Chavicol
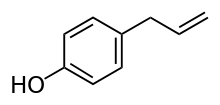
Chavicol (p-allylphenol) is a natural phenylpropene, a type of organic compound.[1] Its chemical structure consists of a benzene ring substituted with a hydroxy group and a propenyl group. It is a colorless liquid found together with terpenes in betel oil.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-(Prop-2-en-1-yl)phenol | |
| Other names
4-Allylphenol; p-Allylphenol; para-Allylphenol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.209 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O | |
| Molar mass | 134.18 g/mol |
| Density | 1.020 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 16 °C (61 °F; 289 K) |
| Boiling point | 238 °C (460 °F; 511 K) (123 °C at 16 mmHg) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Properties and reactions
Chavicol is miscible with alcohol, ether, and chloroform. Dimerization of chavicol gives the neo-lignan magnolol.
Uses
Chavicol is used as an odorant in perfumery and as a flavor. It is found in many essential oils, including anise and Gardenia.[2]
References
- Lide, D. R., ed. (2005). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (86th ed.). Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0486-5.
- http://www.thegoodscentscompany.com/data/rw1015241.html
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.