Provinces of Ecuador
Ecuador is divided into 24 provinces (Spanish: provincias, singular – provincia). The provinces of Ecuador and their capitals are:
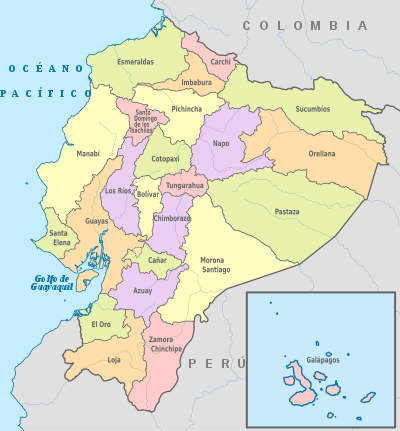
Provinces of Ecuador
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Ecuador |
|
|
Legislative
|
|
Judiciary
|
|
|
|
|
List
| Map key | Province | Capital | Population (2020)[1] | Area (km²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cuenca | 881,394 | 8,189 | |
| 2 | Guaranda | 209,933 | 4,148 | |
| 3 | Azogues | 281,396 | 3,669 | |
| 4 | Tulcán | 186,869 | 3,790 | |
| 5 | Riobamba | 524,004 | 5,999 | |
| 6 | Latacunga | 488,716 | 6,085 | |
| 7 | Machala | 715,751 | 5,879 | |
| 8 | Esmeraldas | 643,654 | 14,893 | |
| 9 | Puerto Baquerizo Moreno | 33,042 | 8,010 | |
| 10 | Guayaquil | 4,387,434 | 15,927 | |
| 11 | Ibarra | 476,257 | 4,611 | |
| 12 | Loja | 521,154 | 11,100 | |
| 13 | Babahoyo | 921,763 | 7,100 | |
| 14 | Portoviejo | 1,562,079 | 19,427 | |
| 15 | Macas | 196,535 | 23,875 | |
| 16 | Tena | 133,705 | 12,476 | |
| 17 | Puerto Francisco de Orellana | 161,338 | 21,691 | |
| 18 | Puyo | 114,202 | 29,068 | |
| 19 | Quito | 3,228,233 | 9,692 | |
| 20 | Santa Elena | 401,178 | 3,696 | |
| 21 | Santo Domingo de los Colorados | 458,580 | 4,180 | |
| 22 | Nueva Loja | 230,503 | 18,612 | |
| 23 | Ambato | 590,600 | 3,222 | |
| 24 | Zamora | 120,416 | 10,556 | |
| Total | Ecuador | Republic | 14,483,499 | 283,561 square kilometres (109,484 sq mi) |
1 Population as per the census carried out on 2010-11-28[2]
In addition, there were four areas that were non-delimited. These locations were:
- Las Golondrinas: In a referendum held on April 3, 2016, 56.9% of voters voted in favor of Las Golondrinas being incorporated into the Imbabura Province.[3]
- La Manga del Cura: In a referendum held on September 27, 2015, 64.2% of the voters voted in favor of La Manga del Cura being incorporated into the Manabí Province.[4]
- El Piedrero: incorporated into Guayas Province by the Presidential decree in 2017.[5]
- Matilde Esther: incorporated into Guayas Province by the Presidential decree in 2017[6]
Regions and planning areas
Regionalization, or zoning, is the union of two or more adjoining provinces in order to decentralize the administrative functions of the capital, Quito. In Ecuador, there are seven regions, or zones, each shaped by the following provinces:
- Region 1 (42,126 km2, or 16,265 mi2): Esmeraldas, Carchi, Imbabura, and Sucumbios. Administrative city: Ibarra
- Region 2 (43,498 km2, or 16,795 mi2): Pichincha, Napo, and Orellana. Administrative city: Tena
- Region 3 (44,710 km2, or 17,263 mi2): Chimborazo, Tungurahua, Pastaza, and Cotopaxi. Administrative city: Riobamba
- Region 4 (22,257 km2, or 8,594 mi2): Manabí and Santo Domingo de los Tsachilas. Administrative city: Ciudad Alfaro
- Region 5 (38,420 km2, or 14,834 mi2): Santa Elena, Guayas, Los Ríos, Galápagos, and Bolívar. Administrative city: Milagro
- Region 6 (38,237 km2, or 14,763 mi2): Cañar, Azuay, and Morona Santiago. Administrative city: Cuenca
- Region 7 (27,571 km2, or 10,645 mi2): El Oro, Loja, and Zamora Chinchipe. Administrative city: Loja
Quito and Guayaquil are Metropolitan Districts. Galápagos, despite being included within Region 5,[7] is also under a special unit.[8]
See also
References
- La población corresponde al .
- "Ecuador: Urban Places", https://www.citypopulation.de/php/ecuador,php, accessed 10 July 2017
- "Las Golondrinas le pertenece a Imbabura" (in Spanish). Retrieved 16 October 2016.
- "La Manga del Cura decide pertenecer a Manabí" (in Spanish). Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- "Con 7 decretos ejecutivos, Correa define los límites de Guayas". El Telégrafo (in Spanish). 20 May 2017. Retrieved 15 June 2019.
- "Con 7 decretos ejecutivos, Correa define los límites de Guayas". El Telégrafo (in Spanish). 20 May 2017. Retrieved 15 June 2019.
- "Niveles administrativos de planificación". Secretaría Nacional de Planificación y Desarrollo. Archived from the original on September 24, 2015. Retrieved September 24, 2015.
- "Región 4 – Santo Domingo, Manabí y Galápagos". Ministry of Production, Employment and Competitiveness Coordination. Archived from the original on November 27, 2011. Retrieved February 20, 2012.
External links
- "Provinces of Ecuador". Statoids.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
.svg.png)