Choco languages
| Chocoan | |
|---|---|
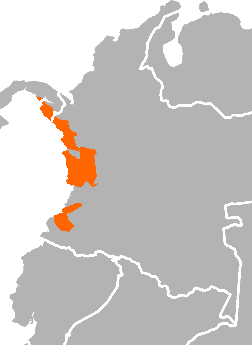
| Geographic distribution | Colombia & Panama |
| Linguistic classification | One of the world's primary language families |
| Subdivisions |
|
| Glottolog | choc1280[1] |
 | |

Poet and politician Eduardo Cote Lamus on his journey in Rio San Juan (Choco, Colombia) in 1958 with some of the people speaking Choco languages
The Choco languages (also Chocoan, Chocó, Chokó) are a small family of Native American languages spread across Colombia and Panama.
Family division
Choco consists of half a dozen known languages, all but two of them extinct.
- The Emberá languages (also known as Chocó proper, Cholo)
- Noanamá (also known as Waunana, Woun Meu)
- Anserma (†)
- Arma (†) ? (unattested)
- Sinúfana (Cenufara) (†) ?
- Caramanta (†) ?
Anserma, Arma, and Sinúfana are extinct.
The Emberá group consists of two languages mainly in Colombia with over 60,000 speakers that lie within a fairly mutually intelligible dialect continuum. Ethnologue divides this into 6 languages. Kaufman (1994) considers the term Cholo to be vague and condescending. Noanamá has some 6,000 speakers on the Panama-Colombia border.
Genetic relations
Choco has been included in a number of hypothetical phylum relationships:
- within Morris Swadesh's Macro-Leco
- Antonio Tovar, Jorge A. Suárez, and Robert Gunn: related to Cariban
- Čestmír Loukotka (1944): Southern Emberá may be related to Paezan, Noanamá to Arawakan
- within Paul Rivet and Loukotka's (1950) Cariban
- Constenla Umaña and Margery Peña: may be related to Chibchan
- within Joseph Greenberg's Nuclear Paezan, most closely related to Paezan and Barbacoan
See also
References
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Chocoan". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
Bibliography
- Campbell, Lyle. (1997). American Indian languages: The historical linguistics of Native America. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-509427-1.
- Constenla Umaña, Adolfo; & Margery Peña, Enrique. (1991). Elementos de fonología comparada Chocó. Filología y lingüística, 17, 137-191.
- Greenberg, Joseph H. (1987). Language in the Americas. Stanford: Stanford University Press.
- Gunn, Robert D. (Ed.). (1980). Claificación de los idiomas indígenas de Panamá, con un vocabulario comparativo de los mismos. Lenguas de Panamá (No. 7). Panama: Instituto Nacional de Cultura, Instituto Lingüístico de Verano.
- Kaufman, Terrence. (1990). Language history in South America: What we know and how to know more. In D. L. Payne (Ed.), Amazonian linguistics: Studies in lowland South American languages (pp. 13–67). Austin: University of Texas Press. ISBN 0-292-70414-3.
- Kaufman, Terrence. (1994). The native languages of South America. In C. Mosley & R. E. Asher (Eds.), Atlas of the world's languages (pp. 46–76). London: Routledge.
- Loewen, Jacob. (1963). Choco I & Choco II. International Journal of American Linguistics, 29.
- Licht, Daniel Aguirre. (1999). Embera. Languages of the world/materials 208. LINCOM.
- Mortensen, Charles A. (1999). A reference grammar of the Northern Embera languages. Studies in the languages of Colombia (No.7); SIL publications in linguistics (No. 134). SIL.
- Rivet, Paul; & Loukotka, Cestmír. (1950). Langues d'Amêrique du sud et des Antilles. In A. Meillet & M. Cohen (Eds.), Les langues du monde (Vol. 2). Paris: Champion.
- Suárez, Jorge. (1974). South American Indian languages. The new Encyclopædia Britannica (15th ed.). Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica.
- Swadesh, Morris. (1959). Mapas de clasificación lingüística de México y las Américas. México: Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México.
- Tovar, Antonio; & Larrucea de Tovar, Consuelo. (1984). Catálogo de las lenguas de América del Sur (nueva ed.). Madrid: Editorial Gedos. ISBN 84-249-0957-7.
External links
- Proel: Familia Chocó
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.