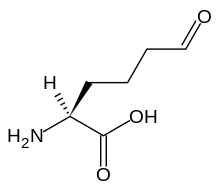
Allysine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-amino-6-oxo-hexanoic acid | |
| Other names
2-aminoadipate semialdehyde, 2-amino-5-formylvaleric acid, norvaline, 6-oxo-DL-norleucine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | allysine |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H11NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 145.16 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.74g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 295.2 °C (563.4 °F; 568.3 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 132.3 °C (270.1 °F; 405.4 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Allysine is a derivative of lysine, used in the production of elastin and collagen. It is produced by the actions of the enzyme lysyl oxidase in the extracellular matrix and is essential in the crosslink formation that stabilizes collagen and elastin.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ Pinnell, SR; Martin, GR (October 1968). "The cross-linking of collagen and elastin: enzymatic conversion of lysine in peptide linkage to alpha-aminoadipic-delta-semialdehyde (allysine) by an extract from bone" (PDF). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 61 (2): 708–13, 716. doi:10.1073/pnas.61.2.708. PMC 225217. PMID 5246001.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.