. Archived from the original on 2007-08-15. Retrieved 2008-11-07.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "All Features - All Provinces". The Atlas of Canada. Retrieved 2008-11-11.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query - Barrie Reach: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- 1 2 Riveiros, Natalia Vázquez; R. Timothy Patterson (2005–2006). "AN ILLUSTRATED GUIDE TO FJORD FORAMINIFERA FROM THE SEYMOUR-BELIZE ..." Forams from BC. Plain-Language & Multilingual Abstracts. Retrieved 2008-11-07.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query - Belize Inlet: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ Villholth Jensen & Associates Ltd. (August 1999). "AGGREGATE EXPORT FACILITY Bella Coola, B.C." (PDF). Project Description And Design Criteria. File: 99124. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ 127/_5883470_Alexandra+Fiord.html#local_map "Canadian Landscapes Photo Collection" Check
|url=value (help). Newfoundland and Labrado Gros Morne National Park Area. Government of Cnanada. 2005–2006. Retrieved 2008-11-07. - ↑ "GeoNames Query - Bonne Bay: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Archived from the original on 2008-09-17. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query - Burke Channel: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- 1 2 Lincoln S. Hollister, Glenn Woodsworth; Ron M. Clowes; Michael Rawson; et al. (2008-11-09). "BATHOLITHS How the Coast Mountains of British Columbia formed A Canada, USA EArth Science Research Project" (pdf). BATHOLITHS: Project description for Seismic Research Component. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ Kendrick, John (1990). The Voyage of Sutil and Mexicana, 1792: The last Spanish exploration of the Northwest Coast of America. Spokane, Washington: The Arthur H. Clark Company. p. 19. ISBN 0-87062-203-X.
- ↑ Robson, Robson (2007). "Hakluyt edition of Vancouver's journals". W. Kaye Lamb, editor, Vol. 2, p 605. Archived from the original on 2007-06-22. Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ "Dean River, BC. Fishing the Dean River, British Columbia". Interactive Broadcasting Corporation. 1996–2008. Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query - Desolation Sound: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "Topographic Map Index: 103H Douglas Channel, British Columbia". Federal Publications Inc.,. 1998–2008. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query - Devastation Channel: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "Douglas Channel". BC Geographical Names.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 "All Features - Newfoundland and Labrador". The Atlas of Canada. Retrieved 2008-11-11.
- ↑ "Home " Explore Our Maps " Toporama – Topographic Maps " Toporama – Topographic Maps". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2006-02-06. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query - Fisher Channel: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "British Columbia Cruising Adventures & Suppliers - Central BC Coast". Interactive Broadcasting Corporation. 1995–2008. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ Troniks, Meka (2008). "TAGEO - FITZ HUGH SOUND BRITISH COLUMBIA CANADA Geography ." Tageo.com GPS city index & satellite map. Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query - Frederick Sound: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "Gardener Canal - Kitlope River Valley". Ray Morgan and Avondale Technologies Ltd. 1997–2005. Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ "Howe Sound, British Columbia, Canada". Web Design by Sage Internet Solutions. Shangaan Webservices Inc. 1998–2008. Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ Meka, Troniks (2008). "TAGEO -Ijellirtung Fiord- NUNAVUT CANADA Geography Population Map cities coordinates location - Tageo.com". World>>Canada>>Nunavut>>Ijellirtung Fiord. Meteo365.com Ltd. Retrieved 2008-11-07.
- ↑ "BC Parks - Indian Arm Provincial Park, North Vancouver". Shangaan Webservices Inc. 1998–2008. Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ↑ Hitz, Charles W.(2003).Through the Rapids - The History of Princess Louisa Inlet, p.30. Sitka 2 Publishing Archived 2008-11-22 at the Wayback Machine.., Kirkland, WA. ISBN 0-9720255-0-2.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query - Kiltuish Inlet: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query - Kitimat Armt: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query - Knight Inlet: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query - Kwatna Inlet: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query - Kyuquot Sound: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query -Labouchere Channel: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query -Loughborough Inlet: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query -Narrows Inlet: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query -Nass Bay: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query North Bentinck Arm: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query Nugent Sound: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query Observatory Inlet: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ Ruble, Shirley (1995–2008). "Cruising the North Coast of British Columbia". Portland Inlet and Portland Canal (Stewart and Hyder):. Interactive Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 2008-11-09. Observatory Inlet goes inland towards Eagle Cove, Perry Cove, Alice Arm Settlement, Hastings Arm and the ghost town of Anyox.
- ↑ Ruble, Shirley (1995–2008). "Cruising the North Coast of British Columbia". Portland Inlet and Portland Canal (Stewart and Hyder):. Interactive Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 2008-11-09. Pearl Harbour or Port Simpson are settlements along Portland Inlet. The Portland Inlet takes you by the Tongass Passage Nass River mouth, the Observatory Inlet, Alice Arms and into Hastings Arm.
- ↑ Ruble, Shirley (September 19, 2007). 145903&SearchSource= Main&Ship= 2 "Princess Louisa Inlet, British Columbia, Sechelt, Canada" Check
|url=value (help). Daily Expedition Reports From the Sea Bird in the Pacific Northwest. 2007 Lindblad Expeditions & National Geographic. Retrieved 2008-11-09. Jervis Inlet is a long fjord encompassing Prince of Wales Reach and Queens Reach... Princess Louisa Inlet. - 1 2 Golden, L (1998–2008). "The Prince Rupert Harbour Complex". Based on the book Title:"Biophysical Suitability of the North Coast and Queen Charlotte Islands Regions of British Columbia for Salmonid Farming in Net Cages" MAFF (1992). Retrieved 2008-11-09.
The very immense, Prince Rupert Harbour, is a complex of basins or channel waterways and sills. In alphabetical order the channels, and their respective sills are:
- Fern Passage (29 m (95 ft), surrounded by sills of 7 m (23 ft) and 2.1 m (6 ft 11 in))
- Kloiya Bay (23.5 m (77 ft) depth, Denise Inlet 39 m (128 ft))
- Morse Basin (7 m (23 ft) depth, silled off)
- Porpoise Channel (51 m (167 ft) depth across Flora Bank, 20 m (66 ft) outside sill)
- Porpoise Harbour (25 m (82 ft)) depth
- Prince Rupert Main Harbour (91 m (299 ft) depth, with 3 entrance sills -each 38 m (125 ft))
- Tuck Inlet, is "silled-off" fjord (80 m (260 ft) depth, with entrance sill of 10.5 m (34 ft))* Upper Harbour (60 m (200 ft) depth, with entrance sill of 45 m (148 ft))
- Venn Passage around the north end of Digby Island (22 m (72 ft) depth contained by several wide sills of 4.9 m (16 ft), 3 m (9.8 ft), 6.4 m (21 ft) and 6.1 m (20 ft))
- Wainwright Basin (5.7 m (19 ft), with sills of 3.7 m (12 ft), 9.1 m (30 ft) and 0.9 m (2 ft 11 in))
- ↑ Ruble, Shirley (2008). "Princess Louisa Inlet, British Columbia, Sechelt, Canada". Hotel Reviews, Hotel Ratings. TravelPost.com, part of the SideStep Network. Retrieved 2008-11-09. Chatterbox Falls is listed at List of waterfalls in Canada as having a 37 metres (121 ft). It empties into Princess Louisa Inlet.
- ↑ "Earls Cove, British Columbia, Canada". Shangaan Webservices Inc. 1998–2008. Retrieved 2008-11-09. Jervis Inlet, proceeds inland to Hotham Sound, Agamemnon Channel, Sechelt Inlet, Prince of Wales Reach, Princess Royal Reach, and into Queens Reach.
- ↑ Austin, William C. (15–19 February 1999). "Rare and Endangered Marine Invertebrates in British Columbia" (pdf). Marine Ecology Station and Khoyatan Marine Laboratory. Proc. Biology and Management of Species and Habitats at Risk, Kamloops, B.C.,. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "BRITISH COLUMBIA MARINE ECOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION: MARINE ." Individual Thematic Analysis. Province of British Columbia. 1997. Archived from the original on June 28, 2009. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "Egmont, British Columbia, Canada". Shangaan Webservices Inc. 1998–2008. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "Rivers Inlet, British Columbia, Canada". Shangaan Webservices Inc. 1998–2008. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query -Saanich Inlet: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query -Salmon Inlet: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ Riveiros, Natalia Vázquez; R. Timothy Patterson (2005–2006). "AN ILLUSTRATED GUIDE TO FJORD FORAMINIFERA FROM THE SEYMOUR-BELIZE ." Forams from BC. Plain-Language & Multilingual Abstracts. Retrieved 2008-11-07. The Sechelt Inlet complex (British Columbia, Canada), Including Narrows Inlet and Salmon Inlet. Narrows Inlet (14 km (8.7 mi)) is separated from the main inlet system by a shallow sill (11 m (36 ft)) at Tzoonie Narrows.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query -Skookumchuck Narrows: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query -Telegraph Passage: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "Toba Inlet, British Columbia, Canada". Shangaan Webservices Inc. 1998–2008. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query - Ursula Channel: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query - Wakeman Sound: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "Western Brook Pond". World Lakes Database. Archived from the original on 2007-07-15. Retrieved 2008-03-05.
- ↑ "Whidbey Reach". BC Geographical Names.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query - Whidbey Reach: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- ↑ "GeoNames Query - Work Channel: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Fjords of Canada. |







