Bautzen
Bautzen (pronounced [ˈbaʊ̯t͡sn̩] (![]()
![]()
Bautzen Budyšin | |
|---|---|
Historical centre of the town | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Bautzen within Bautzen district 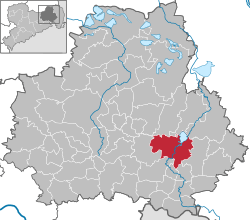 | |
 Bautzen  Bautzen | |
| Coordinates: 51°10′53″N 14°25′27″E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Saxony |
| District | Bautzen |
| Subdivisions | 15 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Alexander Ahrens (SPD) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 66.62 km2 (25.72 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 204 m (669 ft) |
| Population (2018-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 39,087 |
| • Density | 590/km2 (1,500/sq mi) |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) |
| Postal codes | 02625 |
| Dialling codes | 03591 |
| Vehicle registration | BZ, BIW, HY, KM |
| Website | www.bautzen.de |
Bautzen is often regarded as the unofficial, but historical capital of Upper Lusatia. The town is also the most important cultural centre of the Sorbian minority, which constitutes about 10 percent of Bautzen's population.[2] Its hilltop position and multiple towers are often compared to some of the hilltop towns of Tuscany. The town has a long association with mustard (Bautz'ner Senf) and is one of the few places in the world to boast a mustard museum.
Asteroid 11580 Bautzen is named in honour of the city.
Geography
Geographical situation
The town on the River Spree is situated about 50 km (31 mi) east of Dresden between the Lusatian highland and the lowlands in the north, amidst the region of Upper Lusatia. To the north stretches the Bautzen Reservoir, which was flooded in 1974. This is the former location of the villages of Malsitz (Małšecy) and Nimschütz (Hněwsecy).
Expansion of the urban area
The old part of Bautzen is located on the plateau above the Spree, whose top is marked by the Ortenburg (de) castle. It is bordered by the city walls. The later-built more recent quarters in the east were enclosed by the city ramparts. After their removal, the city expanded further east and to the left bank of the river. However, there has only been a small urban area west of the Spree until today. In the 1970s, the development areas of "Gesundbrunnen" and "Allendeviertel" were erected. After 1990, several neighbouring villages were incorporated.
Bordering municipalities
The city is bordered by Radibor, Großdubrau and Malschwitz in the North, Kubschütz in the East, Großpostwitz, Obergurig and Doberschau-Gaußig in the South, as well as Göda in the West. All of these belong to the Bautzen district.
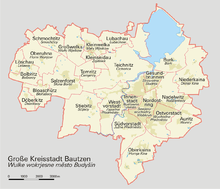
Subdivisions
The 15 city districts are:
| Name | Population (as of 1 January 2009) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| German | Upper Sorbian | English translation | |
| Innenstadt | Nutřkowne město | City centre | 5,278 |
| Südvorstadt | Južne Předměsto | Southern outskirts | 1,738 |
| Westvorstadt | Zapadne Předměsto | Western outskirts | 3,505 |
| Gesundbrunnen | Strowotna studnja | – | 8,178 |
| Nordostring | Sewjerowuchodny Wobkruh | North-eastern ring | 10,727 |
| Ostvorstadt | Wuchodne Předměsto | Eastern outskirts | 6,360 |
| Teichnitz | Ćichońca | – | 377 |
| Nadelwitz | Nadźankecy | – | 268 |
| Burk | Bórk | – | 325 |
| Oberkaina | Hornja Kina | – | 832 |
| Niederkaina | Delnja Kina | – | 522 |
| Stiebitz | Sćijecy | – | 510 |
| Kleinwelka | Mały Wjelkow | – | 1,314 |
| Salzenforst-Bolbritz | Słona Boršć-Bolborcy | – | 839 |
| Auritz | Wuricy | – | 458 |
History
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

In the 3rd century AD an eastern Germanic settlement existed here, but excavations have proved that the region was already inhabited as early as the late Stone Age. Sorbs arrived in the area during the Migration period in the 6h century AD.
The first written evidence of the city is from 1002 under the name Budusin (Polish: Budziszyn, Upper Sorbian: Budyšyn).[3] In 1018 the Peace of Bautzen was signed between the German king Henry II and the Polish ruler Bolesław I the Brave. The treaty left Budziszyn under Polish rule. In 1032 the town passed to the Margraviate of Meissen within the Holy Roman Empire, in 1075 to the Czech (Bohemian) Duchy, elevated to a kingdom in 1198 (with short periods of Brandenburgian and Hungarian rule), in 1635 to Saxony, and from 1697 to 1763 it was also under rule of Polish kings in personal union. One of two main routes connecting Warsaw and Dresden ran through the town at that time.[4]
From 1346 to 1815 it was a member of the Six Cities' Alliance of the Upper Lusatian cities of Görlitz, Zittau, Löbau, Kamenz, Lubań and Bautzen.
In 1429 and 1431 the town was unsuccessfully besieged by the Hussites.[3] In 1634 it was destroyed by the Swedes during the Thirty Years' War.[3] It was the site of one of the battlefields of the Napoleonic War Battle of Bautzen in 1813. In 1868 the name was officially changed to the more Germanized form Bautzen.[3]
In 1839 the Sorbian student organization Societas Slavica Budissenensis was founded in the city. In 1845 the Sorbian national anthem was publicly performed for the first time in the city. The Sorbian House (Upper Sorbian: Serbski Dom), a Sorbian cultural centre, was opened in the city in 1904.
After the Nazi Party came to power in Germany in 1933, many political prisoners were held in the Bautzen I and Bautzen II prisons, built in 1904 and 1906, respectively.[3] During the Kristallnacht in 1938, local Jews were persecuted and Jewish-owned businesses were destroyed.[3] During World War II, the AL Bautzen subcamp of the Groß-Rosen concentration camp operated in Bautzen.[5] At least 600 men, mostly Poles, but also of other nationalities, were imprisoned there, about 310 of whom died.[5] Ernst Thälmann was imprisoned there before being deported to Buchenwald. In April 1945, the Germans evacuated many prisoners on foot to Mikulášovice, where they were liberated by Polish troops on May 8, 1945, while the remaining prisoners were liberated in Bautzen by the Soviets on April 20, 1945.[5] Between 21 April and 30 April 1945, the Battle of Bautzen was fought.
Bautzen was infamous throughout East Germany for its two penitentiaries. "Bautzen I" was used as an official prison, soon to be nicknamed Gelbes Elend ("Yellow Misery") due to its outer colour, whereas the more secretive "Bautzen II" was used as a prison for political prisoners, dissidents and prisoners of conscience. Bautzen I is still actively used as a criminal prison. Bautzen II has served as an open memorial since 1993. It is accessible to the public at no charge, the entire premises being largely open.
In 2002 the city commemorated its 1000th birthday. In 2010 it was hit by a flood.[3]
Population development
(as of December 31 unless otherwise stated)
- 1849 – 10,518
- 1868 – 12,623[6]
- 1875 – 14,709
- 1890 – 21,516
- 1933 – 41,951
- 1950 – 41,592 (as of August 31)
- 1960 – 41,613
- 1984 – 51,208
- 1995 – 44,763
- 2000 – 43,353
- 2005 – 42,150
- 2010 – 40,573
- 2015 – 40,501
Mayors
- Konrad Johannes Kaeubler, Lord Mayor (1890-1918)
- Gottfried Franz Hermann Niedner, (1872-1945), Lord Mayor 1918-1933
- Christian Schramm (born 1952), (CDU), (Lord)Mayor 1990–2015
- Alexander Ahrens (born 1966), (independent), Lord Mayor since 2015
Main sights

Bautzen has a very compact and well-preserved medieval town centre with numerous churches and towers and a city wall on the steep embankment to the river Spree, with one of the oldest preserved waterworks in central Europe (built 1558).
Sites of interest include:
- The Reichenturm, one of the steepest leaning and still passable towers north of the Alps
- Ortenburg Castle
- The Old Waterworks, an architectural monument and museum
- Saint Peter's Cathedral, Eastern Germany's only historic interdenominational church edifice
- Hexenhaus (Witch's House), oldest preserved residential building (built in 1604)
There are six museums in Bautzen, including the Stadtmuseum Bautzen ("Bautzen city Museum"), the Sorbisches Museum ("Sorbian Museum", Sorbian: Serbski muzej) and the Senfmuseum (Mustard Museum).
Sorbian institutions
Bautzen is the seat of several institutions of the cultural self-administration of the Sorbian people:
- Foundation for the Sorbian People (Stiftung für das sorbische Volk, Załožba za serbski lud)
- Domowina (poet. Sorbic for „Homeland“, actually: Zwjazk Łužiskich Serbow z. t., Bund Lausitzer Sorben e. V.) - the umbrella organisation of Sorbian cultural associations and institutions
- Sorbic Language Radio (Serbski rozhłós) [7]
- Sorbian National Ensemble and the German Sorbian People's Theater (Němsko-serbske ludowe dźiwadło)
- Bautzen Sorbian Boarding School
Economy
The mustard Bautz'ner Senf is produced in Bautzen. It is the market leader in the new states of Germany with a market share of 65 percent.[8]
Notable citizens of the town


- Karl Gustav Brescius (1824–1864), railway engineer
- Rudolf Buchheim, (1820–1879), German pharmacologist
- Wilhelm Buck (1869–1945), Prime Minister of the Free State of Saxony
- Friedrich August Carus (1770–1807), psychologist and philosopher
- Kurt Dinter (1868–1945), botanist and explorer in South West Africa
- Werner von Erdmannsdorff (1891–1945), General of Infantry in World War II
- Will Grohmann (1887–1968), art historian and art critic
- Erhard Heinz (1924-2017), mathematician
- Hermann Hunger, (born 1942), Austrian assyriologist
- Hermann Lotze, (1817–1881), German philosopher and logician
- August Gottlieb Meißner (1753–1807), writer, founder of the German crime novel
- Harald Metzkes (born 1929), painter and graphic artist
- Ferdinand Neuling (1885–1960), General of Infantry in World War II
- Caspar Peucer, (1525–1602), German-Sorbian reformer, physician and scholar
- Charles Gottlieb Raue, (1820–1896), American homeopathic physician
- Georg-Hans Reinhardt (1887–1963), Colonel-General of the German Wehrmacht
- Simone Ritscher (born 1959), actress
- Friedrich Wilhelm Ehrenfried Rost (1768–1835), theologian and philosopher
- Hans von Tettau (1888–1956), Infantry General
- Hans Unger, (1872–1936), German painter
- Karl Friedrich Gottlob Wetzel (1779–1819), writer
- Handrij Zejler (1804–1872), born in the district Salzenforst, founder of modern Sorbian poetry
International relations
Bautzen is twinned with:[9]



References
- "Bevölkerung des Freistaates Sachsen jeweils am Monatsende ausgewählter Berichtsmonate nach Gemeinden" (PDF). Statistisches Landesamt des Freistaates Sachsen (in German). July 2019.
- "2 + 2=1". brand eins (in German). Retrieved 2020-05-10.
- "The History of Bautzen". Bautzen.de. Retrieved 14 June 2020.
- "Informacja historyczna". Dresden-Warszawa (in Polish). Retrieved 14 June 2020.
- "Subcamps of KL Gross- Rosen". Gross-Rosen Museum in Rogoźnica. Retrieved 1 June 2020.
- Geschichte der Stadt Bautzen, Richard Reymann, Druck und Verlag: Gebrüder Müller, 1902, S. 720. Die Angaben stammen ursprünglich aus einem Zeitdokument, das am 10. September 1868 in die Turmkugel des Reichenturms gelegt wurde. Demnach waren unter den 12.623 Einwohnern 2579 Wenden. Zudem waren darunter [...] 11.419 Lutheraner, 1153 Katholiken, 29 Reformierte, 5 Angelikaner, 7 Deutschkatholiken, 1 Griechisch-Katholik und 9 Juden.
- http://www.mdr.de/serbski-program/rozhlos/index.html
- "Bautz'ner Senf wird 60". Focus Online (in German). Retrieved 2020-05-10.
- "Partnerstädte". bautzen.de (in German). Bautzen. Retrieved 2019-11-27.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bautzen. |

- Official website
- Interactive sightseeing tour through Bautzen (German)
- . New International Encyclopedia. 1905.


