Chinese mountain cat
| Chinese mountain cat | |
|---|---|
_in_XiNing_Wild_Zoo.jpg) | |
| Chinese mountain cat in Xining Zoo | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Felidae |
| Subfamily: | Felinae |
| Genus: | Felis |
| Species: | F. bieti[2] |
| Binomial name | |
| Felis bieti[2] Milne-Edwards, 1892 | |
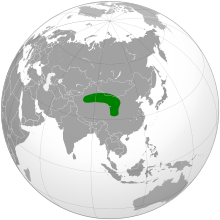 | |
| Distribution of the Chinese mountain cat (in green) | |
The Chinese mountain cat (Felis bieti), also known as the Chinese desert cat and the Chinese steppe cat, is a wild cat endemic to western China that has been listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List since 2002, as the effective population size may be fewer than 10,000 mature breeding individuals.[1]
It was classified as F. silvestris bieti, a wildcat subspecies, in 2007 based on genetic analysis.[3]
Characteristics
The Chinese mountain cat has sand-coloured fur with dark guard hairs. Faint dark horizontal stripes on the face and legs are hardly visible. Its ears have black tips. It has a relatively broad skull, and long hair growing between the pads of their feet. It is whitish on the belly, and its legs and tail bear black rings. The tip of the tail is black. It is 69–84 cm (27–33 in) long in head and body with a 29–41 cm (11–16 in) long tail. Adults weigh from 6.5 to 9 kilograms (14 to 20 lb).[4]
Distribution and habitat
The Chinese mountain cat is endemic to China and lives on the north-eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. It was recorded only in eastern Qinghai and north-western Sichuan.[5] It inhabits high-elevation steppe grassland, alpine meadow, alpine shrubland and coniferous forest edges between 2,500 and 5,000 m (8,200 and 16,400 ft) elevation. It has not been confirmed in true desert or heavily forested mountains.[6]
The first photographs of a wild Chinese mountain cat were taken by camera traps during light snow in May 2007 at 3,570 m (11,710 ft) altitude in Sichuan. These photographs were taken in rolling grasslands and brush-covered mountains.[7] One individual was observed and photographed in May 2015 in the Ruoergai grasslands.[8] In 2018, employees of the Shanshui Conservation Center found a den of a mother cat and her two kittens in Yushu, and captured them over three days using a camera trap.[9]
Ecology and behaviour
The Chinese mountain cat is active at night and preys on pikas, rodents and birds. It breeds between January and March. Females give birth to two to four kittens in a secluded burrow.[6]
Until 2007, the Chinese mountain cat was known only from six individuals, all living in Chinese zoos, and a few skins in museums.[7]
Threats
The Chinese mountain cat is threatened due to the organised poisoning of pikas. The poison used diminishes prey species and also kills cats unintentionally.[5]
Conservation
Felis bieti is listed on CITES Appendix II.[1] It is protected in China.
Taxonomic history
Alphonse Milne-Edwards first described the Chinese mountain cat in 1892 based on a skin collected in Sichuan Province. He named it Felis Bieti after the French missionary Félix Biet.[10]
Some authorities consider the chutuchta and vellerosa subspecies of the wildcat as Chinese mountain cat subspecies.[2]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Riordan, P.; Sanderson, J.; Bao, W.; Abdukadir, A.; Shi, K. (2015). "Felis bieti". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. IUCN. 2015: e.T8539A50651398. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T8539A50651398.en. Retrieved 13 January 2018.
- 1 2 3 Wozencraft, W.C. (2005). "Order Carnivora". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 534. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ↑ Driscoll, C. A.; Menotti-Raymond, M.; Roca, A. L.; Hupe, K.; Johnson, W. E.; Geffen, E.; Harley, E. H.; Delibes, M.; Pontier, D.; Kitchener, A. C.; Yamaguchi, N.; O’Brien, S. J.; Macdonald, D. W. (2007). "The Near Eastern Origin of Cat Domestication" (PDF). Science. 317 (5837): 519–523. doi:10.1126/science.1139518. PMC 5612713. PMID 17600185.
- ↑ Sunquist, M.; Sunquist, F. (2002). Wild cats of the World. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 57–59. ISBN 0-226-77999-8.
- 1 2 He L., Garcia-Perea R., Li M., Wei F. (2004). "Distribution and conservation status of the endemic Chinese mountain cat Felis bieti". Oryx. 38: 55–61. doi:10.1017/s0030605304000092.
- 1 2 Liao Y. (1988). Some biological information of desert cat in Qinhai. Acta Theriologica Sinica 8: 128–131.
- 1 2 Yin Y., Drubgyal N., Achu, Lu Z., Sanderson J. (2007). First photographs in nature of the Chinese mountain cat. Cat News 47: 6–7.
- ↑ Francis, S., Muzika, Y. (2015). Chinese Mountain Cat in the Ruoergai Grasslands. Small Wild Cat Conservation News 1 (1): II.
- ↑ "Chinese Mountain Cat". 12 October 2018.
- ↑ Milne-Edwards, A. (1892). Observations sur les mammifères du Thibet. Revue générale des sciences pures et appliquées. Tome III: 670–671.
External links
| Wikispecies has information related to Felis bieti |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Felis bieti. |