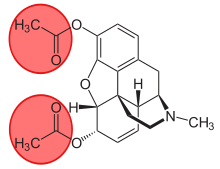
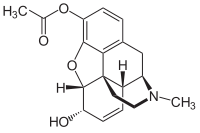
3-Monoacetylmorphine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 3-Acetylmorphine, O(3)-monoacetylmorphine |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard |
100.208.392 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H21NO4 |
| Molar mass | 327.1471 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
3-Monoacetylmorphine (3-MAM) or 3-acetylmorphine is a less active metabolite of heroin (diacetylmorphine), the other two being morphine and more active 6-monoacetylmorphine (6-MAM).
Because of the acetyl-group in 3-position, 3-MAM has relatively weak affinity to μ-opioid receptors.
As 3-O-acetylmorphine-6-O-sulfate (C19H23NO7S), where 6-OH is changed to 6-O-SO3, it can act as a potent, centrally acting morphine derivative and has important analgesic properties.[1][2][3]
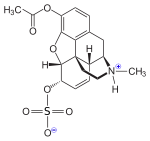
3-MAM-6-Sulfate (M3A6S)
References
- ↑ Houdi, Abdulghani A.; Kottayil, Santosh; Crooks, Peter A.; Butterfield, D.Alan (1996). "3-O-Acetylmorphine-6-O-sulfate: A potent, centrally acting morphine derivative". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 53: 665–671. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(95)02067-5.
- ↑ 3-O-Acetylmorphine-6-O-sulfate
- ↑ Dihydromorphine-6-O-sulfate
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.