Federal Parliament of Nepal
| Federal Parliament of Nepal संघीय संसद, नेपाल | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses |
National Assembly, House of Representatives |
| History | |
| Founded | 5 March 2018 |
| Preceded by | Legislature Parliament of Nepal |
| Leadership | |
Chairman of the National Assembly | |
Deputy Chairman of the National Assembly | |
Speaker of the House of Representatives | |
Deputy Speaker of the House of Representatives | |
Leader of the House of Representatives | |
| Structure | |
| Seats |
334 59 assemblymen 275 representatives |
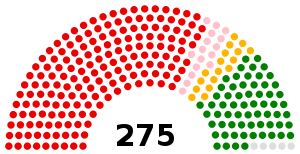 | |
House of Representatives political groups |
Government (190) Opposition (85)
|
National Assembly political groups |
Government (44) Opposition (15) |
| Elections | |
| First-past-the-post & Proportional representation | |
| Single transferable vote | |
House of Representatives last election | 26 November and 07 December 2017 |
National Assembly last election | 07 February 2018 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| International Convention Centre, New Baneshwor, Kathmandu, Nepal | |
| Website | |
|
www | |
| Constitution | |
| Constitution of Nepal | |
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Nepal |
|
Executive:
Judiciary:
|
|
|
|
Related topics |
The Federal Parliament of Nepal (Nepali: संघीय संसद नेपाल, Saṅghīya Sansada Nēpāl) is the federal and supreme legislative body of Nepal. It is a bicameral federal legislature that consists of the National Assembly as upper house and the House of Representatives, as lower house.
History
Legislatures of Kingdom of Nepal
The former Parliament of Nepal was dissolved by King Gyanendra in 2002, on the grounds that it was incapable of handling the Maoist rebels. The country's five main political parties have staged protests against the king, arguing that he must either call fresh elections or reinstate the elected legislature. In 2004, the king announced that parliamentary elections would be held within twelve months; in April 2006, in response to major pro-democratic protests, it was announced that Parliament would be reestablished.[3]The current prime minister of Nepal is Khadga Prasad Oli.
Interim Legislature of Nepal
After the success of the April 2006 people's movement, on January 15, 2007, the old parliament was dissolved and replaced by the 330-member interim legislature of Nepal. By the legislature an Interim Constitution was promulgated and a constituent assembly election was held in April 2008. The 601-member assembly on 28 May 2008 abolished the 238-year-old monarchy and declared the country a republic. The parliament constituent assembly, which was initially given two years to draft a new constitution, was dissolved on 27 May 2012 after its failure to draft a new constitution due to differences over restructuring the state.
Legislature Parliament of Nepal
The Legislature Parliament of Nepal was expired by 21 January 2018 (7 Magh, 2074 BS).[4]
The second Nepalese Constituent Assembly was converted into legislative parliament of Nepal after the promulgation of the constitution on September 20, 2015.[5] The second Nepalese Constituent Assembly was formed after failure of first Constituent Assembly to draft a new constitution. The second Nepalese Constituent Assembly has completed its task by successfully promulgating the constitution on September 20, 2015.
Composition
According to the Constitution of Nepal 2015 Nepal has a two chamber Parliament (संसद)[6]. The House of Representatives (प्रतिनिधि सभा) has 275 members elected for a five year term, 165 from single-seat constituencies and 110 from a proportional party list. The National Assembly (राष्ट्रिय सभा) has 59 members elected for six years term. Among the 59 members three members are nominated by the President. The remaining 56 are elected from 7 provinces equally (Eight each) including 3 female 1 Dalits and 1 from differently abled groups.
President of Nepal
House of Representatives
National Assembly
Parliamentary committees
House of Representatives
Finance
International Relations
Industry, Commerce, Labour and Consumer Interest
Law, Justice, and Human Rights
Agriculture Cooperative and Natural Resources
Women and Social
State Affairs
Development and Technology
Education and Health
Public Account
National Assembly
Sustainable Development and Good Governance
Legislative Management
Delegated Management
National Interest and Coordination
Both
Parliamentary Hearing
State Direction, Principle Rules and Responsibility
Women's Representation
Nepal currently has a woman as deputy speaker of the Parliament. On 16th March 2018 Shiva Maya Tumbahamphe elected as the deputy speaker of the house.[7] Women’s representation in the Parliament of Nepal has increased in the Constituent Assembly, which will have immense role to draft the future constitution of Nepal.[3]
Parliament House
See also
References
- ↑ "Krishna Bahadur Mahara Elected Speaker". Nepal Republic Media. Kathmandu, Nepal. 10 March 2018. Archived from the original on 15 March 2018.
- 1 2 "FSF-N to join NCP-led govt". 28 May 2018.
- 1 2 "Nepal's Political Development: Nepal Constituent Assembly Portal". Nepalcaportal.org. Retrieved 2010-04-10.
- ↑ "संविधानसभा प्रथम". parliament.gov.np. Retrieved 13 December 2017.
- ↑ "Nepal elects first woman speaker of parliament - Times of India".
- ↑
- ↑ "CPN-UML leader Tumbahamphe elected to Deputy Speaker of HoR". 16 March 2018.