Tingloy, Batangas
Tingloy, officially the Municipality of Tingloy (Tagalog: Bayan ng Tingloy), is a 5th class municipality in the province of Batangas, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 17,919 people.[5]
Tingloy | |
|---|---|
| Municipality of Tingloy | |
 | |
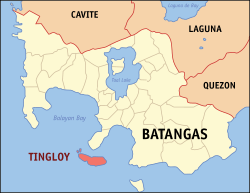 Map of Batangas with Tingloy highlighted | |
OpenStreetMap 
| |
.svg.png) Tingloy Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 13°39′N 120°52′E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Calabarzon (Region IV-A) |
| Province | Batangas |
| District | 2nd District |
| Founded | June 17, 1955 [1] |
| Barangays | 15 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Bayan |
| • Mayor | Lauro F. Alvarez |
| • Vice Mayor | Rolando D. Masangkay |
| • Congressman | Raneo E. Abu |
| • Electorate | 11,954 voters (2019) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 33.07 km2 (12.77 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 33.1 m (108.6 ft) |
| Population (2015 census)[5] | |
| • Total | 17,919 |
| • Density | 540/km2 (1,400/sq mi) |
| • Households | 4,054 |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 5th municipal income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 26.22% (2015)[6] |
| • Revenue (₱) | 52,654,842.25 (2016) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 4203 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)43 |
| Climate type | tropical monsoon climate |
| Native languages | Tagalog |
The municipality comprises Maricaban Island, Caban Island, and other minor islets, all just south of the Calumpang Peninsula. Visitors to its beaches and diving facilities are a source of income.
History
The name "Tingloy" was, according to legend, derived from a plant of almost the same name, "tinghoy", which is no longer found in abundance on the island.
The first people to inhabit the island almost a century ago came from Taal and Bauan, presumably to escape the brutalities perpetrated by the Spanish "conquistadors". They came in family groups and finding the place a haven, settled down in definite areas later forming the various barrios now comprising the created political subdivision. It is said that the former barrio of Tingloy was founded by Jose Martinez, a Taaleño.[7]
At several times the island was placed under the jurisdiction of different towns. The island was originally part of the town of San Luis. In 1917, it was placed under the jurisdiction of Bauan, only to be separated from it a year later when the municipality of Mabini was formed. In 1921, it was again placed under the jurisdiction of Bauan.
During the Spanish regime, people were educated at home learning to read the "Cartillas" and the "Caton" "Christiana". During American occupation schools were established. Ireneo Martinez together with Flaviano Gamben, initiated a movement for a model schoolhouse for the former barrio of Tingloy. This movement became a success when a model schoolhouse was constructed in the present poblacion of the Municipality of Tingloy sometime in 1921.[7]
During the second Regular Session of the third Congress of the Republic of the Philippines, the barrios of Tingloy, Maricaban, Papaya, Pisa, Gamao, and Talahib were separated from the Municipality of Bauan and constituted into the newly created municipality of Tingloy.[8] President Ramon Magsaysay, on June 17, 1955, appointed the first municipal Officials headed by Ramon De Claro as Mayor.
Geography
According to the Philippine Statistics Authority, the municipality has a land area of 33.07 square kilometres (12.77 sq mi) [3] constituting 1.06% of the 3,119.75-square-kilometre- (1,204.54 sq mi) total area of Batangas.
Just off the southwest coast of the Batangas mainland, about two nautical miles (3.7 kilometres) south, lies the radish-shaped island of Maricaban. It has a land area of about 14 square miles (36 square kilometres) of rugged hills and sloping mountains with occasional lowland plains and valleys.
Barangays
Tingloy is politically subdivided into 15 barangays.[9]
| PSGC | Barangay | Population | ±% p.a. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015[5] | 2010[10] | |||||
| 041033001 | Corona | 4.8% | 861 | 870 | −0.20% | |
| 041033003 | Gamao | 5.9% | 1,062 | 1,039 | 0.42% | |
| 041033004 | Makawayan | 5.5% | 977 | 982 | −0.10% | |
| 041033005 | Marikaban | 6.8% | 1,221 | 1,112 | 1.80% | |
| 041033006 | Papaya | 9.7% | 1,747 | 1,732 | 0.16% | |
| 041033007 | Pisa | 6.6% | 1,181 | 965 | 3.92% | |
| 041033008 | Barangay 13 (Poblacion 1) | 4.9% | 876 | 794 | 1.89% | |
| 041033009 | Barangay 14 (Poblacion 2) | 4.9% | 886 | 812 | 1.67% | |
| 041033010 | Barangay 15 (Poblacion 3) | 4.8% | 867 | 722 | 3.55% | |
| 041033011 | San Isidro | 9.4% | 1,686 | 1,459 | 2.79% | |
| 041033012 | San Jose | 8.0% | 1,428 | 1,197 | 3.42% | |
| 041033013 | San Juan | 10.7% | 1,916 | 1,821 | 0.97% | |
| 041033014 | San Pedro | 2.7% | 477 | 527 | −1.88% | |
| 041033015 | Santo Tomas | 9.3% | 1,673 | 1,677 | −0.05% | |
| 041033016 | Talahib | 5.9% | 1,061 | 1,161 | −1.70% | |
| Total | 17,919 | 16,870 | 1.16% | |||
Climate
| Climate data for Tingloy, Batangas | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 28 (82) |
29 (84) |
30 (86) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
28 (82) |
29 (85) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 22 (72) |
21 (70) |
22 (72) |
23 (73) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
22 (72) |
24 (74) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 48 (1.9) |
32 (1.3) |
41 (1.6) |
54 (2.1) |
257 (10.1) |
410 (16.1) |
466 (18.3) |
422 (16.6) |
429 (16.9) |
300 (11.8) |
137 (5.4) |
92 (3.6) |
2,688 (105.7) |
| Average rainy days | 10.8 | 8.0 | 9.8 | 11.7 | 23.1 | 27.5 | 29.2 | 28.7 | 28.7 | 25.5 | 18.2 | 12.8 | 234 |
| Source: Meteoblue [11] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Population census of Tingloy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[5][10][12][13] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In the 2015 census, Tingloy had a population of 17,919.[5] The population density was 540 inhabitants per square kilometre (1,400/sq mi).
Attractions


- Masasa Beach (Barangay San Juan) is one of the most visited beaches of the place, and is known for its white sand and beautiful sunset. It is located in the other side of the Island which can is accessible by foot or tricycle.
- Mag-Asawang Bato is one of the two peaks of the island, and this is the most visited peak by mountaineers and nature enthusiasts, where a 360° view of the whole island can be seen.
- Isla Sombrero (Sombrero Island) is a small uninhabited island located at the eastern tip of Maricaban. It can be reached through a medium-sized motor-boat or banka, and is one of the most visited beach attractions in the island.
- Batalang-Bato (Pulang Buli) is a Fish Sanctuary between Barangay Santo Tomas and Barangay Talahib. For research diving and snorkeling, permission is needed from the BBMC and the barangay councils of Santo Tomas and Talahib.
- Caban Island is also considered as one of the tourist spots because of its white sand and scattered beaches surrounding the island. Among this is Mapating Beach, Layag Layag Point, Caban Island Beach, Fortales Beach and Bahay Kambing.
- Diving is a major attraction because of different dive spots situated in the area.
References
- "Republic Act No. 1344 : REPUBLIC ACTS - PHILIPPINE LAWS STATUTES and CODES - CHANROBLES VIRTUAL LAW LIBRARY".
- "Municipality". Quezon City, Philippines: Department of the Interior and Local Government. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- "Province: Batangas". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- "Tingloy, Batangas Profile". PhilAtlas.com. Retrieved 15 June 2020.
- Census of Population (2015). "Region IV-A (Calabarzon)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- "PSA releases the 2015 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Quezon City, Philippines. Retrieved 1 January 2020.
- "TINGLOY TOWN", TINGLOY TOWN FIESTA SOUVENIR PROGRAM, 1979-10-18
- "Republic Act No. 1344 - An Act to Create the Municipality of Tingloy in the Province of Batangas". Chan Robles Virtual Law Library. 17 June 1955. Retrieved 11 December 2016.
- "Municipal: Tingloy, Batangas". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region IV-A (Calabarzon)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- "Tingloy: Average Temperatures and Rainfall". Meteoblue. Retrieved 5 May 2020.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region IV-A (Calabarzon)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- "Province of Batangas". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tingloy, Batangas. |