Sicani
The Sicani (Greek Σικανοί Sikanoi) or Sicanians were one of three ancient peoples of Sicily present at the time of Phoenician and Greek colonization. The Sicani dwelt east of the Elymians and west of the Sicels, having, according to Diodorus Siculus,[2] the boundary with the last in the ancient Himera river (Salso) after a series of battles between these tribes.
| Sicanian | |
|---|---|
| Sicana | |
| Region | Sicily |
| Extinct | approximately 300 BCE |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | sxc |
sxc | |
| Glottolog | sica1234[1] |
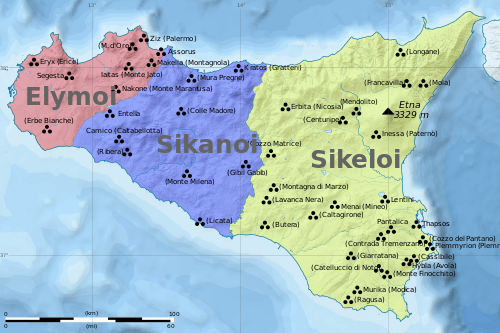 Approximate locations of the Sicani and their neighbors, the Elymians and the Sicels, in Sicily around 11th century BC (before the arrival of the Phoenicians and the Greeks). | |
 Tribes of Hellenic Sicily | |
History
The Sicani are the oldest inhabitants of Sicily with a recorded name. In the 5th century BCE, the Greek historian Thucydides,[3] claims that the Sicani originated on the Iberian Peninsula, from around a river they called "Sicanus" and had migrated to Sicily following an invasion by the Ligurians.[4][5] (The name Sicanus has been linked to the modern river known in Spanish as the Júcar .) Thucydides' source is unknown, although he often draws on the Sicilian historian Antiochus of Syracuse.[6] Conversely, Timaeus of Tauromenium (writing c. 300 BCE) considers the Sicani to be indigenous to Sicily.[7] A third theory, put forward by some modern scholars, suggests that the Sicani were Illyrian emigrés, who gained control of areas previously inhabited by native tribes.[8] Archaeological research suggests that the Sicani were influenced at an early stage by the Mycenaeans (prior to the Greek colonisation of Sicily).[9]
It is generally agreed by scholars that the Sicani preceded other inhabitants of Sicily in prehistory, namely the Elymians and Sicels. The Elymians are thought to be the next recorded people to settle Sicily, perhaps from the Aegean, Anatolia, or Liguria. They settled in the north-west corner of the island, forcing the Sicanians to move across eastward. The Sicels were the next to arrive, from mainland Italy, and settled in the east. The arrival of the Sicels is thought to have occurred during the thirteenth or eleventh century BCE. The Sicanians area after this became limited to the south-western part of the island with settlements in the area of Gela and Agrigentum.[10]
The Sicani enter the historical record with the Phoenicians, who established colonies during the 11th century BCE – preceding the Greeks, who founded the colony of Syracuse. While many other Greek colonies were established around the island, by 734 BCE Syracuse had become the largest city in the Greek-speaking world. The Sicani were gradually absorbed by these colonizing peoples. They disappeared as a distinct people following the annexation of Sicily by the Roman Empire.
Life Expectancy
In 2012 the article, “Centenarians and diet: what they eat in the Western part of Sicily,” written by Sonya Vasto, Claudia Rizzo and Calogero Caruso, was published. They reported that in the Sicani Mountain zone there were more centenarians with respect to the Italian average. In fact, in five villages - namely Giuliana, Bisacquino, Castronovo, Chiusa Scalafani and Prizzi - there were 19 people aged 100 to 107 years from a total population of 18,328 inhabitants. This represented a four-fold increase in Italy’s average life expectancy. The report stated that the main reason for this is their Mediterranean diet, characterized by a high intake of monounsaturated fat, plant proteins, whole grains (fish is not always present), moderate intake of alcohol, and low consumption of red meat, refined grains and sweets. Further, the consumption of large amount of olive oil and olives in meals dominates the Mediterranean cuisine.[11]
Herodotus and King Minos
Minos, according to tradition, went to Sicania, or Sicily, as it is now called, in search of Daedalus, and there perished by a violent death.[12]
Language
A few short inscriptions using the Greek alphabet have been found in the extinct Sicanian language.[13] Except for names, they have not been translated, and the language is unclassified due to lack of data.[14]
See also
- Ancient peoples of Italy
- Prehistoric Italy
References
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Sicana". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- Diod., v.6.3-4
- Thucydides, His. VI,2,3,4.
- "Sicily: Encyclopedia II – Sicily – History". Experience Festival. 7 October 2007. Archived from the original on 31 December 2013.
- "Aapologetico de la literatura española contra los opiniones". Ensayo historico. 7 October 2007.
- "Greek Identity in the Western Mediterranean". 2004.
- As reported in Diodorus Siculus V,6,1-3.
- Fine, John (1985). The ancient Greeks: a critical history. Harvard University Press. p. 72. ISBN 0-674-03314-0.
- Fine, p.72
- Le Glay, Marcel (2009). A history of Rome. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4051-8327-7. OCLC 760889060.
- Vasto, Sonya; Rizzo, Claudia; Caruso, Calogero (23 April 2012). "Centenarians and diet: what they eat in the Western part of Sicily". Immunity & Ageing. 9 (1): 10. doi:10.1186/1742-4933-9-10. PMC 3412743. PMID 22524271.
- Herodotus, The History, George Rawlinson, trans., (New York: Dutton & Co., 1862
- The World's Writing Systems. 1996:301.
- 'Sicanian' at Linguist List