Vineyard Sound
| Vineyard Sound | |
|---|---|
|
Vineyard Sound is the body of water located behind the Gay Head Cliffs of Martha's Vineyard. | |
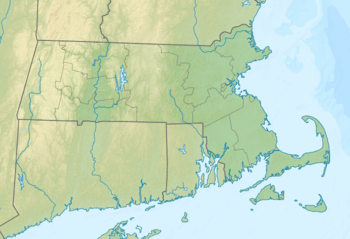 Vineyard Sound Location of Vineyard Sound within Massachusetts  Vineyard Sound Vineyard Sound (the US) | |
| Coordinates | 41°26′30″N 70°46′28″W / 41.4417764°N 70.7744748°WCoordinates: 41°26′30″N 70°46′28″W / 41.4417764°N 70.7744748°W, 41°28′45″N 70°39′59″W / 41.4792768°N 70.6664182°W, 41°23′59″N 70°53′43″W / 41.3998309°N 70.8953114°W, 41°21′45″N 70°47′48″W / 41.3626116°N 70.7966964°W, 41°32′35″N 70°28′56″W / 41.5431664°N 70.4822496°W, 41°31′47″N 70°33′43″W / 41.5298323°N 70.5619732°W[1] |
| Part of | Atlantic Ocean |
Vineyard Sound is the stretch of the Atlantic Ocean which separates the Elizabeth Islands and the southwestern part of Cape Cod from the island of Martha's Vineyard, located offshore from the state of Massachusetts in the United States. To the west, it joins Rhode Island Sound, and on its eastern end it connects to Nantucket Sound.[2]
Vineyard Sound holds some of the largest summer flounder in Massachusetts.[3]
References
- ↑ "Vineyard Sound". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2018-08-10.
- ↑ "Massachusetts Tidal In-Stream Energy Conversion (TISEC): Survey and Characterization of Potential Project Sites". Electric Power Research Institute, accessed September 28, 2011.
- ↑ Luftglass, Manny. "Gone Fishin': Massachusetts' 100 Best Waters". Hanover, N.H.: University Press of New England, 2008, p. 192, ISBN 978-1-58465-686-9.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.