China Railways JF2
The China Railways JF2 (解放2, Jiěfàng, "liberation") class steam locomotive was a class of 2-8-2 steam locomotives for goods trains operated by the China Railway. They were originally built for the South Manchuria Railway (Mantetsu) by several American and Japanese manufacturers, as well as by Mantetsu's Shahekou Works, between 1924 and 1932.[1]
| China Railways JF2 (解放2) Mantetsu Mikani class (ミカニ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
.png) Builder's photo of ミカニ1614. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
History
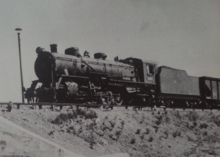
To fill the need for powerful locomotives to haul heavy goods trains from the Fushun Coal Mines and Dalian, Mantetsu ordered the first five Mikani class locomotives from the American Locomotive Company of Schenectady, New York in 1924. After completion of the superheated three-cylinder locomotives,[1] extensive performance tests were conducted, the results of which attracted considerable attention from the railway industry; despite a wheel diameter of only 1,370 mm (54 in), they reached a maximum speed of 101.4 km/h (63.0 mph).[2] They were immediately successful, and production of copies began at Mantetsu's Shahekou Works in 1926. They were the first Mantetsu locomotives to weigh over 100 t (98 long tons; 110 short tons), as well as the first to be built with automatic stokers. Although their performance was excellent, the complexity of the three-cylinder arrangement led to consideration of a superheated 2-10-2 tender locomotive design as a replacement. However, this plan was abandoned, and more Mikanis were built instead. After a number of incidents involving broken crankshafts, the Mikashi class was designed as the successor to the class in 1933.[3]
| Owner | Class & numbers (1924–1938) | Class & numbers (1938–1945) | Builder | Year | Works numbers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mantetsu | ミカニ1600–ミカニ1604 | ミカニ1–ミカニ5 | ALCO | 1924 | 65435–65439 |
| Mantetsu | ミカニ1605–ミカニ1608 | ミカニ6–ミカニ9 | South Manchuria Ry. Shahekou Works | 1926 | |
| Mantetsu | ミカニ1609–ミカニ1613 | ミカニ10–ミカニ14 | Shahekou Works | 1927 | |
| Mantetsu | ミカニ1614–ミカニ1616 | ミカニ15–ミカニ17 | Kawasaki | 1927 | 1248–1250 |
| Mantetsu | ミカニ1617–ミカニ1620 | ミカニ18–ミカニ21 | Kisha Seizō | 1928 | 1012–1015 |
| Mantetsu | ミカニ1621–ミカニ1626 | ミカニ22–ミカニ27 | Shahekou Works | 1928 | |
| Mantetsu | ミカニ1627–ミカニ1634 | ミカニ28–ミカニ35 | Shahekou Works | 1929 | |
| Mantetsu | ミカニ1635–ミカニ1637 | ミカニ36–ミカニ38 | Shahekou Works | 1930 | |
| Mantetsu | ミカニ1638–ミカニ1639 | ミカニ39–ミカニ40 | Shahekou Works | 1931 | |
| Mantetsu | ミカニ1640 | ミカニ41 | Shahekou Works | 1932 |
Postwar
.jpg)
At the end of the Pacific War, the 41 Mikani class locomotives were divided between the Dalian (35) and the Fengtian (6) depots, and all were taken over by the Republic of China Railway. Following the establishment of the People's Republic and the subsequent creation of the current China Railway, they became class ㄇㄎ貳 (MK2) in 1951, and class 解放2 (JF2, jiěfàng, "liberation") in 1959. Numbered in the 2501–2550 range, they were assigned to the Wafangdian locomotive depot in Dalian and used primarily on heavy goods trains. JF2 2525 is preserved at the Shenyang Steam Locomotive Museum.
References
- Ichihara, Yoshizumi, 写真集南満洲鉄道 (South Manchuria Railway Photo Collection) pp. 64-65, 1998 Seibundo Shinkosha Publishing Co. Ltd. (in Japanese)
- 鉄道車輌用ころがり軸受と台車の戦前・戦後史 (History of Roller Bearings and Trucks for Rolling Stock; in Japanese; p. 40)
- 鉄道車輌用ころがり軸受と台車の戦前・戦後史 (History of Roller Bearings and Trucks for Rolling Stock; in Japanese; p. 110)