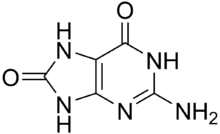
8-Oxoguanine
8-Oxoguanine (8-hydroxyguanine, 8-oxo-Gua, or OH8Gua) is one of the most common DNA lesions resulting from reactive oxygen species [2] modifying guanine, and can result in a mismatched pairing with adenine resulting in G to T and C to A substitutions in the genome.[3] In humans, it is primarily repaired by DNA glycosylase OGG1. It can be caused by ionizing radiation, in connection with oxidative metabolism.


 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Amino-7,9-dihydro-1H-purine-6,8-dione | |
| Other names
7,8-Dihydro-8-oxoguanine; 8-Oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.024.578 |
| MeSH | 8-hydroxyguanine |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H5N5O2 | |
| Molar mass | 167.128 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
In body fluids
Increased concentrations of 8-oxoguanine in body fluids have been found to be associated with increased risk of mutagenesis and carcinogenesis.[4][5]
Care must be taken in the assay of 8-oxoguanine due to the ease with which it can be oxidised during extraction and the assay procedure.[6]
Cancer, aging, infertility
The role of the deoxyriboside form of 8-oxoguanine, 8-oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine (abbreviated 8-oxo-dG or 8-OHdG) in cancer and aging also applies to 8-oxoguanine. Oxoguanine glycosylase is employed in the removal of 8-oxoguanine from DNA by the process of base excision repair. As described in oxoguanine glycosylase, deficient expression of this enzyme causes 8-oxoguanine to accumulate in DNA. This accumulation may then lead upon replication of DNA to mutations including some that contribute to carcinogenesis. 8-oxoguanine is usually formed by the interaction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) with the guanine base in DNA under conditions of oxidative stress; as noted in the article about them, such species may have a role in aging and male infertility, and 8-oxoguanine can be used to measure such stress.
References
- 8-hydroxyguanine - Compound Summary, PubChem
- Kanvah, S.; et al. (2010). ", Oxidation of DNA: Damage to Nucleobases". Acc. Chem. Res. 43 (2): 280–287. doi:10.1021/ar900175a.
- Cheng KC; Cahill DS; Kasai H; Nishimura S; Loeb LA (Jan 5, 1992). "8-Hydroxyguanine, an abundant form of oxidative DNA damage, causes G→T and C→A substitutions". J Biol Chem. 267 (1): 166–72. PMID 1730583.
- Kasai, H (December 1997). "Analysis of a form of oxidative DNA damage, 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine, as a marker of cellular oxidative stress during carcinogenesis". Mutation Research. 387 (3): 147–63. doi:10.1016/s1383-5742(97)00035-5. PMID 9439711.
- Halliwell, B (December 1998). "Can oxidative DNA damage be used as a biomarker of cancer risk in humans? Problems, resolutions and preliminary results from nutritional supplementation studies". Free Radical Research. 29 (6): 469–86. doi:10.1080/10715769800300531. PMID 10098453.
- Ravanat, JL; Douki, T; Duez, P; Gremaud, E; Herbert, K; Hofer, T; Lasserre, L; Saint-Pierre, C; Favier, A; Cadet, J (November 2002). "Cellular background level of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine: an isotope based method to evaluate artefactual oxidation of DNA during its extraction and subsequent work-up". Carcinogenesis. 23 (11): 1911–8. doi:10.1093/carcin/23.11.1911. PMID 12419840.