History of coffee
The history of coffee dates back to the 15th century, and possibly earlier with a number of reports and legends surrounding its first use. The earliest substantiated evidence of either coffee drinking or knowledge of the coffee tree is from the early 15th century, in the Sufi monasteries of Yemen,[1] spreading soon to Mecca and Cairo. By the 16th century, it had reached the rest of the Middle East, South India (Karnataka), Persia, Turkey, the Horn of Africa, and northern Africa. Coffee then spread to the Balkans, Italy, and to the rest of Europe, as well as Southeast Asia and then to America,[2] despite bans imposed during the 15th century by religious leaders in Mecca and Cairo, and later by the Catholic Church.


_(part_of_a_service)_MET_DT5506.jpg)
Etymology
The word "coffee" entered the English language in 1582 via the Dutch koffie,[3] borrowed from the Ottoman Turkish kahve, in turn borrowed from the Arabic qahwah (قهوة).[4]
The Arabic word qahwah originally referred to a type of wine, whose etymology is given by Arab lexicographers as deriving from the verb qahā (قها, "to lack hunger") in reference to the drink's reputation as an appetite suppressant.[4][5] The word qahwah is sometimes alternatively traced to the Arabic quwwa ("power, energy"), or to Kaffa, a medieval kingdom in Ethiopia whence the plant was exported to Arabia.[4] These etymologies for qahwah have all been disputed, however. The name qahwah is not used for the berry or plant (the products of the region), which are known in Arabic as bunn and in Somali and Oromo as būn. Semitic languages had the root qhh, "dark color", which became a natural designation for the beverage. According to this analysis, the feminine form qahwah (also meaning "dark in color, dull(ing), dry, sour") was likely chosen to parallel the feminine khamr (خمر, "wine"), and originally meant "the dark one".[6]
First use
There are several legendary accounts of the origin of the drink itself. One account involves the Moroccan Sufi mystic Ghothul Akbar Nooruddin Abu al-Hasan al-Shadhili.[7] When traveling in Ethiopia, the legend goes, he observed birds of unusual vitality feeding on berries, and, upon trying the berries, experienced the same vitality. Other accounts attribute the discovery of coffee to Sheikh Abu al-Hasan ash-Shadhili's disciple, Omar. According to the ancient chronicle (preserved in the Abd-Al-Kadir manuscript), Omar, who was known for his ability to cure the sick through prayer, was once exiled from Mecca to a desert cave near Ousab. Starving, Omar chewed berries from nearby shrubbery, but found them to be bitter. He tried roasting the beans to improve the flavor, but they became hard. He then tried boiling them to soften the bean, which resulted in a fragrant brown liquid. Upon drinking the liquid Omar was revitalized and sustained for days. As stories of this "miracle drug" reached Mecca, Omar was asked to return and was made a saint.[8]
Studies of genetic diversity have been performed on Coffea arabica varieties, which were found to be of low diversity but with retention of some residual heterozygosity from ancestral materials, and closely related diploid species Coffea canephora and C. liberica;[9] however, no direct evidence has ever been found indicating where in Africa coffee grew or who among the natives might have used it as a stimulant or known about it there earlier than the seventeenth century.[1] The original domesticated coffee plant is said to have been from Harar, and the native population is thought to be derived from Ethiopia with distinct nearby populations in Sudan and Kenya.[10][11]
Coffee was primarily consumed in the Islamic world where it originated and was directly related to religious practices.[12] For example, coffee helped its consumers fast in the day and stay awake at night, during the Muslim celebration of Ramadan.[13]
It [coffee] became associated with Muhammad's birthday. Indeed, various legends ascribed coffee’s origins to Muhammad, who, through the archangel Gabriel, brought it to man to replace the wine which Islam forbade.
Another account involves a 9th-century Ethiopian goat-herder, Kaldi, who, noticing the energizing effects when his flock nibbled on the bright red berries of a certain bush, chewed on the fruit himself. His exhilaration prompted him to bring the berries to a monk in a nearby monastery. But the monk disapproved of their use and threw them into the fire, from which an enticing aroma billowed, causing other monks to come and investigate. The roasted beans were quickly raked from the embers, ground up, and dissolved in hot water, yielding the world's first cup of coffee. Since this story is not known to have appeared in writing before 1671, 800 years after it was supposed to have taken place, it is highly likely to be apocryphal.[1]
History
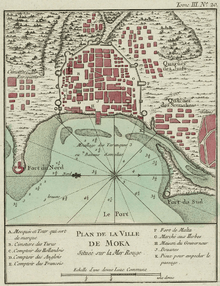

The earliest credible evidence of either coffee drinking or knowledge of the coffee tree appears in the late 15th century, by Sufi Imam Muhammad Ibn Said Al Dhabhani who is known to have imported goods from Ethiopia to Yemen.[1] Coffee was first exported out of Ethiopia to Yemen by Somali merchants from Berbera and Zeila, which was procured from Harar and the Abyssinian interior. According to Captain Haines, who was the colonial administrator of Aden (1839-1854), Mocha historically imported up to two-thirds of their coffee from Berbera-based merchants before the coffee trade of Mocha was captured by British-controlled Aden in the 19th century. Thereafter, much of the Ethiopian coffee was exported to Aden via Berbera.[15]
"Berbera not only supplies Aden with horned cattle and sheep to a very large extent, but the trade between Africa and Aden is steadily increasing greatly every year. In the article of coffee alone there is considerable export, and ' Berbera' coffee stands in the Bombay market now before Mocha. The coffee shipped at Berbera comes from far in the interior from Hurrar, Abyssinia, and Kaffa. It will be to the advantage of all that the trade should come to Aden through one port, and Berbera is the only place on the coast there that has a protected port, where vessels can lie in smooth water.”[16]
Sufis in Yemen used the beverage as an aid to concentration and as a kind of spiritual intoxication when they chanted the name of God.[17] Sufis used it to keep themselves alert during their nighttime devotions. A translation of Al-Jaziri's manuscript[18] traces the spread of coffee from Arabia Felix (present-day Yemen) northward to Mecca and Medina, and then to the larger cities of Cairo, Damascus, Baghdad, and Constantinople. By 1414, the plant was known in Mecca, and in the early 1500s was spreading to the Mameluke Sultanate of Egypt and North Africa from the Yemeni port of Mocha.[10][17] Associated with Sufism, myriad coffee houses grew up in Cairo (Egypt) around the religious University of the Azhar. These coffee houses also opened in Syria, especially in the cosmopolitan city of Aleppo,[17] and then in Istanbul, the capital of the Ottoman Empire, in 1554.[17] In 1511, it was forbidden for its stimulating effect by conservative, orthodox imams at a theological court in Mecca.[19] However, these bans were to be overturned in 1524 by an order of the Ottoman Turkish Sultan Suleiman I, with Grand Mufti Mehmet Ebussuud el-İmadi issuing a fatwa allowing the consumption of coffee.[20] In Cairo a similar ban was instituted in 1532, and the coffeehouses and warehouses containing coffee beans were sacked.[21] During the 16th century, it had already reached the rest of the Middle East, the Safavid Empire and the Ottoman Empire. From the Middle East, coffee drinking spread to Italy, then to the rest of Europe, and coffee plants were transported by the Dutch to the East Indies and to the Americas.[2]
Similarly, coffee was banned by the Ethiopian Orthodox Church some time before the 18th century.[22] However, in the second half of the 19th century, Ethiopian attitudes softened towards coffee drinking, and its consumption spread rapidly between 1880 and 1886; according to Richard Pankhurst, "this was largely due to Emperor Menelik, who himself drank it, and to Abuna Matewos who did much to dispel the belief of the clergy that it was a Muslim drink."[23]
The earliest mention of coffee noted by the literary coffee merchant Philippe Sylvestre Dufour[24] is a reference to bunchum in the works of the 10th century CE Persian physician Muhammad ibn Zakariya al-Razi, known as Rhazes in the West,[25] but more definite information on the preparation of a beverage from the roasted coffee berries dates from several centuries later. One of the most important of the early writers on coffee was Abd al-Qadir al-Jaziri, who in 1587 compiled a work tracing the history and legal controversies of coffee entitled Umdat al safwa fi hill al-qahwa عمدة الصفوة في حل القهوة.[19][26] He reported that one Sheikh, Jamal-al-Din al-Dhabhani (d. 1470), mufti of Aden, was the first to adopt the use of coffee (circa 1454).
He found that among its properties was that it drove away fatigue and lethargy, and brought to the body a certain sprightliness and vigour.[1]
Europe

Coffee was first introduced to Europe on the island of Malta in the 16th century. It was introduced there through slavery. Turkish Muslim slaves had been imprisoned by the Knights of St John in 1565—the year of the Great Siege of Malta, and they used to make their traditional beverage. Domenico Magri mentioned in his work Virtu del Kafé, "Turks, most skilful makers of this concoction." Also the German traveller Gustav Sommerfeldt in 1663 wrote "the ability and industriousness with which the Turkish prisoners earn some money, especially by preparing coffee, a powder resembling snuff tobacco, with water and sugar." Coffee was a popular beverage in Maltese high society—many coffee shops opened.[27]
Coffee was also noted in Aleppo by the German physician botanist Leonhard Rauwolf, the first European to mention it, as chaube, in 1573; Rauwolf was closely followed by descriptions from other European travellers.[28]
The vibrant trade between the Republic of Venice and the people of North Africa, Egypt, and the East brought a large variety of African goods, including coffee, to this leading European port. Venetian merchants introduced coffee-drinking to the wealthy in Venice, charging them heavily for the beverage.[29] In this way, coffee was introduced to the mainland of Europe. In 1591 Venetian botanist-physician Prospero Alpini became the first to publish a description of the coffee plant in Europe.[30] The first European coffee house apart from those in the Ottoman Empire and in Malta was opened in Venice in 1645.[2]
Austria
The first coffeehouse in Austria opened in Vienna in 1683 after the Battle of Vienna, by using supplies from the spoils obtained after defeating the Turks. The officer who received the coffee beans, Jerzy Franciszek Kulczycki, a Polish military officer of Ukrainian origin, opened the coffee house and helped popularize the custom of adding sugar and milk to the coffee.[31] Melange is the typical Viennese coffee, which comes mixed with hot foamed milk and a glass of water.
England

According to Leonhard Rauwolf's 1583 account, coffee became available in England no later than the 16th century, largely through the efforts of the Levant Company.[32] The first coffeehouse in England was opened in St. Michael's Alley in Cornhill, London. The proprietor was Pasqua Rosée, the servant of Daniel Edwards, a trader in Turkish goods. Edwards imported the coffee and assisted Rosée in setting up the establishment. Coffee was also brought in through the British East India Company and the Dutch East India Company in the 17th century. Oxford's Queen's Lane Coffee House, established in 1654, is still in existence today. By 1675, there were more than 3,000 coffeehouses throughout England, but there were many disruptions in the progressive movement of coffeehouses between the 1660s and 1670s.[33] During the enlightenment, these early English coffee houses became gathering places used for deep religious and political discussions among the populace. This practice became so common, and potentially subversive, that Charles II made an attempt to crush coffee houses in 1675.[34][35][36][37]
The banning of women from coffeehouses was not universal, for example, women frequented them in Germany, but it appears to have been commonplace elsewhere in Europe, including in England.[38]
Many in this period believed coffee to have medicinal properties. Renowned and eminent physicians often recommended coffee for medicinal purposes and some prescribed it as a cure for nervous disorders.[39] A 1661 tract entitled "A character of coffee and coffee-houses", written by one "M.P.", lists some of these perceived benefits:
'Tis extolled for drying up the Crudities of the Stomack, and for expelling Fumes out of the Head. Excellent Berry! which can cleanse the English-man's Stomak of Flegm, and expel Giddinesse out of his Head.
This new commodity proved controversial among some subjects, however. For instance, the anonymous 1674 "Women's Petition Against Coffee" declared:
the Excessive Use of that Newfangled, Abominable, Heathenish Liquor called COFFEE ...has...Eunucht our Husbands, and Crippled our more kind Gallants, that they are become as Impotent, as Age.[40]
France
Antoine Galland (1646–1715) in his aforementioned translation described the Muslim association with coffee, tea and chocolate: "We are indebted to these great [Arab] physicians for introducing coffee to the modern world through their writings, as well as sugar, tea, and chocolate." Galland reported that he was informed by Mr. de la Croix, the interpreter of King Louis XIV of France, that coffee was brought to Paris by a certain Mr. Thevenot, who had travelled through the East. On his return to that city in 1657, Thevenot gave some of the beans to his friends, one of whom was de la Croix.
In 1669, Soleiman Agha, Ambassador from Sultan Mehmed IV, arrived in Paris with his entourage bringing with him a large quantity of coffee beans. Not only did they provide their French and European guests with coffee to drink, but they also donated some beans to the royal court. Between July 1669 and May 1670, the Ambassador managed to firmly establish the custom of drinking coffee among Parisians.
Germany
In Germany, coffeehouses were first established in North Sea ports, including Bremen (1673) and Hamburg (1677). Initially, this new beverage was written in the English form coffee, but during the 1700s the Germans gradually adopted the French word café, then slowly changed the spelling to Kaffee, which is the present word. In the 18th century the popularity of coffee gradually spread around the German lands, and was taken up by the ruling classes. Coffee was served at the court of the Great Elector, Frederick William of Brandenburg, as early as 1675, but Berlin's first public coffee house did not open until 1721.[41]

Composer Johann Sebastian Bach, who was cantor of St. Thomas Church, Leipzig, in 1723–50, conducted a musical ensemble at Café Zimmermann in that Saxon city. Sometime in 1732–35 he composed the secular "Coffee Cantata" Schweigt stille, plaudert nicht (BWV 211), in which a young woman, Lieschen, pleads with her disapproving father to accept her devotion to drinking coffee, then a newfangled fashion. The libretto includes such lines as:
Ei! wie schmeckt der Coffee süße,
Lieblicher als tausend Küsse,
Milder als Muskatenwein.
Coffee, Coffee muss ich haben,
Und wenn jemand mich will laben,
Ach, so schenkt mir Coffee ein!
(Oh! How sweet coffee does taste,
Better than a thousand kisses,
Milder than muscat wine.
Coffee, coffee, I've got to have it,
And if someone wants to perk me up, *
Oh, just give me a cup of coffee!)
Italy
In Italy, like in most of Europe, coffee arrived in the second half of the 16th century through the commercial routes of the Mediterranean Sea. In 1580 the Venetian botanist and physician Prospero Alpini imported coffee into the Republic of Venice from Egypt,[42] and soon coffee shops started opening one by one when coffee spread and became the drink of the intellectuals, of social gatherings, even of lovers as plates of chocolate and coffee were considered a romantic gift. By the year 1763 Venice alone accounted for more than 200 shops,[43] and the health benefits of the miraculous drink were celebrated by many. Some representatives of the Catholic Church opposed coffee at its first introduction in what today is Italy, believing it to be the "Devil's drink",[44] but Pope Clement VIII, after trying the aromatic drink himself, gave it his blessing, thus boosting further its commercial success and diffusion. In Turin, in 1933, Alfonso Bialetti invented the first moka pot by observing the lisciveuse,[45] a steam pot utilized at that time for laundry. In 1946 his son Renato started industrial production, selling millions of moka pots in one year, versus only 70000 sold by his father in the previous 10, making the coffee maker (as well as coffee) an icon of Italy in the world. Naples, albeit being known today as the city of coffee, has seen it later, probably through the ships coming in the ports of Sicily and Naples itself. Some date the neapolitan discovery of coffee back to 1614, when the composer, explorer and musicologist Pietro Della Valle sent news from the Holy Land, in his letters to the dear friend, physician, poet, Greek scholar and Mario Schipano and his gathering of intellectuals, of a drink (called kahve)[46] the Arab Muslims brewed in hot pots. Some believe coffee arrived in Naples earlier, from Salerno and its Schola Medica Salernitana, where the plant came to be used for its medicinal properties between the XIV and XV century. Celebrated by neapolitan art, literature, music and daily social life, coffee soon became a protagonist in Naples, where it was prepared with great care in the "cuccumella", the typical neapolitan filter coffee pot derived by the invention of the parisian Morize in 1819. Neapolitan artisans came in touch with it when brought, once again through the sea commercial routes, to the Port of Naples. An indication of the approach of neapolitans to coffee as a social drink, is the practice of the suspended coffee (the act of paying in advance for a coffee to be consumed by the next customer) invented there and defined by the neapolitan philosopher and writer Luciano De Crescenzo a coffee "given by an individual to mankind".[47]
Netherlands
The race among Europeans to obtain live coffee trees or beans was eventually won by the Dutch in 1616. Pieter van den Broecke, a Dutch merchant, obtained some of the closely guarded coffee bushes from Mocha, Yemen, in 1616. He took them back to Amsterdam and found a home for them in the Botanical gardens, where they began to thrive. This apparently minor event received little publicity, but was to have a major impact on the history of coffee.
The beans that van der Broecke acquired from Mocha forty years earlier adjusted well to conditions in the greenhouses at the Amsterdam Botanical Garden and produced numerous healthy Coffea arabica bushes. In 1658 the Dutch first used them to begin coffee cultivation in Ceylon (now Sri Lanka) and later in southern India. They abandoned this cultivation to focus on their Javanese plantations in order to avoid lowering the price by oversupply.
Within a few years, the Dutch colonies (Java in Asia, Suriname in the Americas) had become the main suppliers of coffee to Europe.
Poland
Coffee reached the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in the 17th century, primarily through merchants trading with the Ottomans.[48] The first coffee shops opened a century later.[49] Usage of coffee has grown since, though it was a luxury commodity during the communist era of the Polish People's Republic. Consumption of coffee has grown since the transformation of Poland into a democratic, capitalistic country in 1989, though it still remains lower per capita than in most West European countries.[50]
Americas
.jpg)
Gabriel de Clieu brought coffee seedlings to Martinique in the Caribbean in 1720. Those sprouts flourished and 50 years later there were 18,680 coffee trees in Martinique enabling the spread of coffee cultivation to Saint-Domingue (Haiti), Mexico and other islands of the Caribbean. The French territory of Saint-Domingue saw coffee cultivated starting in 1734, and by 1788 supplied half the world's coffee. Coffee had a major influence on the geography of Latin America.[51] The French colonial plantations relied heavily on African slave laborers. However, the dreadful conditions that the slaves worked in on coffee plantations were a factor in the soon-to-follow Haitian Revolution. The coffee industry never fully recovered there.[52]
Coffee also found its way to the Isle of Bourbon, now known as Réunion, in the Indian Ocean. The plant produced smaller beans and was deemed a different variety of arabica known as var. Bourbon. The Santos coffee of Brazil and the Oaxaca coffee of Mexico are the progeny of that Bourbon tree. Circa 1727, the King of Portugal sent Francisco de Melo Palheta to French Guiana to obtain coffee seeds to become a part of the coffee market. Francisco initially had difficulty obtaining these seeds, but he captivated the French Governor's wife and she sent him enough seeds and shoots to commence the coffee industry of Brazil. However, cultivation did not gather momentum until independence in 1822,[53] leading to the clearing of massive tracts of the Atlantic Forest, first from the vicinity of Rio and later São Paulo for coffee plantations.[54] In 1893, the coffee from Brazil was introduced into Kenya and Tanzania (Tanganyika), not far from its place of origin in Ethiopia, 600 years prior, ending its transcontinental journey.[55]
After the Boston Tea Party of 1773, large numbers of Americans switched to drinking coffee during the American Revolution because drinking tea had become unpatriotic.[56]
Cultivation was taken up by many countries in the latter half of the 19th century, and in almost all of them it involved the large-scale displacement and exploitation of indigenous people. Harsh conditions led to many uprisings, coups and bloody suppressions of peasants.[57] For example, Guatemala started producing coffee in the 1500s but lacked the manpower to harvest the coffee beans. As a result, the Guatemalan government forced indigenous people to work on the fields. This led to a strain in the indigenous and Guatemalan people's relationship that still exists today.[58][59] A notable exception is Costa Rica where a lack of ready labor prevented the formation of large farms. Smaller farms and more egalitarian conditions ameliorated unrest over the 19th and 20th centuries.
In the 20th century Latin American countries faced a possible economic collapse. Before World War II Europe was consuming large amounts of coffee. Once the war started Latin America lost 40% of its market and was on the verge of economic collapse. Coffee was and is a Latin American commodity. The United States saw this and talked with the Latin American countries and as a result the producers agreed on an equitable division of the U.S. market. The U.S. government monitored this agreement. For the period that this plan was followed the value of coffee doubled, which greatly benefited coffee producers and the Latin American countries.[60]
Brazil became the largest producer of coffee in the world by 1852 and it has held that status ever since. It dominated world production, exporting more coffee than the rest of the world combined, from 1850 to 1950. The period since 1950 saw the widening of the playing field due to the emergence of several other major producers, notably Colombia, Ivory Coast, Ethiopia, and, most recently, Vietnam, which overtook Colombia and became the second-largest producer in 1999 and reached 15% market share by 2011.[61]
Around the turn of the century an organization named Fair Trade[62] emerged. In the past 20 years Fair trade coffee has become very popular. The idea of fair trade is to pay the farmers more money, so the farmers can have better lives. Most fair Trade's farmers come from Latin America. There is controversy about the effectiveness of Fair Trade. The proponents argue that Fair Trade helps the farmer receive a larger salary which allows them to live better lives.[63] Opponents argue that Fair Trade does not keep records and therefore cannot be accountable.[64]
A recent change to the coffee market are lattes, Frappuccinos and other sugary coffee drinks. With the rise of lattes and Frappuccinos becoming more popular this has caused coffee houses to be able to use cheaper coffee beans in their coffee, which has hurt the Latin American countries' economy. The cheaper coffee beans are called Robusta and they contain more caffeine than the more expensive beans. The cheaper beans' higher caffeine content is also a factor in their popularity. These cheaper beans hurt the Latin American economy because the producers receive less money for the production of the cheaper beans than they do for the production of the higher quality beans. Since the producers get paid less, they are receiving a smaller income, which in turn hurts the economy of Latin America.[65]
Asia
India
Also see Coffee production in India

Coffee came to India well before the East India company, through an India Sufi saint named "Baba Budan".[66] The first record of coffee growing in India is following the introduction of coffee beans from Yemen by Baba Budan to the hills of Chikmagalur, Karnataka in 1670.[67] Since then coffee plantations have become established in the region, extending south to Kodagu.[66]
Coffee production in India is dominated in the hill tracts of South Indian states, with the state of Karnataka accounting 53% followed by Kerala 28% and Tamil Nadu 11% of production of 8,200 tonnes. Indian coffee is said to be the finest coffee grown in the shade rather than direct sunlight anywhere in the world.[68] There are approximately 250,000 coffee growers in India; 98% of them are small growers.[69] As of 2009, the production of coffee in India was only 4.5% of the total production in the world. Almost 80% of the country's coffee production is exported.[70] Of that which is exported, 70% is bound for Germany, Russian federation, Spain, Belgium, Slovenia, United States, Japan, Greece, Netherlands and France, and Italy accounts for 29% of the exports. Most of the export is shipped through the Suez Canal.[68]
Coffee is grown in three regions of India with Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu forming the traditional coffee growing region of South India, followed by the new areas developed in the non-traditional areas of Andhra Pradesh and Orissa in the eastern coast of the country and with a third region comprising the states of Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Tripura, Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh of Northeastern India, popularly known as "Seven Sister States of India".[71]
Indian coffee, grown mostly in southern India under monsoon rainfall conditions, is also termed as "Indian monsooned coffee". Its flavour is defined as: "The best Indian coffee reaches the flavour characteristics of Pacific coffees, but at its worst it is simply bland and uninspiring".[72] The two well known species of coffee grown are the Arabica and Robusta. The first variety that was introduced in the Baba Budan Giri hill ranges of Karnataka in the 17th century[73] was marketed over the years under the brand names of Kent and S.795. Coffee is sold by the name of "filter coffee" by small restaurants and small chains like MTR's, Narasu's, etc. Recently, larger coffee outlet chains like Coffee Day and Starbucks have been opening up in larger cities and towns.
Chikmagalur
Coffee is the cornerstone of Chikmagalur's economy. Chikmagalur is the birthplace of coffee in India, where the seed was first sown about 350 years ago. Coffee Board is the department located in Chikmagalur town that oversees the production and marketing of coffee cultivated in the district. Coffee is cultivated in Chikmagalur district in an area of around 85,465 hectares with Arabica being the dominant variety grown in upper hills and Robusta being the major variety in the low level hills. There are around 15000 coffee growers in this district with 96% of them being small growers with holdings of less than or equal to 4 hectares. The average production is 55,000 MT: 35,000 MT of Arabica and 20,000 MT of Robusta. The average productivity per hectare is 810 kg for Arabica and 1110 kg of Robusta, which are higher than the national average. Arabica is a species of coffee that is also known as the "coffee shrub of Arabia", "mountain coffee" or "arabica coffee". Coffea arabica is believed to be the first species of coffee to be cultivated, being grown in southwest Arabia for well over 1,000 years. It is considered to produce better coffee than the other major commercially grown coffee species, Coffea canephora (robusta). Arabica contains less caffeine than any other commercially cultivated species of coffee. Robusta is a species of coffee which has its origins in western Africa. It is grown mostly in Africa and Brazil, where it is often called Conillon. It is also grown in Southeast Asia where French colonists introduced it in the late 19th century. In recent years Vietnam, which only produces robusta, has surpassed Brazil, India, and Indonesia to become the world's single largest exporter. Approximately one third of the coffee produced in the world is robusta.
Japan
Coffee was introduced to Japan by the Dutch in the 17th century, but remained a curiosity until the lifting of trade restrictions in 1858. The first European-style coffeehouse opened in Tokyo in 1888, and closed four years later.[74] By the early 1930s there were over 30,000 coffeehouses across the country; availability in the wartime and immediate postwar period dropped to nearly zero, then rapidly increased as import barriers were removed. The introduction of freeze-dried instant coffee, canned coffee, and franchises such as Starbucks and Doutor Coffee in the late 20th century continued this trend, to the point that Japan is now one of the leading per capita coffee consumers in the world.[75]
see: Coffee in Japan
South Korea
Coffee's first notable Korean enthusiasts were 19th century emperors Sunjong and Gojong, who preferred to consume it after western-style banquets.[76] By the 1980s instant coffee and canned coffee had become fairly popular, with a more minor tradition of independently owned coffeehouses in larger cities; toward the end of the century the growth of franchises such as Caffe Bene and Starbucks brought about a greater demand for European-style coffee.[77]
Indonesia
Coffee was first introduced by the Dutch during colonization in the late 17th century. After several years coffee was planted on Indonesia Archipelago. Many coffee specialties are from the Indonesian Archipelago. The colloquial name for coffee, Java, comes from the time when most of Europe and America's coffee was grown in Java. Today Indonesia is one of the largest coffee producers in the world, mainly for export. However coffee is enjoyed in various ways around the archipelago like traditional "Kopi Ende" which is with ginger to fancy new ways.
Philippines
The Philippines is one of the few countries that produces the four varieties of commercially viable coffee: Arabica, Liberica (Barako), Excelsa and Robusta. Climatic and soil conditions in the Philippines – from the lowland to mountain regions – make the country suitable for all four varieties.
In the Philippines, coffee has a history as rich as its flavor. The first coffee tree was introduced in Lipa, Batangas in 1740 by a Spanish Franciscan friar. From there, coffee growing spread to other parts of Batangas like Ibaan, Lemery, San Jose, Taal, and Tanauan. Batangas owed much of its wealth to the coffee plantations in these areas and Lipa eventually became the coffee capital of the Philippines.
By the 1860s, Batangas was exporting coffee to America through San Francisco. When the Suez Canal was opened, a new market started in Europe as well. Seeing the success of the Batangeños, Cavite followed suit by growing the first coffee seedlings in 1876 in Amadeo. In spite of this, Lipa still reigned as the center for coffee production in the Philippines and Batangas barako was commanding five times the price of other Asian coffee beans. In 1880, the Philippines was the fourth largest exporter of coffee beans, and when the coffee rust hit Brazil, Africa, and Java, it became the only source of coffee beans worldwide.
The glory days of the Philippine coffee industry lasted until 1889 when coffee rust hit the Philippine shores. That, coupled with an insect infestation, destroyed virtually all the coffee trees in Batangas. Since Batangas was a major producer of coffee, this greatly affected national coffee production. In two years, coffee production was reduced to 1/6th its original amount. By then, Brazil had regained its position as the world's leading producer of coffee. A few of the surviving coffee seedlings were transferred from Batangas to Cavite, where they flourished. This was not the end of the Philippines' coffee growing days, but there was less area allotted to coffee because many farmers had shifted to other crops.
During the 1950s, the Philippine government, with the help of the Americans, brought in a more resistant variety of coffee. It was also then that instant coffee was being produced commercially, thus increasing the demand for beans. Because of favorable market conditions, many farmers went back to growing coffee in the 1960s. But the sudden proliferation of coffee farms resulted in a surplus of beans around the world, and for a while importation of coffee was banned in order to protect local coffee producers. When Brazil was hit by a frost in the 1970s, world market coffee prices soared. The Philippines became a member of the International Coffee Organization (ICO) in 1980.
Vietnam
Vietnam is one of the world's main coffee exporters (according to 2005 statistics). Arabica is the first imported coffee variety to Vietnam since 1857. The first is the trial planting in the northern provinces such as Ha Nam, Phu Ly, then expanding to provinces like Thanh Hoa, Nghe An, Ha Tinh. Then spread to the central provinces. Finally, coffee grows in the Central Highlands and it is recognized that the Central Highlands is a good place to grow coffee.
In 1908, French imported two coffee varieties - Robusta and Liberica. After a while, the French colonialists found that coffee arabica was not effective so it brought Congo coffee into the Central Highlands. Here, coffee trees grow very strongly. And the Central Highlands became the largest coffee growing area in the country, famous in the world, especially coffee "Buon Me Thuoc".
Coffee of Trung Nguyen is a No. 1 coffee brand in Vietnam and has exported to over 60 countries around the world. It was founded in 1996 Dang Le Nguyen Vu.
Production
The first step in Europeans' wresting the means of production was effected by Nicolaes Witsen, the enterprising burgomaster of Amsterdam and member of the governing board of the Dutch East India Company who urged Joan van Hoorn, the Dutch governor at Batavia that some coffee plants be obtained at the export port of Mocha in Yemen, the source of Europe's supply, and established in the Dutch East Indies;[78] the project of raising many plants from the seeds of the first shipment met with such success that the Dutch East India Company was able to supply Europe's demand with "Java coffee" by 1719.[79] Encouraged by their success, they soon had coffee plantations in Ceylon, Sumatra and other Sunda islands.[80] Coffee trees were soon grown under glass at the Hortus Botanicus of Leiden, whence slips were generously extended to other botanical gardens. Dutch representatives at the negotiations that led to the Treaty of Utrecht presented their French counterparts with a coffee plant, which was grown on at the Jardin du Roi, predecessor of the Jardin des Plantes, in Paris.
The introduction of coffee to the Americas was effected by Captain Gabriel des Clieux, who obtained cuttings from the reluctant botanist Antoine de Jussieu, who was loath to disfigure the king's coffee tree.[81] Clieux, when water rations dwindled during a difficult voyage, shared his portion with his precious plants and protected them from a Dutchman, perhaps an agent of the Provinces jealous of the Batavian trade.[82] Clieux nurtured the plants on his arrival in the West Indies, and established them in Guadeloupe and Saint-Domingue in addition to Martinique, where a blight had struck the cacao plantations, which were replaced by coffee plantations in a space of three years, is attributed to France through its colonization of many parts of the continent starting with the Martinique and the colonies of the West Indies where the first French coffee plantations were founded.
The first coffee plantation in Brazil occurred in 1727 when Lt. Col. Francisco de Melo Palheta smuggled seeds, still essentially from the germ plasm originally taken from Yemen to Batavia,[83] from French Guiana. By the 1800s, Brazil's harvests would turn coffee from an elite indulgence to a drink for the masses. Brazil, which like most other countries cultivates coffee as a commercial commodity, relied heavily on slave labor from Africa for the viability of the plantations until the abolition of slavery in 1888. The success of coffee in 17th-century Europe was paralleled with the spread of the habit of tobacco smoking all over the continent during the course of the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648).
For many decades in the 19th and early 20th centuries, Brazil was the biggest producer of coffee and a virtual monopolist in the trade. However, a policy of maintaining high prices soon opened opportunities to other nations, such as Venezuela, Colombia,[84] Guatemala, Nicaragua, Indonesia and Vietnam, now second only to Brazil as the major coffee producer in the world. Large-scale production in Vietnam began following normalization of trade relations with the US in 1995.[85] Nearly all of the coffee grown there is Robusta.[86]
Despite the origins of coffee cultivation in Ethiopia, that country produced only a small amount for export until the twentieth century, and much of that not from the south of the country but from the environs of Harar in the northeast. The Kingdom of Kaffa, home of the plant, was estimated to produce between 50,000 and 60,000 kilograms of coffee beans in the 1880s. Commercial production effectively began in 1907 with the founding of the inland port of Gambela. 100,000 kilograms of coffee was exported from Gambela in 1908, while in 1927–8 over 4 million kilograms passed through that port.[87] Coffee plantations were also developed in Arsi Province at the same time, and were eventually exported by means of the Addis Ababa – Djibouti Railway. While only 245,000 kilograms were freighted by the Railway, this amount jumped to 2,240,000 kilograms by 1922, surpassed exports of "Harari" coffee by 1925, and reached 9,260,000 kilograms in 1936.[88]
Australia is a minor coffee producer, with little product for export, but its coffee history goes back to 1880 when the first of 500 acres (2.0 km2) began to be developed in an area between northern New South Wales and Cooktown. Today there are several producers of Arabica coffee in Australia that use a mechanical harvesting system invented in 1981.[89]
See also
- Economics of coffee
- International Coffee Agreement
- Anacafé
- Federación Nacional de Cafeteros de Colombia
- National Coffee Association
- Specialty Coffee Association of America
- A History of the World in 6 Glasses, by Tom Standage: a review by blaqswans.org
- Dorothee Wierling: Coffee during the World War I, in: 1914-1918-online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War.
Footnotes
- Weinberg, Bennett Alan; Bealer, Bonnie K. (2001). The world of caffeine. Routledge. pp. 3–4. ISBN 978-0-415-92723-9.
- Meyers, Hannah (7 March 2005). "'Suave Molecules of Mocha' – Coffee, Chemistry, and Civilization". Archived from the original on 21 February 2007. Retrieved 3 February 2007.
- OED, s.v. "Coffee".
- Oxford English Dictionary, 1st ed. "coffee, n." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1891.
- قها. الباحث العربي (in Arabic). Retrieved 25 September 2011.
- Kaye, Alan S. (1986). "The etymology of 'coffee': The dark brew". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 106 (3): 557–558. doi:10.2307/602112. JSTOR 602112.
- "Discovery of Coffee". shazuli.com. Archived from the original on 16 January 2010. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- Ukers, William (1935). All About Coffee. New York: The Tea & Coffee Trade Journal Company. pp. 9–10.
- Steiger, L.; Nagal, C.; et al. (2002). "AFLP analysis of genetic diversity within and among Coffea arabica cultivars". Theoretical and Applied Genetics. 105 (2–3): 209–215. doi:10.1007/s00122-002-0939-8. PMID 12582521.
- John K. Francis. "Coffea arabica L. RUBIACEAE" (PDF). Factsheet of U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 August 2007. Retrieved 27 July 2007.
- Wild, Anthony (2003). "Coffee: A dark history". Basic Reference. USA: Fourth Estate. 28: 217–229. Retrieved 27 April 2012.
- Grigg, David (2002). "The worlds of tea and coffee: Patterns of consumption". GeoJournal. 57 (4): 283–294. doi:10.1023/b:gejo.0000007249.91153.c3. JSTOR 41147739.
- Topik, Steven (2009). Cultural Critique, No. 71, Drugs in Motion: Mind- and Body-Altering Substances in the World's Cultural Economy. Minnesota: University of Minnesota Press. pp. 88–89.
- Topik, Steven (2009). Cultural Critique, No. 71, Drugs in Motion: Mind- and Body-Altering Substances in the World's Cultural Economy. Minnesota: University of Minnesota Press. p. 89.
- R. J., Gavin (1975). Aden Under British Rule, 1839-1967. C. Hurst & Co. Publishers. p. 53.
- Precis of Papers Regarding Aden, pg. 166, 1838-1872
- "Coffee and qahwa: How a drink for Arab mystics went global". BBC News.
- Al-Jaziri's manuscript work is of considerable interest with regard to the history of coffee in Europe as well. A copy reached the French royal library, where it was translated in part by Antoine Galland as De l'origine et du progrès du café.
- "عمدة الصفوة في حل القهوة – resource for Arabic books". alwaraq.net.
- Schneider, Irene (2001). "Ebussuud". In Stolleis, Michael (ed.). Juristen: ein biographisches Lexikon; von der Antike bis zum 20. Jahrhundert (in German) (2nd ed.). München: Beck. p. 193. ISBN 3-406-45957-9.
- J. E. Hanauer (1907). "About Coffee". Folk-lore of the Holy Land. pp. 291 f.
[All] the coffee-houses [were] closed, and their keepers pelted with the sherds of their pots and cups. This was in 1524, but by an order of Selìm I., the decrees of the learned were reversed, the disturbances in Egypt quieted, the drinking of coffee declared perfectly orthodox
- Aregay, Merid W. (1988). "The Early History of Ethiopia's Coffee Trade and the Rise of Shawa". The Journal of African History. 29 (1, Special Issue in Honour of Roland Oliver): 20. doi:10.1017/s0021853700035969. JSTOR 182236.
- Richard Pankhurst, Economic History of Ethiopia (Addis Ababa: Haile Selassie I University, 1968), p. 198
- Dufour, Traitez nouveaux et curieux du café, du thé et du chocolat (Lyon, 1684, etc).
- In later editions Dufour casts doubt on the identity of Rhazes' bunchum, which is shared by Edward Forbes Robinson, The Early History of Coffee Houses in England (London, 1893), noted by Ukers 1922:
- The 19th-century orientalist Antoine Isaac Silvestre de Sacy edited the first two chapters of al-Jaziri's manuscript and included it in the second edition of his Chrestomathie Arabe (Paris, 1826, 3 vols.). Antoine Galland's De l'origine et du progrès du Café (1699) was recently reissued (Paris: Editions La Bibliothèque, 1992).
- "Maltese history through a sweet tooth". tenzo.fr. Retrieved 23 August 2016.
- William Harrison Ukers, All About Coffee :2.
- A Venetian merchant dying in 1575 had coffee-making equipment in his estate. https://www.bbc.co.uk/sounds/play/m000c4x1
- "De plantis Aegypti". Mumac. 1 March 2018. Retrieved 27 September 2019.
- "Jerzy Franciszek Kulczycki – the founder of the first café in Vienna". www.wilanow-palac.pl. Retrieved 27 September 2019.
- Wood, Alfred C (2013). A History of the Levant Company. Routledge. p. 203. ISBN 9781136237348.
- "History of Coffee". Nestlé Professional. Archived from the original on 1 August 2012. Retrieved 31 December 2009.
- Cowan, Brian William (2005). The Social Life of Coffee: The emergence of the British Coffee house. New Haven Conn: Yale University Press..
- Wild, Anthony. Coffee A Dark History. W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 500 Fifth Avenue, New York, N.Y. 10110.
- "The surprising history of London's lost coffee houses". The Daily Telegraph. 20 March 2012.
- Zappiah, Nat (2007). "Coffee Houses and Culture". Huntington Library Quarterly. 70 (4): 671–677. JSTOR 10.1525/hlq.2007.70.4.671.
- "Coffee History". Archived from the original on 15 September 2007. Retrieved 27 October 2007.
- Cowen, Brian (2005). The Social Life of Coffee: The Emergence of the British Coffeehouse. Connecticut: Yale University Press. p. 49.
- "The women's petition against coffee representing to publick consideration the grand inconveniences accruing to their sex from the excessive use of that drying, enfeebling liquor". Archived from the original on 10 August 2006. Retrieved 18 June 2006.
- "8. THE INTRODUCTION OF COFFEE INTO GERMANY". www.web-books.com. Retrieved 27 September 2019.
- Ukers, William Harrison (1935). All about Coffee. Library of Alexandria. ISBN 9781465523976.
- Orey, Cal (31 July 2012). The Healing Powers of Coffee: A Complete Guide to Nature's Surprising Superfood. Kensington Publishing Corp. ISBN 9780758279972.
- Ukers, William H. (18 October 2012). All about Coffee: A History of Coffee from the Classic Tribute to the World's Most Beloved Beverage. Simon and Schuster. ISBN 9781440556326.
- Morganti, Vittoria (12 February 2015). Volevo la torta di mele. Piccolo viaggio sentimentale a tavola: Piccolo viaggio sentimentale a tavola (in Italian). FrancoAngeli. ISBN 9788891720764.
- Bausilio, Giovanni (11 June 2018). Origini (in Italian). Key Editore. ISBN 9788827901380.
- Crescenzo, Luciano De (7 October 2010). Il caffè sospeso (in Italian). Edizioni Mondadori. ISBN 9788852014161.
- "Kawa w Polsce – historia i styl picia – Koneserzy.pl". www.koneserzy.pl. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 30 November 2015.
- "Otwarcie kawiarni Duvala w Warszawie – Muzeum Historii Polski". muzhp.pl. Retrieved 30 November 2015.
- "SPRZEDAŻ KAWY W POLSCE" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016.
- Rice, Robert A. (1999). "A Place Unbecoming: The Coffee Farm of Northern Latin America". Geographical Review. 89 (4): 554–579. doi:10.2307/216102. JSTOR 216102.
- Pendergrast, p. 16
- Pendergrast, p. 19
- Pendergrast, pp. 20–24
- Kenneth Davids, Coffee: a guide to buying, brewing, and enjoying, 2001, ISBN 0-312-24665-X, p. 13.
- (1) Adams, John (6 July 1774). "John Adams to Abigail Adams". The Adams Papers: Digital Editions: Adams Family Correspondence, Volume 1. Massachusetts Historical Society. Archived from the original on 26 February 2014. Retrieved 25 February 2014.
I believe I forgot to tell you one Anecdote: When I first came to this House it was late in the Afternoon, and I had ridden 35 miles at least. 'Madam' said I to Mrs. Huston, 'is it lawfull for a weary Traveller to refresh himself with a Dish of Tea provided it has been honestly smuggled, or paid no Duties?'
'No sir, said she, we have renounced all Tea in this Place. I cant make Tea, but I'le make you Coffee.' Accordingly I have drank Coffee every Afternoon since, and have borne it very well. Tea must be universally renounced. I must be weaned, and the sooner, the better.
(2) Stone, William L. (1867). "Continuation of Mrs. General Riedesel's Adventures". Mrs. General Riedesel: Letters and Journals relating to the War of Independence and the Capture of the Troops at Saratoga (Translated from the Original German). Albany: Joel Munsell. p. 147.She then became more gentle, and offered me bread and milk. I made tea for ourselves. The woman eyed us longingly, for the Americans love it very much; but they had resolved to drink it no longer, as the famous duty on the tea had occasioned the war.
At Google Books. Note: Fredricka Charlotte Riedesel was the wife of General Friedrich Adolf Riedesel, commander of all German and Indian troops in General John Burgoyne's Saratoga campaign and American prisoner of war during the American Revolution.
(3) Heiss, Mary Lou; Heiss, Robert .J (2007). "A History of Tea: The Boston Tea Party". The Story of Tea: A Cultural History and Drinking Guide. pp. 21–24. At Google Books.
(4) Zuraw, Lydia (24 April 2013). "How Coffee Influenced The Course of History". NPR. Archived from the original on 26 February 2014. Retrieved 25 February 2014.
(5) DeRupo, Joseph (3 July 2013). "American Revolution: Stars, Stripes—and Beans?". NCA News. National Coffee Association. Archived from the original on 26 February 2014. Retrieved 25 February 2014.
(6) Luttinger, Nina; Dicum, Gregory (2006). The coffee book: anatomy of an industry from crop to the last drop. The New Press. p. 33. At Google Books. - Pendergrast, pp. 33–34
- McCreery, David. "Coffee and Indigenous Labor in Guatemala". The Global Coffee Economy in Africa, Asia, and Latin America, 1500–1989: 192–208.
- Corntassel, Jeff; Holder, Cindy (2008). "Who's Sorry Now? Government Apologies, Truth Commissions, and Indigenous Self-Determination in Australia, Canada, Guatemala, and Peru". Human Rights Review. 9 (4): 465–489. doi:10.1007/s12142-008-0065-3.
- Williamson, W.F. (Fall 2017). "The Place of Coffee in Trade with Latin America". Journal of Marketing: 149–151.
- "UNCTAD – Coffee Production History". Archived from the original on 18 September 2015.
- "Fair Trade". International Trade Forum Magazine. No. 2. 2006.
- transfairusa. "Santiago's Story". Retrieved 28 November 2017.
- Griffiths, Peter. "Fairtrade is not fair". Youtube. Retrieved 28 November 2017.
- Scholer, Mortan (Fall 2017). "Bitter or Better Future for Coffee Farmers". International Trade Forum: 9–12.
- Wild, Anthony (10 April 1995). The East India Company Book of Coffee. Harper Collins. ISBN 0004127390.
- "BABA BUDAN GIRI". chickmagalur.nic.in. Archived from the original on 20 November 2010. Retrieved 27 November 2010.
- Yeboah, Salomey (8 March 2005). "Value Addition to Coffee in India". Cornell Education:Intag 602. Retrieved 5 October 2010.
- Lee, Hau Leung; Lee, Chung-Yee (2007). Building supply chain excellence in emerging economies. pp. 293–94. ISBN 0-387-38428-6.
- Illy, Andrea; Viani, Rinantonio (2005). Espresso coffee: the science of quality. Academic Press. p. 47. ISBN 0-12-370371-9.
- "Coffee Regions – India". Indian Coffee Organization. Archived from the original on 25 December 2008. Retrieved 6 October 2010.
- "Indian Coffee". Coffee Research Organization. Archived from the original on 28 December 2010. Retrieved 6 October 2010.
- Robertson, Carol (2010). The Little Book of Coffee Law. American Bar Association. pp. 77–79. ISBN 1-60442-985-2. Retrieved 29 November 2010.
- "Brief history of Coffee in Japan". d-cage.
- "Countries Compared by Lifestyle > Food and drink > Coffee > Consumption. International Statistics at NationMaster.com". nationmaster.com.
- "The Korean Coffee Myth". The Marmot's Hole. Archived from the original on 16 January 2013.
- Lee, Hyo-sik (11 April 2012). "Why do coffee shops keep popping up?". Korea Times. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- William Law, The History of Coffee, including a chapter on chicory (London) 1850:14, on the authority of Hermann Boerhaave, director of the botanical garden at Leiden.
- E. M. Jacobs, Merchant in Asia: the trade of the Dutch East India Company during the "Coffee from Mocha and the highlands of Batavia" :260ff describes the introduction of coffee plantations in detail
- Henry Mills Alden, "A Cup of coffee", Harper's new monthly magazine 44 (1872:241).
- Toussaint-Samat 2008:530.
- The story appeared in J.J.C. Goube, Histoire du duché de Normandie (1815, vol. III:191), of which a translated excerpt was contributed to The Gentleman's Magazine (February 1840:136) "Generosity of M. Desclieux – The Coffee-tree at Martinique". The date of this event is variously reported: in Goube it is 1726.
- "Des Clieux's cutting was the ancestor of all the coffee trees of Martinique, the West Indies, Brazil and Colombia, and some of them went back across the Atlantic to become a source of income to the African colonies that have now gained their independence" (Toussaint-Samat 2008:531).
- Palacios, Marco (2002). Coffee in Colombia, 1850–1970: An Economic, Social and Political History. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-52859-3.
- Vietnam: Silent Global Coffee Power by Alex Scofield
- International Coffee Organization. Total Production of Exporting Countries: Crop Years 2000/01 to 2005/06. "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 6 July 2010. Retrieved 13 January 2010.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link). Retrieved 8 December 2006.
- Pankhurst, Economic History, p. 202
- Pankhurst, Economic History, p. 203
- "Australian Coffee History". Retrieved 21 March 2011.
Sources
- "The Blessed Bean – history of coffee". Archived from the original on 8 November 2006. Retrieved 19 June 2006.
- 1949 Encyclopædia Britannica. Otis, McAllister & Co. 1954
- Allen, Stewart Lee (1999). The Devil's Cup: Coffee, the Driving Force in History. Soho Press.
- Birsel, Salâh. – Kahveler kitabı. – 1. baskı. – Istanbul : Koza Yayınları, 1975. – (Olaylar-belgeler-anılar ; 8).
- Burn, Jacob Henry, d. (1869). A descriptive catalogue of the London traders, tavern, and coffee-house toke. 2nd ed. London.
- Chew, Samual C (1974). The Crescent and the Rose. Oxford University Press, New York.
- Darby, M. (1983) The Islamic Perspective, An aspect of British Architecture and Design in the 19th century. Leighton House Gallery, London.
- Davids, Kenneth (1991). Coffee.
- De Crescenzo, Luciano (2008). Il caffè sospeso. Arnoldo Mondadori Editore, Milan.
- Ellis, Aytoun (1956). The Penny Universities : A History of the Coffee-Houses. London : Secker & Warburg.
- Galland, Antoine (1699) De l'origine et du progrez du café, Éd. originale J. Cavelier Paris, 1992– La Bibliothèque, coll. L'Écrivain Voyageur
- Illy, Francesco & Riccardo (1989). From Coffee to Espresso
- Ibn al-ʿImād al-Ḥanbalī (d.1089 AH/1679 AD). Shadharāt al-dhahab fi akhbār man dhahab, al-Juz' 8. Cairo, 1931.
- Malecka, Anna (2015). "How Turks and Persians Drank Coffee: A Little-known Document of Social History by Father J. T. Krusiński". Turkish Historical Review. 6 (2): 175–193. doi:10.1163/18775462-00602006.
- Pendergrast, Mark (2001) [1999]. Uncommon Grounds: The History of Coffee and How It Transformed Our World. London: Texere. ISBN 1-58799-088-1.
- Weinberg, Bennett Alan; Bealer, Bonnie K. (2001). The world of caffeine. Routledge. pp. 3–4. ISBN 0-415-92723-4.
- Liss, David. The Coffee Trader (2003). A well-researched historical novel about (among other things) the beginnings of the coffee business in 17th century Amsterdam. Includes extensive bibliography.
- "Fairtrade is not fair," YouTube Video, 09:33, Why Fair Trade is Bad on December 01, 2009, posted by "Peter Griffiths," October 5, 2017.
- McCreery, David. "Coffee and Indigenous Labor in Guatemala, 1871–1980." In The Global Coffee Economy in Africa, Asia and Latin America, 1500–1989. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003.192–208.
- James, Deborah. "Justice and Java." NACLA Report on the Americas 34, no. 2 (September 2000): 11–12. Academic Search Complete, EBSCOhost (accessed September 30, 2017). *Johannessen, Silje, and Harold Wilhite. "Who Really Benefits from Fairtrade? An Analysis of Value Distribution in Fairtrade Coffee." Globalizations 7, no. 4 (December 2010): 525–544. Academic Search Complete, EBSCOhost (accessed October 5, 2017).
- "Santiago’s Story," YouTube Video, 06:18, First Hand Account on March 26, 2008, posted by "Fair Trade Certified," October 1, 2017,
- Scholer, Morten. "Bitter or Better Future for Coffee Producers?" International Trade Forum no. 2 (June 2004): 9–12. Business Source Complete, EBSCOhost (accessed October 1, 2017).
- Topik, Steven C. "Coffee Anyone? Recent Research on Latin American Coffee Societies." Hispanic American Historical Review 80, no. 2 (May 2000): 225–266. Humanities International Complete, EBSCOhost (accessed September 27, 2017).
- Williamson, W. F. (1942). "The Place of Coffee in Trade with Latin America". Journal of Marketing. 6 (4): 149–151. doi:10.2307/1246099. JSTOR 1246099.

