Luxembourg (Belgium)
Luxembourg (French: Luxembourg; Dutch: ![]()
Province of Luxembourg Luxemburg (Dutch, German) | |
|---|---|
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 49.92°N 5.42°E | |
| Country | |
| Region | |
| Capital (and largest city) | Arlon |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Olivier Schmitz |
| Area | |
| • Total | 4,459 km2 (1,722 sq mi) |
| Population (1 January 2019)[2] | |
| • Total | 284,638 |
| • Density | 64/km2 (170/sq mi) |
| HDI (2017) | 0.887[3] very high · 8th |
| Website | www |
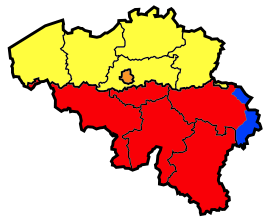
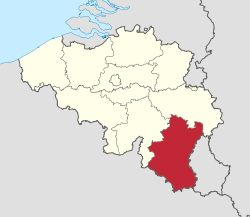
It has an area of 4,459 km2 (1,722 sq mi), making it the largest Belgian province. With around 285,000 residents, it is also the least populated province, with a density of 64/km2 (170/sq mi), making it a relatively sparsely settled part of a very densely populated region.
It is significantly larger (70%), but much less populous than the neighbouring Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. About eighty percent of the province is part of the densely wooded Ardennes region. The southernmost region of the province is called Gaume or Belgian Lorraine (main city: Virton).
The Arelerland or Arlon region (in red on the map of arrondissements, below) bordering the neighbouring Grand-Duchy of Luxembourg has the particularity that many of its residents have historically spoken Luxembourgish, a language closely related to German, rather than the French or Walloon spoken elsewhere in the province.
The province was separated from the neighbouring Luxembourg by the Third Partition of Luxembourg, de jure in 1830–31 by the Conference of London dealing with the consequences of the Belgian Revolution of 1830, de facto in 1839, after William I, King of the Netherlands and Grand-Duke of Luxembourg, agreed to its decisions and thus the province was given to the newly created Kingdom of Belgium.
Subdivisions
-fr.png)
Luxembourg province is divided into five administrative districts (French: arrondissements) containing a total of 44 municipalities (French: communes).
| Map no. | Municipality | Arrondissement |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Arlon | Arlon |
| 2 | Attert | Arlon |
| 3 | Aubange | Arlon |
| 4 | Bastogne | Bastogne |
| 5 | Bertogne | Bastogne |
| 6 | Bertrix | Neufchâteau |
| 7 | Bouillon | Neufchâteau |
| 8 | Chiny | Virton |
| 9 | Daverdisse | Neufchâteau |
| 10 | Durbuy | Marche-en-Famenne |
| 11 | Érezée | Marche-en-Famenne |
| 12 | Étalle | Virton |
| 13 | Fauvillers | Bastogne |
| 14 | Florenville | Virton |
| 15 | Gouvy | Bastogne |
| 16 | Habay | Virton |
| 17 | Herbeumont | Neufchâteau |
| 18 | Hotton | Marche-en-Famenne |
| 19 | Houffalize | Bastogne |
| 20 | La Roche-en-Ardenne | Marche-en-Famenne |
| 21 | Léglise | Neufchâteau |
| 22 | Libin | Neufchâteau |
| 23 | Libramont-Chevigny | Neufchâteau |
| 24 | Manhay | Marche-en-Famenne |
| 25 | Marche-en-Famenne | Marche-en-Famenne |
| 26 | Martelange | Arlon |
| 27 | Meix-devant-Virton | Virton |
| 28 | Messancy | Arlon |
| 29 | Musson | Virton |
| 30 | Nassogne | Marche-en-Famenne |
| 31 | Neufchâteau | Neufchâteau |
| 32 | Paliseul | Neufchâteau |
| 33 | Rendeux | Marche-en-Famenne |
| 34 | Rouvroy | Virton |
| 35 | Sainte-Ode | Bastogne |
| 36 | Saint-Hubert | Neufchâteau |
| 37 | Saint-Léger | Virton |
| 38 | Tellin | Neufchâteau |
| 39 | Tenneville | Marche-en-Famenne |
| 40 | Tintigny | Virton |
| 41 | Vaux-sur-Sûre | Bastogne |
| 42 | Vielsalm | Bastogne |
| 43 | Virton | Virton |
| 44 | Wellin | Neufchâteau |
Economy
The Gross domestic product (GDP) of the province was 7.0 billion € in 2018, accounting for 1.5% of Belgiums economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was 21,800 € or 72% of the EU27 average in the same year. Luxembourg was the province with the lowest GDP per capita.[6]
See also
References
- https://bestat.statbel.fgov.be/bestat/crosstable.xhtml?view=90c1e218-dc4f-4827-824d-9b25abfefe59
- https://statbel.fgov.be/nl/themas/bevolking/structuur-van-de-bevolking
- "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 2018-09-13.
- "ARDENNE / BELGIAN LUXEMBOURG - Find 2018 Exhibitors - WTM London". london.wtm.com.
- "The Improbable Ales of Belgian Luxembourg". DRAFT. 18 August 2016.
- "Regional GDP per capita ranged from 30% to 263% of the EU average in 2018". Eurostat.
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Luxembourg (Belgium). |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Luxembourg (province). |