Geography of East Timor
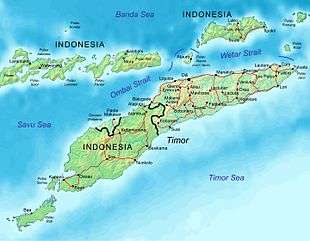
The geography of East Timor exhibits a mountainous terrain on the eastern half of the island of Timor in Southeast Asia (or Oceania depending on definitions).[lower-alpha 1] East Timor includes the eastern half of Timor, the Ocussi-Ambeno region on the northwest portion of the island of Timor, and the islands of Atauro and Jaco. The country is located northwest of Australia in the Lesser Sunda Islands at the eastern end of the Indonesian archipelago. 'Timor' is a Portuguese derivation of 'Timor', the Malay word for "Orient"; the island of Timor is part of the Malay Archipelago and is the largest and easternmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East Timor is the only Asian nation to lie entirely within the Southern Hemisphere. The Loes River is the longest with a length of 80 km (50 mi). This river system covers an area of 2,184 km2 (843 sq mi). It is a small country with a land size of 14,919 km2 (5,760 sq mi). The exclusive economic zone is 70,326 km2 (27,153 sq mi).[1]
 | |
| Continent | Asia |
|---|---|
| Region | Southeast Asia |
| Coordinates | 8°50′S 125°55′E |
| Area | Ranked 154th |
| • Total | 14,919 km2 (5,760 sq mi) |
| • Land | 100% |
| • Water | 0% |
| Coastline | 706 km (439 mi) |
| Borders | Indonesia: 253 km (157 mi) |
| Highest point | Tatamailau (2,963 m or 9,721 ft) |
| Lowest point | Timor Sea, Savu Sea, and Banda Sea 0 m (0 ft) |
| Longest river | Loes River 80 km (50 mi) |
| Largest lake | Ira Lalaro 1.9 km2 (1 sq mi) |
| Climate | Tropical |
| Terrain | Mountainous and rugged |
| Natural Resources | Gold, petroleum, natural gas, manganese, marble |
| Natural Hazards | Landslides are common; earthquakes; and tsunamis. |
| Environmental Issues | deforestation and soil erosion |
| Exclusive economic zone | 70,326 km2 (27,153 sq mi) |
Statistics
- Area
- Total: 14,874 km²
- Land: 14,874 km²
- Water: 0 km²
- Land boundaries
- Total: 2,538 km (1,577 mi)
- Border countries: Indonesia (253 km or 157 mi)
- Coastline
- 706 km (439 mi)
- Maritime claims
- Territorial sea: 12 nmi
- Contiguous zone: 24 nmo
- Exclusive economic zone: 70,326 km2 (27,153 sq mi) and 200 nmi
Elevation extremes
- Lowest point: Timor Sea, Savu Sea, and Banda Sea 0 m
- Highest point: Tatamailau (2,963 m or 9,721 ft)
- Natural resources
- Gold, petroleum, natural gas, manganese, marble
- Land use
- Arable land: 10.1%
- Permanent crops: 4.9%
- Permanent pasture: 10.1%
- Forest: 49.1%
- Other: 25.8% (2011)
- Irrigated land
- 346.5 km2 (134 sq mi) (2003)
Climate
- Tropical; hot and humid with distinct rainy and dry seasons. Tropical cyclones do occur along with floods.
Environment
- Natural hazards
- Landslides are common; earthquakes; and tsunamis.
- Environment - current issues
- Widespread use of slash and burn agriculture has led to deforestation and soil erosion.
- Environment - international agreements
- Biodiversity, climate change, climate change-Kyoto Protocol, desertification
References
- See Boundaries between continents#Asia and Oceania
- Exclusive Economic Zones – Sea Around Us Project – Fisheries, Ecosystems & Biodiversity – Data and Visualization.
- Much of the material in this article is adapted from the CIA World Factbook 2000 and 2012.
