Dimercaptosuccinic acid
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | Succimer /ˈsʌksɪmər/ |
| Trade names | Chemet, others |
| Synonyms |
(2R,3S)-2,3-Dimercaptosuccinic acid meso-2,3-Dimercaptosuccinic acid Succimer APRD01236 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard |
100.005.597 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C4H6O4S2 |
| Molar mass | 182.21 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 125 °C (257 °F) |
| |
| |
Dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA), also called succimer, is a medication used to treat lead, mercury, and arsenic poisoning.[1] When radiolabeled with technetium-99m, it is used in a number of types of diagnostic testing.[2] It is taken by mouth for 19 days.[1] More than two weeks should pass before a second course is given.[1]
Common side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, rash, and low blood neutrophil levels.[1] Liver problems and allergic reactions may also occur with use.[1] It is unclear if use during pregnancy is safe for the baby.[3] Dimercaptosuccinic acid is in the chelating agent family of medications.[1] It works by binding with lead and a number of other heavy metals allowing them to leave the body in the urine.[1]
Dimercaptosuccinic acid has been used medically since the 1950s.[4][5] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system.[6] In the United States there was no generic version available as of 2015.[7] A course of treatment costs more than US$200 (about $6.63 per 100 mg pill).[7][8] In India, it costs about $1.24 per 100 mg pill.[9]
Medical uses
Dimercaptosuccinic acid is indicated for the treatment of lead poisoning in children with blood level measured above 45 µg/dL. The use of DMSA is not approved for prevention of lead poisoning in anticipation of exposure in known lead contaminated environments. Its elimination half-life is 2.5–3.5 hours. DMSA can cross the blood–brain barrier of mice,[10] but not that of humans, limiting its use to extracting heavy metals from parts of the body other than the central nervous system.[11][12]
DMSA facilitates urinary excretion of lead, and with sufficiently aggressive treatment, can reduce lead content in the brain.[13] DMSA also increases urinary excretion of copper and zinc.[14] DMSA improved cognitive function in rats that had been exposed to lead, but reduced cognitive function in rats that had not been exposed to lead.[13]
The relative activities of a series of novel monoalkyl esters of meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid (MiADMSA) have been examined as agents for the mobilization of cadmium,[15] lead [16] and arsenic [17] owing to the ability of these monoesters to cross cell membranes. The monoesters were found to be more effective than the parent compound DMSA. The complexes (monoesters of DMSA) seem to penetrate cells (not possible in the case of DMSA), which helps in targeting intracellular sites in the body and aids in the removal of toxic metal ions in the cytosol and organelles inside the cell.
Chemistry
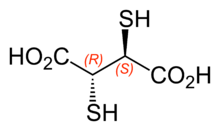
It is the organosulfur compound with the formula HO2CCH(SH)CH(SH)CO2H. This colorless solid contains two carboxylic acid and two thiol groups, the latter being responsible for its mildly unpleasant odour. It occurs in two diastereomers, meso and the chiral dl forms.
The 2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid molecule has two stereocentres (two asymmetric carbons), and can exist as three different stereoisomers. The 2S,3S and 2R,3R isomers are a pair of enantiomers, whereas the 2R,3S isomer is a meso compound and thus optically inactive.
-2%2C3-dimercaptosuccinic-acid-2D-skeletal-A-configurations-labelled.png) |  | -2%2C3-dimercaptosuccinic-acid-2D-skeletal-A-configurations-labelled.png) |
-2%2C3-dimercaptosuccinic-acid-2D-skeletal-B-configurations-labelled.png) | 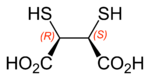 | -2%2C3-dimercaptosuccinic-acid-2D-skeletal-B-configurations-labelled.png) |
(meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid) |
Preparation and reactivity
DMSA may be prepared by reacting acetylenedicarboxylic acid with sodium thiosulfate[18] or thioacetic acid followed by hydrolysis. The dimethyl ester is also known.[19]
Meso 2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid binds to "soft" heavy metals such as Hg2+ and Pb2+, mobilizing these ions for excretion. It binds to metal cations through the thiol groups, which ionize upon complexation.
History
DMSA was first synthesized by V. Nirenburg in the Urals Polytechnic Institute, commissioned by one of the electrical enterprises of Sverdlovsk, which consumed many tons of mercury and was looking for a medicine to prevent poisoning of personnel. In 1957, it was found by Chinese scientists that DMSA can effectively treat antimony poisoning due to overdose of tartar emetic.[20] Pronounced protective effect in animal poisoning with arsenic and mercury was first shown by I. Okonishnikova in 1962. In 1984 the now-defunct Bock Pharmaceutical Company requested the FDA grant approval for Orphan drug status under the trade name Chemet and the FDA approved of this in 1991 providing exclusivity until 1998 which was conveyed to the successor Sanofi in 1996.[21][22]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Succimer". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 16 January 2017. Retrieved 8 January 2017.
- ↑ Biersack, H.-J.; Grünwald, F. (2005). Thyroid Cancer. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 213. ISBN 9783540278450. Archived from the original on 2017-01-13.
- ↑ "Succimer (Chemet) Use During Pregnancy". www.drugs.com. Archived from the original on 16 January 2017. Retrieved 12 January 2017.
- ↑ Miller, Alan (June 1998). "Dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA), a non-toxic, water-soluble treatment for heavy metal toxicity". Alternative Medicine Review. 3 (3): 199–207. PMID 9630737.
- ↑ Chappell, W. R.; Abernathy, C. O.; Calderon, R. L. (1999). Arsenic Exposure and Health Effects III. Elsevier. p. 350. ISBN 9780080527574. Archived from the original on 2017-01-13.
- ↑ "WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (19th List)" (PDF). World Health Organization. April 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- 1 2 Hamilton, Richart (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 472. ISBN 9781284057560.
- ↑ Leikin, Jerrold B.; McFee, Robin B.; Kerscher, Robert (2007). Handbook of Nuclear, Biological, and Chemical Agent Exposures. CRC Press. p. 10. ISBN 9781420044782. Archived from the original on 2017-01-13.
- ↑ Chakrabarty, Narayan (2015). Arsenic Toxicity: Prevention and Treatment. CRC Press. p. 416. ISBN 9781482241976. Archived from the original on 2017-01-13.
- ↑ Aasath, Jan; Dag Jacobsen; Ole Andersen; Elsa Wickstrøm (March 1995). "Treatment of Mercury and Lead Poisonings with Dimercaptosuccinic Acid (DMSA) and Sodium Dimercaptopropanesulfonate (DMPS)". Analyst. 120 (3): 853ff. doi:10.1039/an9952000853.
- ↑ Rooney, James (2007). "The role of thiols, dithiols, nutritional factors and interacting ligands in the toxicology of mercury". Toxicology. 234 (3): 145–156. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2007.02.016. PMID 17408840.
- ↑ Guzzi, GianPaolo; Caterina A.M. La Porta (2008). "Molecular mechanisms triggered by mercury". Toxicology. 244 (1): 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2007.11.002. PMID 18077077.
- 1 2 Smith D, Strupp BJ (2013). "The scientific basis for chelation: animal studies and lead chelation". Journal of Medical Toxicology. 9 (4): 326–338. doi:10.1007/s13181-013-0339-2. PMC 3846979. PMID 24113857.
- ↑ Bradberry S, Sheehan T, Vale A (2009). "Use of oral dimercaptosuccinic acid (succimer) in adult patients with inorganic lead poisoning". QJM: An International Journal of Medicine. 102 (10): 721–732. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcp114. PMID 19700440. Archived from the original on 2016-10-06.
- ↑ Jones MM, Singh PK, Gale GR, Smith AB, Atkins LM (May 1992). "Cadmium mobilization in vivo by intraperitoneal or oral administration of monoalkyl esters of meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid in the mouse". Pharmacology & Toxicology. 70 (5 Pt 1): 336–343. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0773.1992.tb00483.x. PMID 1319053.
- ↑ Walker EM Jr; Stone A; Milligan LB; Gale GR; Atkins LM; Smith AB; Jones MM; Singh PK; Basinger MA. (Nov 1992). "Mobilization of lead in mice by administration of monoalkyl esters of meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid". Toxicology. 76 (1): 79–87. doi:10.1016/0300-483x(92)90020-f. PMID 1335621.
- ↑ Kreppel H, Reichl FX, Kleine A, Szinicz L, Singh PK, Jones MM (Jul 1995). "Antidotal efficacy of newly synthesized dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) monoesters in experimental arsenic poisoning in mice". Fundamental and Applied Toxicology. 26 (2): 239–245. doi:10.1093/toxsci/26.2.239. PMID 7589912.
- ↑ US 4550193, Lindemann, Martin K. O. & Lukenbach, Elvin R., "Process for the preparation of 2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid and its lower alkyl esters", assigned to Johnson & Johnson Baby Products
- ↑ M. Gerecke; E. A. H. Friedheim; A. Brossi (1961). "Zur Kenntnis der 2,3-Dimercapto-bernsteinsäuren". Helvetica Chimica Acta. 44 (4): 955–960. doi:10.1002/hlca.19610440410.
- ↑ Liang, Y., Chu. C, Tsen, Y., Ting, K. (1957). "Studies on antibilharzial drugs. Vl. The antidotal effects of sodium dimercaptosuccinate and BAL-glucoside against tartar emetic". Acta Physiol. Sin. 21: 24–32.
- ↑ "Search Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals". Searchable database for Orphan Designated and or Approved Products. FDA. 2013. Archived from the original on 6 November 2014. Retrieved 5 November 2014.
- ↑ "Sanofi Buying An American Drug Concern". New York Times. New York, NY. July 17, 1996. Archived from the original on 6 November 2014. Retrieved 5 November 2014.
Further reading
- Aposhian, H.V.; Aposhian, M.M. (1990). "Meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid: Chemical, pharmacological and toxicological properties of an orally effective metal chelating agent". Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology. 30 (1): 279–306. doi:10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.001431. PMID 2160791.