Gamma
Gamma /ˈɡæmə/[1] (uppercase Γ, lowercase γ; Greek: γάμμα gámma) is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. In Ancient Greek, the letter gamma represented a voiced velar stop /ɡ/. In Modern Greek, this letter represents either a voiced velar fricative or a voiced palatal fricative.
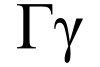 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Greek alphabet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Use in other languages | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Related topics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

In the International Phonetic Alphabet and other modern Latin-alphabet based phonetic notations, it represents the voiced velar fricative.
History
The Greek letter Gamma Γ was derived from the Phoenician letter for the /g/ phoneme (𐤂 gīml), and as such is cognate with Hebrew gimel ג.
Based on its name, the letter has been interpreted as an abstract representation of a camel's neck,[2] but this has been criticized as contrived,[3] and it is more likely that the letter is derived from an Egyptian hieroglyph representing a club or throwing stick.[4]
In Archaic Greece, the shape of gamma was closer to a classical lambda (Λ), while lambda retained the Phoenician L-shape (𐌋).
Letters that arose from the Greek gamma include Etruscan (Old Italic) 𐌂, Roman C and G, Runic kaunan ᚲ, Gothic geuua 𐌲, the Coptic Ⲅ, and the Cyrillic letters Г and Ґ.[5]
Greek phoneme
The Ancient Greek /g/ phoneme was the voiced velar stop, continuing the reconstructed proto-Indo-European *g, *ǵ.
The modern Greek phoneme represented by gamma is realized either as a voiced palatal fricative (/ʝ/) before a front vowel (/e/, /i/), or as a voiced velar fricative /ɣ/ in all other environments. Both in Ancient and in Modern Greek, before other velar consonants (κ, χ, ξ k, kh, ks), gamma represents a velar nasal /ŋ/. A double gamma γγ represents the sequence /ŋɡ/ (phonetically varying [ŋɡ~ɡ]) or /ŋɣ/.
Phonetic transcription
Lowercase Greek gamma is used in the Americanist phonetic notation and Uralic Phonetic Alphabet to indicate voiced consonants.
The gamma was also added to the Latin alphabet, as Latin gamma, in the following forms: majuscule Ɣ, minuscule ɣ, and superscript modifier letter ˠ.
In the International Phonetic Alphabet the minuscule letter is used to represent a voiced velar fricative and the superscript modifier letter is used to represent velarization. It is not to be confused with the character ɤ, which looks like a lowercase Latin gamma that lies above the baseline rather than crossing, and which represents the close-mid back unrounded vowel. In certain nonstandard variations of the IPA, the uppercase form is used.
It is as a full-fledged majuscule and minuscule letter in the alphabets of some of languages of Africa such as Dagbani, Dinka, Kabye, and Ewe,[6] and Berber languages using the Berber Latin alphabet.
It is sometimes also used in the romanization of Pashto.
Mathematics and science
Lowercase
The lowercase letter is used as a symbol for:
- Chromatic number of in graph theory
- Gamma radiation in nuclear physics
- The photon, the elementary particle of light and other electromagnetic radiation
- Surface energy in materials science
- The Lorentz factor in the theory of relativity
- In mathematics, the lower incomplete gamma function
- The heat capacity ratio Cp/Cv in thermodynamics
- The activity coefficient in thermodynamics
- The gyromagnetic ratio in electromagnetism
- Gamma waves in neuroscience
- Gamma motor neurons in neuroscience
- A non-SI metric unit of measure of mass equal to one microgram (1 μg).[7] This always-rare use is currently deprecated.
- A non-SI unit of measure of magnetic flux density, sometimes used in geophysics, equal to 1 nanotesla (nT).
- The power by which the luminance of an image is increased in gamma correction
- The Euler–Mascheroni constant
- In civil and mechanical engineering:
- Specific weight
- The shear rate of a fluid is represented by a lowercase gamma with a dot above it:
- Austenite (also known as γ-iron), a metallic non-magnetic allotrope or solid solution of iron.
- The gamma carbon, the third carbon attached to a functional group in organic chemistry and biochemistry; see Alpha and beta carbon
The lowercase Latin gamma ɣ can also be used in contexts (such as chemical or molecule nomenclature) where gamma must not be confused with the letter y, which can occur in some computer typefaces.
Uppercase
The uppercase letter is used as a symbol for:
- In mathematics, the gamma function (usually written as -function) is an extension of the factorial to complex numbers
- In mathematics, the upper incomplete gamma function
- The Christoffel symbols in differential geometry
- In probability theory and statistics, the gamma distribution is a two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions.
- Circulation in fluid mechanics
- As reflection coefficient in physics and electrical engineering
- The tape alphabet of a Turing machine
- The Feferman–Schütte ordinal
- One of the Greeks in mathematical finance
Encoding
HTML
The HTML entities for uppercase and lowercase gamma are Γ and γ.
Unicode
- Greek Gamma
| Character | Γ | γ | ᴦ | ᵞ | ᵧ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | GREEK CAPITAL LETTER GAMMA | GREEK SMALL LETTER GAMMA | GREEK LETTER SMALL CAPITAL GAMMA | MODIFIER LETTER SMALL GREEK GAMMA | GREEK SUBSCRIPT SMALL LETTER GAMMA | |||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 915 | U+0393 | 947 | U+03B3 | 7462 | U+1D26 | 7518 | U+1D5E | 7527 | U+1D67 |
| UTF-8 | 206 147 | CE 93 | 206 179 | CE B3 | 225 180 166 | E1 B4 A6 | 225 181 158 | E1 B5 9E | 225 181 167 | E1 B5 A7 |
| Numeric character reference | Γ | Γ | γ | γ | ᴦ | ᴦ | ᵞ | ᵞ | ᵧ | ᵧ |
| Named character reference | Γ | γ | ||||||||
- Coptic Gamma
| Character | Ⲅ | ⲅ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | COPTIC CAPITAL LETTER GAMMA | COPTIC SMALL LETTER GAMMA | ||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 11396 | U+2C84 | 11397 | U+2C85 |
| UTF-8 | 226 178 132 | E2 B2 84 | 226 178 133 | E2 B2 85 |
| Numeric character reference | Ⲅ | Ⲅ | ⲅ | ⲅ |
- Latin Gamma / phonetic Gamma
| Character | Ɣ | ɣ | ˠ | ɤ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER GAMMA | LATIN SMALL LETTER GAMMA | MODIFIER LETTER SMALL GAMMA | LATIN SMALL LETTER RAMS HORN | ||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 404 | U+0194 | 611 | U+0263 | 736 | U+02E0 | 612 | U+0264 |
| UTF-8 | 198 148 | C6 94 | 201 163 | C9 A3 | 203 160 | CB A0 | 201 164 | C9 A4 |
| Numeric character reference | Ɣ | Ɣ | ɣ | ɣ | ˠ | ˠ | ɤ | ɤ |
- CJK Square Gamma
| Character | ㌏ | |
|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | SQUARE GAMMA | |
| Encodings | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 13071 | U+330F |
| UTF-8 | 227 140 143 | E3 8C 8F |
| Numeric character reference | ㌏ | ㌏ |
- Technical / Mathematical Gamma
| Character | ℾ | ℽ | 𝚪 | 𝛄 | 𝛤 | 𝛾 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | DOUBLE-STRUCK CAPITAL GAMMA | DOUBLE-STRUCK SMALL GAMMA | MATHEMATICAL BOLD CAPITAL GAMMA | MATHEMATICAL BOLD SMALL GAMMA | MATHEMATICAL ITALIC CAPITAL GAMMA | MATHEMATICAL ITALIC SMALL GAMMA | ||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 8510 | U+213E | 8509 | U+213D | 120490 | U+1D6AA | 120516 | U+1D6C4 | 120548 | U+1D6E4 | 120574 | U+1D6FE |
| UTF-8 | 226 132 190 | E2 84 BE | 226 132 189 | E2 84 BD | 240 157 154 170 | F0 9D 9A AA | 240 157 155 132 | F0 9D 9B 84 | 240 157 155 164 | F0 9D 9B A4 | 240 157 155 190 | F0 9D 9B BE |
| UTF-16 | 8510 | 213E | 8509 | 213D | 55349 57002 | D835 DEAA | 55349 57028 | D835 DEC4 | 55349 57060 | D835 DEE4 | 55349 57086 | D835 DEFE |
| Numeric character reference | ℾ | ℾ | ℽ | ℽ | 𝚪 | 𝚪 | 𝛄 | 𝛄 | 𝛤 | 𝛤 | 𝛾 | 𝛾 |
| Character | 𝜞 | 𝜸 | 𝝘 | 𝝲 | 𝞒 | 𝞬 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | MATHEMATICAL BOLD ITALIC CAPITAL GAMMA | MATHEMATICAL BOLD ITALIC SMALL GAMMA | MATHEMATICAL SANS-SERIF BOLD CAPITAL GAMMA | MATHEMATICAL SANS-SERIF BOLD SMALL GAMMA | MATHEMATICAL SANS-SERIF BOLD ITALIC CAPITAL GAMMA | MATHEMATICAL SANS-SERIF BOLD ITALIC SMALL GAMMA | ||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 120606 | U+1D71E | 120632 | U+1D738 | 120664 | U+1D758 | 120690 | U+1D772 | 120722 | U+1D792 | 120748 | U+1D7AC |
| UTF-8 | 240 157 156 158 | F0 9D 9C 9E | 240 157 156 184 | F0 9D 9C B8 | 240 157 157 152 | F0 9D 9D 98 | 240 157 157 178 | F0 9D 9D B2 | 240 157 158 146 | F0 9D 9E 92 | 240 157 158 172 | F0 9D 9E AC |
| UTF-16 | 55349 57118 | D835 DF1E | 55349 57144 | D835 DF38 | 55349 57176 | D835 DF58 | 55349 57202 | D835 DF72 | 55349 57234 | D835 DF92 | 55349 57260 | D835 DFAC |
| Numeric character reference | 𝜞 | 𝜞 | 𝜸 | 𝜸 | 𝝘 | 𝝘 | 𝝲 | 𝝲 | 𝞒 | 𝞒 | 𝞬 | 𝞬 |
These characters are used only as mathematical symbols. Stylized Greek text should be encoded using the normal Greek letters, with markup and formatting to indicate text style.
See also
| Look up Γ or γ in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Look up Ɣ or ɣ in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
References
- "gamma". Oxford English Dictionary (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press. September 2005. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- Russell, Bertrand (1972). A history of western philosophy (60th print. ed.). New York: Touchstone book. ISBN 9780671314002.
- Powell, Barry B. (2012). Writing: Theory and History of the Technology of Civilization. John Wiley & Sons. p. 182. ISBN 978-1-118-29349-2.
- Hamilton, Gordon James (2006). The Origins of the West Semitic Alphabet in Egyptian Scripts. Catholic Biblical Association of America. pp. 53–6. ISBN 978-0-915170-40-1.
- "Greek Alphabet Symbols". Rapid Tables. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- Practical Orthography of African Languages
- François Cardarelli (2003). Encyclopaedia of Scientific Units, Weights and Measures. Springer-Verlag London Ltd. ISBN 978-1-4471-1122-1.