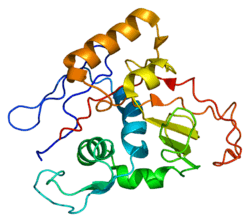
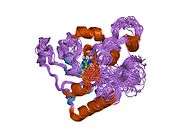
ATPase, Na+/K+ transporting, alpha 1
| Gastric H+/K+-ATPase, N terminal domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 tfe-induded structure of the n-terminal domain of pig gastric h/k-atpase | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | H-K_ATPase_N | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF09040 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR015127 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha-1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATP1A1 gene.[5]
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the family of P-type cation transport ATPases, and to the subfamily of Na+/K+-ATPases. Na+/K+-ATPase is an integral membrane protein responsible for establishing and maintaining the electrochemical gradients of Na and K ions across the plasma membrane. These gradients are essential for osmoregulation, for sodium-coupled transport of a variety of organic and inorganic molecules, and for electrical excitability of nerve and muscle. This enzyme is composed of two subunits, a large catalytic subunit (alpha) and a smaller glycoprotein subunit (beta). The catalytic subunit of Na+/K+-ATPase is encoded by multiple genes. This gene encodes an alpha 1 subunit. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified.[5]
In melanocytic cells ATP1A1 gene expression may be regulated by MITF.[6]
Clinical relevance
Mutations in this gene have been associated with aldosterone-producing adenomas and secondary hypertension.[7]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000163399 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000033161 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: ATP1A1 ATPase, Na+/K+ transporting, alpha 1 polypeptide".
- ↑ Hoek KS, Schlegel NC, Eichhoff OM, Widmer DS, Praetorius C, Einarsson SO, Valgeirsdottir S, Bergsteinsdottir K, Schepsky A, Dummer R, Steingrimsson E (December 2008). "Novel MITF targets identified using a two-step DNA microarray strategy". Pigment Cell & Melanoma Research. 21 (6): 665–76. doi:10.1111/j.1755-148X.2008.00505.x. PMID 19067971.
- ↑ Beuschlein F, Boulkroun S, Osswald A, Wieland T, Nielsen HN, Lichtenauer UD, Penton D, Schack VR, Amar L, Fischer E, Walther A, Tauber P, Schwarzmayr T, Diener S, Graf E, Allolio B, Samson-Couterie B, Benecke A, Quinkler M, Fallo F, Plouin PF, Mantero F, Meitinger T, Mulatero P, Jeunemaitre X, Warth R, Vilsen B, Zennaro MC, Strom TM, Reincke M (April 2013). "Somatic mutations in ATP1A1 and ATP2B3 lead to aldosterone-producing adenomas and secondary hypertension". Nature Genetics. 45 (4): 440–4, 444e1–2. doi:10.1038/ng.2550. PMID 23416519.
Further reading
- Lingrel JB, Orlowski J, Shull MM, Price EM (1990). "Molecular genetics of Na,K-ATPase". Progress in Nucleic Acid Research and Molecular Biology. 38: 37–89. doi:10.1016/S0079-6603(08)60708-4. PMID 2158121.
- Dunbar LA, Caplan MJ (August 2001). "Ion pumps in polarized cells: sorting and regulation of the Na+, K+- and H+, K+-ATPases". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (32): 29617–20. doi:10.1074/jbc.R100023200. PMID 11404365.
- Wangemann P (March 2002). "K+ cycling and the endocochlear potential". Hearing Research. 165 (1–2): 1–9. doi:10.1016/S0378-5955(02)00279-4. PMID 12031509.
- Xie Z, Cai T (May 2003). "Na+-K+--ATPase-mediated signal transduction: from protein interaction to cellular function". Molecular Interventions. 3 (3): 157–68. doi:10.1124/mi.3.3.157. PMID 14993422.
- Shull MM, Pugh DG, Lingrel JB (March 1990). "The human Na, K-ATPase alpha 1 gene: characterization of the 5'-flanking region and identification of a restriction fragment length polymorphism". Genomics. 6 (3): 451–60. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(90)90475-A. PMID 1970326.
- Herrera VL, Ruiz-Opazo N (August 1990). "Alteration of alpha 1 Na+,K(+)-ATPase 86Rb+ influx by a single amino acid substitution". Science. 249 (4972): 1023–6. doi:10.1126/science.1975705. PMID 1975705.
- Kawakami K, Ohta T, Nojima H, Nagano K (August 1986). "Primary structure of the alpha-subunit of human Na,K-ATPase deduced from cDNA sequence". Journal of Biochemistry. 100 (2): 389–97. PMID 2430951.
- Yang-Feng TL, Schneider JW, Lindgren V, Shull MM, Benz EJ, Lingrel JB, Francke U (February 1988). "Chromosomal localization of human Na+, K+-ATPase alpha- and beta-subunit genes". Genomics. 2 (2): 128–38. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(88)90094-8. PMID 2842249.
- Sverdlov ED, Broude NE, Sverdlov VE, Monastyrskaya GS, Grishin AV, Petrukhin KE, Akopyanz NS, Modyanov NN (August 1987). "Family of Na+,K+-ATPase genes. Intra-individual tissue-specific restriction fragment length polymorphism". FEBS Letters. 221 (1): 129–33. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(87)80366-6. PMID 2887455.
- Chehab FF, Kan YW, Law ML, Hartz J, Kao FT, Blostein R (November 1987). "Human placental Na+,K+-ATPase alpha subunit: cDNA cloning, tissue expression, DNA polymorphism, and chromosomal localization". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 84 (22): 7901–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.22.7901. PMC 299443. PMID 2891135.
- Monastyrskaya GS, Broude NE, Allikmets RL, Melkov AM, Malyshev IV, Dulubova IE, Petrukhin KE (March 1987). "The family of human Na+,K+-ATPase genes. A partial nucleotide sequence related to the alpha-subunit". FEBS Letters. 213 (1): 73–80. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(87)81467-9. PMID 3030810.
- Shull MM, Lingrel JB (June 1987). "Multiple genes encode the human Na+,K+-ATPase catalytic subunit". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 84 (12): 4039–43. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.12.4039. PMC 305017. PMID 3035563.
- Sverdlov ED, Monastyrskaya GS, Broude NE, Allikmets RL, Melkov AM, Malyshev IV, Dulobova IE, Petrukhin KE (June 1987). "The family of human Na+,K+-ATPase genes. No less than five genes and/or pseudogenes related to the alpha-subunit". FEBS Letters. 217 (2): 275–8. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(87)80677-4. PMID 3036582.
- Ruiz A, Bhat SP, Bok D (April 1995). "Characterization and quantification of full-length and truncated Na,K-ATPase alpha 1 and beta 1 RNA transcripts expressed in human retinal pigment epithelium". Gene. 155 (2): 179–84. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)00812-7. PMID 7536695.
- Hundal HS, Maxwell DL, Ahmed A, Darakhshan F, Mitsumoto Y, Klip A (1995). "Subcellular distribution and immunocytochemical localization of Na,K-ATPase subunit isoforms in human skeletal muscle". Molecular Membrane Biology. 11 (4): 255–62. doi:10.3109/09687689409160435. PMID 7711835.
- Feschenko MS, Sweadner KJ (June 1995). "Structural basis for species-specific differences in the phosphorylation of Na,K-ATPase by protein kinase C". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 270 (23): 14072–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.23.14072. PMID 7775468.
- Ruiz-Opazo N, Barany F, Hirayama K, Herrera VL (September 1994). "Confirmation of mutant alpha 1 Na,K-ATPase gene and transcript in Dahl salt-sensitive/JR rats". Hypertension. 24 (3): 260–70. doi:10.1161/01.hyp.24.3.260. PMID 8082931.
- Zahler R, Gilmore-Hebert M, Baldwin JC, Franco K, Benz EJ (July 1993). "Expression of alpha isoforms of the Na,K-ATPase in human heart". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1149 (2): 189–94. doi:10.1016/0005-2736(93)90200-J. PMID 8391840.
- Wang J, Schwinger RH, Frank K, Müller-Ehmsen J, Martin-Vasallo P, Pressley TA, Xiang A, Erdmann E, McDonough AA (October 1996). "Regional expression of sodium pump subunits isoforms and Na+-Ca++ exchanger in the human heart". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 98 (7): 1650–8. doi:10.1172/JCI118960. PMC 507599. PMID 8833915.