Dipotassium phosphate
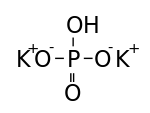 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Potassium hydrogenphosphate Potassium hydrogen(tetraoxidophosphate)(2−) | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Potassium hydroxidotrioxidophosphate(2−) | |
| Other names
Potassium monohydrogen phosphate Phosphoric acid dipotassium salt Potassium phosphate dibasic | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.940 |
| EC Number | 231-834-5 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| K2HPO4 | |
| Molar mass | 174.2 g/mol |
| Appearance | white powder deliquescent |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.44 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | > 465 °C (869 °F; 738 K) decomposes |
| 149.25 g/100 mL (20 °C) | |
| Solubility | slightly soluble in alcohol |
| Acidity (pKa) | 12.4 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 6.8 |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations |
Disodium phosphate Diammonium phosphate |
Related compounds |
Monopotassium phosphate Tripotassium phosphate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dipotassium phosphate (K2HPO4) (also dipotassium hydrogen orthophosphate; potassium phosphate dibasic) is a highly water-soluble salt which is often used as a fertilizer, food additive and buffering agent. It is a common source of phosphorus and potassium.
A dipotassium phosphate solution is formed by the stoichiometric reaction of phosphoric acid with two equivalents of potassium hydroxide:
- H3PO4 + 2 KOH → K2HPO4 + 2 H2O
Uses
As a food additive, dipotassium phosphate is used in imitation dairy creamers, dry powder beverages, mineral supplements, and starter cultures.[1] It is used in non-dairy creamers to prevent coagulation.[2]
Dipotassium phosphate is also used to make buffer solutions and it is used in the production of trypticase soy agar which is used to make agar plates for culturing bacteria.
A 3% gel of dipotassium phosphate is used as the active ingredient in Crest Sensi-Strips, a common tooth sensitivity product.
Safety
As a food additive, dipotassium phosphate is categorized in the United States by the Food and Drug Administration as generally recognized as safe (GRAS).[3]
References
- ↑ John H. Thorngate iii, Seppo Salminen , Larry A . Branen , and Michael P . Davidson, eds. (2001). "Food Phosphates". Food Additives. CRC Press. doi:10.1201/9780824741709.ch25. ISBN 978-0-8247-9343-2.
- ↑ "dipotassium phosphate". Retrieved 2009-01-06. (uses: Food Industry)
- ↑ "Database of Select Committee on GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Reviews". Retrieved 2008-03-22. (listed as "potassium phosphate, dibasic")
The compound is for food uses although it may be bad for consumers to eat vast amounts of it.
