Khanate
A khaganate or khanate was a political entity ruled by a khan, khagan, khatun, or khanum. This political entity is typical for people from the Eurasian Steppe and it can be equivalent to tribal chiefdom, principality, kingdom or empire.
Mongol khanates
After Genghis Khan established appanages for his family in the Mongol Empire during his rule (1206–1227),[1] his sons, daughters,[2] and grandsons inherited separate sections of the empire. The Mongol Empire and Mongolian khanates that emerged from those appanages[3] are listed below. Furthermore, the proto-Mongols also established some khanates (or khaganates) such as the Rouran Khaganate.
- Khamag Mongol Khanate
- Keraite Khanate
- Mergid Khanate
- Naiman Khanate
- Tatar Khanate
- Qara Khitai
- Mongol Empire
- Northern Yuan dynasty, based in Mongolia
- Moghulistan
- Kara Del Khanate
The Oirats established the following khanates in the 17th century:
- Khoshut Khanate
- Kalmyk Khanate, established c.1630 by the Torghut branch of the Mongolian Oirats, settled along the lower Volga River (in modern Russia and Kazakhstan), 1630-1771
- Dzungar Khanate, formed in 1634, covering Xinjiang region of China, Kyrgyzstan, eastern Kazakhstan and western Mongolia; 2 December 1717–1720, also styled Protector of Tibet; 1755 tributary to the Manchu Qing dynasty, 1756 annexed and dissolved in 1758
Turkic khanates
- Second Turkic Khaganate
- Uyghur Khaganate
- Yenisei Kyrgyz Khaganate
- Karakhanids
- Khazar Khaganate
- Turgesh Khaganate
- Cumania
- Pechenegs

- Volga Bulgaria, predecessor to the modern Chuvash Republic and the Chuvash people.
- First Bulgarian Empire, which started as a Turko-Slavic state, also known as Danube Bulgaria (in contrast to Volga Bulgaria, as both were established by members of the same Bulgar clan), but later became fully Slavicized and a Tsardom.
Central Asian Turkic khanates
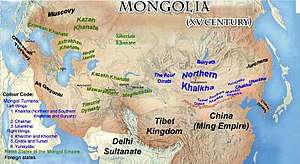
The Turco-Mongol residual states and domains by the 15th century
- Senior Juz
- Middle Juz
- Junior Juz

- Sibirean Khanate – source of the name Siberia, as the first significant conquest during Russia's great eastern expansion across the Urals
- Astrakhan Khanate

- Qasim Khanate (hence modern Kasimov) – named after its founder, a vassal of Moscovia/Russia
- Bukey Horde, Bokei or Buqei; also known as the Inner or Interior Horde – This state founded in 1801 by Sultan Bukey under Russian suzerainty, and restyled as the khanate of the Inner Horde in 1812. 5,000–7,500 families of Kazakhs from the Younger Kazakh Zhuz tribe settled between the Volga and Yaik (Ural) rivers. In 1845 the post of khan was abolished, and Russia took over the region.

- The khanate of Tuva near Outer Mongolia.
- Besh Tau El
- Khanate of Kashgaria – Kashgaria was founded in 1514 as part of Djagataide Khanate; in the 17th century it was divided into several minor khanates without importance, with real power going to the so-called Khwaja, Arabic Islamic religious leaders. It became the Yarkent Khanate which was annexed by the Dzungar Khanate in the Dzungar conquest of Altishahr in 1680.
- Kumul Khanate – a vassal state to Qing dynasty and Republic of China, abolished in 1930
- Kimek Khanate

_Autonomy.svg.png)
- Xueyantuo
- Karluk Khanate
- White Horde
- Oghuz Yabgu State
- West Turkic Khaganate
18th- to early-19th-century Khanates of the Caucasus in the Qajar Empire
- Ardabil Khanate
- Baku Khanate
- Derbent Khanate
- Erivan Khanate
- Ganja Khanate
- Javad Khanate
- Karabakh Khanate
- Karadagh khanate
- Khalkhal Khanate
- Khoy Khanate
- Lankaran Khanate
- Maku Khanate
- Maragheh Khanate
- Marand Khanate
- Nakhchivan Khanate
- Quba Khanate
- Sarab Khanate
- Shaki Khanate
- Shirvan Khanate
- Tabriz Khanate
- Urmia Khanate
- Zanjan Khanate
Manchus
Other khanates
- Pannonian Avar Khaganate


See also
- Rus Khaganate (not an actual Khanate but so named retroactively)
- Afsharid Dynasty
- Beg Khan
- Horde (term)
- Safavid Dynasty
- Timurid Dynasty
References
- Peter Jackson 2000, p. 12
- Jack Weatherford, The Secret History of the Mongol Queens: How the Daughters of Genghis Khan Rescued His Empire, Crown Publishing Group, 2011
- Thomas T. Allsen, "Sharing Out the Empire: Apportioned Lands under the Mongols", in Nomads in the Sedentary World, ed. Anatoly M. Khuzanov and André Wink (Richmond, Surrey: Curzon Press, 2001): 172–190
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.