Contrasting and categorization of emotions
The contrasting and categorization of emotions describes how emotions are thought to relate to each other. Several proposals have been made for organizing them into groups.
Lists of emotions
Humans experience emotion, with evidence used that they influence action, thoughts and behavior. Emotions are categorized into various affects, which correspond to the current situation.[1] An affect is a term used to describe the range of feeling experienced.[2]
Many theories of emotion have been proposed[3], with contrasting views.[4]
Basic emotions
- William James in 1890 proposed four basic emotions: fear, grief, love, and rage, based on bodily involvement.[5]
- Paul Ekman identified six basic emotions: anger, disgust, fear, happiness, sadness and surprise.[6] Wallace V. Friesen and Phoebe C. Ellsworth worked with him on the same basic structure.[7]
- Richard and Bernice Lazarus in 1996 expanded the list to 15 emotions: aesthetic experience, anger, anxiety, compassion, depression, envy, fright, gratitude, guilt, happiness, hope, jealousy, love, pride, relief, sadness, and shame, in the book Passion and Reason.[8][9]
- Psychologists identify 34 categories of emotion: admiration, adoration, aesthetic appreciation, amusement, anger, anxiety, awe, awkwardness, boredom, calmness, confusion, contempt, craving, disgust, empathic pain, entrancement, excitement, fear, horror, interest, joy, nostalgia, relief, romance, sadness, satisfaction, sexual desire and surprise.[10] This was based on 2185 short videos intended to elicit a certain emotion. These were then modelled onto a "map" of emotions.[11]
Contrasting basic emotions
A 2009 review[12] of theories of emotion identifies and contrasts fundamental emotions according to three key criteria for mental experiences that:
- have a strongly motivating subjective quality like pleasure or pain;
- are a response to some event or object that is either real or imagined;
- motivate particular kinds of behavior.
The combination of these attributes distinguishes emotions from sensations, feelings and moods.
| Kind of emotion | Positive emotions | Negative emotions |
|---|---|---|
| Related to object properties | Interest, curiosity, enthusiasm | Indifference, habituation, boredom |
| Attraction, desire, admiration | Aversion, disgust, revulsion | |
| Surprise, amusement | Alarm, panic | |
| Future appraisal | Hope, excitement | Fear, anxiety, dread |
| Event-related | Gratitude, thankfulness | Anger, rage |
| Joy, elation, triumph, jubilation | Sorrow, grief | |
| Patience | Frustration, disappointment | |
| Contentment | Discontentment, restlessness | |
| Self-appraisal | Humility, modesty | Pride, arrogance |
| Social | Charity | Avarice, greed, miserliness, envy, jealousy |
| Sympathy | Cruelty | |
| Cathected | Love | Hate |
HUMAINE's proposal for EARL
The emotion annotation and representation language (EARL) proposed by the Human-Machine Interaction Network on Emotion (HUMAINE) classifies 48 emotions.[13]
- Negative and forceful
- Negative and not in control
- Negative thoughts
- Negative and passive
- Agitation
- Positive and lively
- Caring
- Positive thoughts
- Quiet positive
- Reactive
Parrott's emotions by groups
A tree-structured list of emotions was described in Shaver et al. (1987),[14] and also featured in Parrott (2001).[15]
Plutchik's wheel of emotions
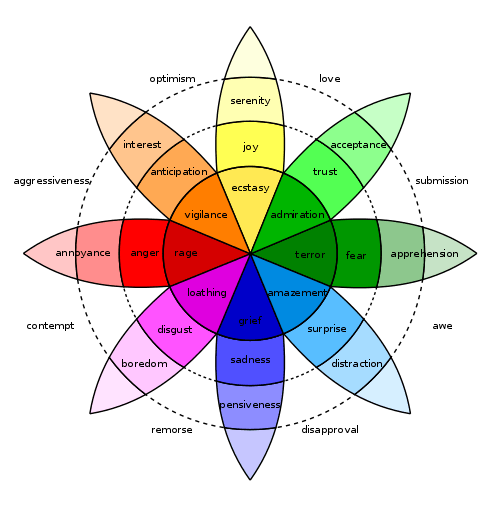
In 1980, Robert Plutchik constructed diagram of emotions visualising eight basic emotions: joy, trust, fear, surprise, sadness, disgust, anger and anticipation. The wheel was inspired by Plutchik's Ten Postulates[17][18] Plutchik also theorized twenty-four "Primary", "Secondary", and "Tertiary" dyads (feelings composed of two emotions).[19][20][21] The wheel emotions can be paired in four groups:
- Primary dyad = one petal apart = Love = Joy + Trust
- Secondary dyad = two petals apart = Envy = Sadness + Anger
- Tertiary dyad = three petals apart = Shame = Fear + Disgust
- Opposite emotions = four petals apart = Anticipation ≠ Surprise
Emotions can be mild or intense;[22] for example, distraction is a mild form of surprise, and rage is an intense form of anger. The kinds of relation between each pair of emotions are:
| Mild emotion | Mild opposite | Basic emotion | Basic opposite | Intense emotion | Intense opposite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serenity | Pensiveness | Joy | Sadness | Ecstasy | Grief |
| Acceptance | Boredom | Trust | Disgust | Admiration | Loathing |
| Apprehension | Annoyance | Fear | Anger | Terror | Rage |
| Distraction | Interest | Surprise | Anticipation | Amazement | Vigilance |
| Human feelings | Emotions | Opposite feelings | Emotions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optimism | Anticipation + Joy | Disapproval | Surprise + Sadness |
| Hope | Anticipation + Trust | Unbelief | Surprise + Disgust |
| Anxiety | Anticipation + Fear | Outrage | Surprise + Anger |
| Love | Joy + Trust | Remorse | Sadness + Disgust |
| Guilt | Joy + Fear | Envy | Sadness + Anger |
| Delight | Joy + Surprise | Pessimism | Sadness + Anticipation |
| Submission | Trust + Fear | Contempt | Disgust + Anger |
| Curiosity | Trust + Surprise | Cynicism | Disgust + Anticipation |
| Sentimentality | Trust + Sadness | Morbidness | Disgust + Joy |
| Awe | Fear + Surprise | Aggressiveness | Anger + Anticipation |
| Despair | Fear + Sadness | Pride | Anger + Joy |
| Shame | Fear + Disgust | Dominance | Anger + Trust |
Plutchik's wheel in Venn format
Jessica Hagy wrote on her blog that Plutchik's wheel of emotions gave a demonstration on emotions, but needed more levels of intensity in the emotion combinations. She observed that the wheel was a Venn diagram format, and expanded the primary dyads.[23]
| Human feelings | Emotions | Opposite feelings | Emotions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bemusement | Interest + Serenity | Dismay | Distraction + Pensiveness |
| Zeal | Vigilance + Ecstasy | Horror | Amazement + Grief |
| Acknowledgement | Serenity + Acceptance | Listlessness | Pensiveness + Boredom |
| Devotion | Ecstasy + Admiration | Shame | Grief + Loathing |
| Acquiescence | Acceptance + Apprehension | Impatience | Boredom + Annoyance |
| Subservience | Admiration + Terror | Hatred | Loathing + Rage |
| Wariness | Apprehension + Distraction | Disfavor | Annoyance + Interest |
| Petrification | Terror + Amazement | Domination | Rage + Vigilance |
The Hourglass of Emotions
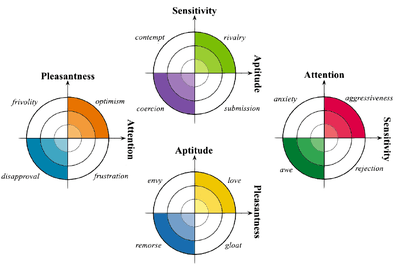
The 2012 book The Hourglass of Emotions was based on Robert Plutchik's model, but categorised the emotions into four sentic dimensions. It contrasted anger, anticipation, joy, and trust as positive emotions, and fear, surprise, sadness and disgust as negative.[24]
,
| Dimensions | High Sensitivity | Low Sensitivity | High Pleasantness | Low Pleasantness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Attention | Aggressiveness | Anxiety | Optimism | Frustration |
| Low Attention | Rejection | Awe | Frivolity | Disapproval |
| High Aptitude | Rivalry | Submission | Love | Envy |
| Low Aptitude | Contempt | Coercion | Gloat | Remorse |
The Book of Human Emotions
Tiffany Watt Smith listed 154 different worldwide emotions and feelings.[25]
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- Fear
- Feeling good (about yourself)
- Formal feeling, a
- Fraud, feeling like a
- Frustration
- G
- H
- Han
- Happiness
- Hatred
- Heebie-Jeebies, the
- Hiraeth
- Hoard, the urge to
- Homefulness
- Homesickness
- Hopefulness
- Huff, in a
- Humble, feeling
- Humiliation
- Hunger
- Hwyl
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- Oime
- Overwhelmed, feeling
- P
- Panic
- Paranoia
- Perversity
- Peur des espaces
- Philoprogenitiveness
- Pique, a fit of
- Pity
- Postal, going
- Pride
- Pronoia
- R
- S
- T
- V
- W
- Z
Mapping facial expressions
Scientists map twenty-one different facial emotions[27][28] [29] expanded from Paul Ekman's six basic emotions of anger, disgust, fear, happiness, sadness, and surprise:
See also
References
- ↑ Lisa Feldman Barrett. "Solving the Emotion Paradox : Categorization and the Experience of Emotion" (PDF). Pdfs.semanticscholar.org. Retrieved 2017-08-25.
- ↑ "Emotions and Moods" (PDF). Catalogue.pearsoned.co.uk. Retrieved 20 October 2017.
- ↑ "Comparing The 5 Theories of Emotion – Brain Blogger". Brainblogger.com. Retrieved 23 November 2017.
- ↑ Candland, Douglas (23 November 2017). "Emotion". iUniverse. Retrieved 23 November 2017 – via Google Books.
- ↑ James, William (1 April 2007). "The Principles of Psychology". Cosimo, Inc. Retrieved 20 October 2017 – via Google Books.
- ↑ Handel, Steven. "Classification of Emotions". Retrieved 30 April 2012.
- ↑ "Are There Basic Emotions?" (PDF). Paulekam.com. Retrieved 20 October 2017.
- ↑ Lazarus, Richard S.; Lazarus, Bernice N. (23 September 1996). "Passion and Reason: Making Sense of Our Emotions". Oxford University Press. Retrieved 23 September 2017 – via Google Books.
- ↑ "Emotional Competency – Recognize these emotions". Emotionalcompetency.com. Retrieved 23 September 2017.
- ↑ "Psychologists Identify Twenty Seven Distinct Categories of Emotion – Psychology". Sci-news.com. Retrieved 23 November 2017.
- ↑ "Interactive web". Retrieved 2017-09-11.
- ↑ Robinson, D. L. (2009). "Brain function, mental experience and personality". The Netherlands Journal of Psychology. pp. 152–167.
- ↑ "HUMAINE Emotion Annotation and Representation Language". Emotion-research.net. Retrieved June 30, 2006.
- ↑ Shaver, P.; Schwartz, J.; Kirson, D. & O'connor, C. (1987). "Emotion knowledge: further exploration of a prototype approach". Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 52 (6): 1061. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.52.6.1061. PMID 3598857.
- ↑ Parrott, W. (2001). Emotions in Social Psychology. Key Readings in Social Psychology. Philadelphia: Psychology Press. ISBN 978-0863776830.
- ↑ Plutchik, Robert (16 September 1991). "The Emotions". University Press of America. p. 110. Retrieved 16 September 2017 – via Google Books.
- ↑ "Basic Emotions—Plutchik". Personalityresearch.org. Retrieved 1 September 2017.
- ↑ Plutchik, R. "The Nature of Emotions". American Scientist. Archived from the original on July 16, 2001. Retrieved 14 April 2011.
- ↑ "Robert Plutchik's Psychoevolutionary Theory of Basic Emotions" (PDF). Adliterate.com. Retrieved 2017-06-05.
- ↑ Jonathan Turner (1 June 2000). On the Origins of Human Emotions: A Sociological Inquiry Into the Evolution of Human Affect. Stanford University Press. p. 76. ISBN 978-0-8047-6436-0.
- ↑ Atifa Athar; M. Saleem Khan; Khalil Ahmed; Aiesha Ahmed; Nida Anwar (June 2011). "A Fuzzy Inference System for Synergy Estimation of Simultaneous Emotion Dynamics in Agents". International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research. 2 (6).
- ↑ "The Nature of Emotions" (PDF). Emotionalcompetency.com. Retrieved 2017-09-16.
- ↑ "Plutchik's Wheel of Emotions – Indexed". Thisisindexed.com. 2012-07-06. Retrieved 2017-05-28.
- ↑ "LNCS 7403 – The Hourglass of Emotions" (PDF). Sentic.net. Retrieved 2017-05-28.
- ↑ Tiffany Watt Smith. "The Book of Human Emotions: An Encyclopedia of Feeling from Anger to Wanderlust" (PDF). Anarchiveforemotions.com. Retrieved 2017-05-28.
- ↑ "Invisibilia: A Man Finds An Explosive Emotion Locked In A Word". Retrieved 2017-12-29.
- ↑ "Happily disgusted? Scientists map facial expressions for 21 emotions | Science". The Guardian. Retrieved 2017-07-16.
- ↑ Jacque Wilson (2014-04-04). "Happily disgusted? 15 new emotions ID'd". KSL.com. Retrieved 2017-07-16.
- ↑ "6 basic emotions".