Tricalcium phosphate
2_from_crystallography.jpg) | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Tricalcium bis(phosphate) | |
| Other names
Tribasic calcium phosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.946 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
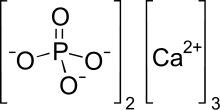
| Ca3(PO4)2 | |
| Molar mass | 310.18 |
| Appearance | White amorphous powder |
| Density | 3.14 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | Liquifies under high pressure at 1670 K (1391 °C) |
| 0.002 g/100 g | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
-4126 kcal/mol (α-form)[1] |
| Pharmacology | |
| A12AA01 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Calcium pyrophosphate |
Other cations |
Trimagnesium phosphate Trisodium phosphate Tripotassium phosphate |
Related compounds |
Monocalcium phosphate Dicalcium phosphate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tricalcium phosphate (sometimes abbreviated TCP) is a calcium salt of phosphoric acid with the chemical formula Ca3(PO4)2. It is also known as tribasic calcium phosphate and bone phosphate of lime (BPL). It is a white solid of low solubility. Most commercial samples of "tricalcium phosphate" are in fact hydroxyapatite.[2]
It exists as three crystalline polymorphs α, α', and β. The α and α' states are stable at high temperatures. As mineral, it is found in Whitlockite.[2]
Nomenclature
Calcium phosphate refers to numerous materials consisting of calcium ions (Ca2+) together with orthophosphates (PO43−), metaphosphates or pyrophosphates (P2O74−) and occasionally oxide and hydroxide ions. Especially, the common mineral apatite has formula Ca5(PO4)3X, where X is F, Cl, OH, or a mixture; it is hydroxyapatite if the extra ion is mainly hydroxide. Much of the "tricalcium phosphate" on the market is actually powdered hydroxyapatite.
Preparation
Tricalcium phosphate is produced commercially by treating hydroxyapatite with phosphoric acid and slaked lime.[2]
It cannot be precipitated directly from aqueous solution. Typically double decomposition reactions are employed, involving a soluble phosphate and calcium salts, e.g. (NH4)2HPO4 + Ca(NO3)2.[3] is performed under carefully controlled pH conditions. The precipitate will either be "amorphous tricalcium phosphate", ATCP, or calcium deficient hydroxyapatite, CDHA, Ca9(HPO4)(PO4)5(OH), (note CDHA is sometimes termed apatitic calcium triphosphate).[3][4][5] Crystalline tricalcium phosphate can be obtained by calcining the precipitate. β-Ca3(PO4)2 is generally formed, higher temperatures are required to produce α-Ca3(PO4)2.
An alternative to the wet procedure entails heating a mixture of a calcium pyrophosphate and calcium carbonate:[4]
- CaCO3 + Ca2P2O7 → Ca3(PO4)2 + CO2
Structure of β-, α- and α'- Ca3(PO4)2 polymorphs
Tricalcium phosphate has three recognised polymorphs, the rhombohedral β- form (shown above), and two high temperature forms, monoclinic α- and hexagonal α'-. β-tricalcium phosphate has a crystallographic density of 3.066 g cm−3 while the high temperature forms are less dense, α-tricalcium phosphate has a density of 2.866 g cm−3 and α'-tricalcium phosphate has a density of 2.702 g cm−3 All forms have complex structures consisting of tetrahedral phosphate centers linked through oxygen to the calcium ions.[6] The high temperature forms each have two types of columns, one containing only calcium ions and the other both calcium and phosphate.[7]
There are differences in chemical and biological properties between the beta and alpha forms, the alpha form is more soluble and biodegradeable. Both forms are available commercially and are present in formulations used in medical and dental applications.[7]
Occurrence
Calcium phosphate is one of the main combustion products of bone (see bone ash). Calcium phosphate is also commonly derived from inorganic sources such as mineral rock.[8] Tricalcium phosphate occurs naturally in several forms, including:
- as a rock in Morocco, Israel, Philippines, Egypt, and Kola (Russia) and in smaller quantities in some other countries. The natural form is not completely pure, and there are some other components like sand and lime which can change the composition. In terms of P2O5, most calcium phosphate rocks have a content of 30% to 40% P2O5 in weight.
- in the skeletons and teeth of vertebrate animals
- in milk.
Biphasic tricalcium phosphate, BCP
Biphasic tricalcium phosphate, BCP, was originally reported as tricalcium phosphate, but X-Ray diffraction techniques showed that the material was an intimate mixture of two phases, hydroxyapatite, HA, and β-tricalcium phosphate.[9] It is a ceramic.[10] Preparation involves the sintering causing the irreversible decomposition of calcium deficient apatites[4] alternatively termed non-stoichiometric apatites or basic calcium phosphate,[11] an example is:[12]
- Ca10−δ(PO4)6−δ(HPO4)δ(OH)2−δ → (1-δ)Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 + 3δCa3(PO4)2
β-TCP can contain impurities, for example calcium pyrophosphate, CaP2O7 and apatite. β-TCP is bioresorbable. The biodegradation of BCP involves faster dissolution of the β-TCP phase followed by elimination of HA crystals. β-TCP does not dissolve in body fluids at physiological pH levels, dissolution requires cell activity producing acidic pH.[4]
Uses
Tricalcium phosphate is used in powdered spices as an anticaking agent, e.g. to prevent table salt from caking. It is also found in baby powder and toothpaste.[2]
Biomedical
It is also used as a nutritional supplement[13] and occurs naturally in cow milk , although the most common and economical forms for supplementation are calcium carbonate (which should be taken with food) and calcium citrate (which can be taken without food).[14] There is some debate about the different bioavailabilities of the different calcium salts.
It can be used as a tissue replacement for repairing bony defects when autogenous bone graft is not feasible or possible.[15][16][17] It may be used alone or in combination with a biodegradable, resorbable polymer such as polyglycolic acid.[18] It may also be combined with autologous materials for a bone graft.[19][20]
Porous beta-Tricalcium phosphate scaffolds are employed as drug carrier systems for local drug delivery in bone.[21]
References
- ↑ Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles 6th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company. p. A21. ISBN 0-618-94690-X.
- 1 2 3 4 Klaus Schrödter; Gerhard Bettermann; Thomas Staffel; Friedrich Wahl; Thomas Klein; Thomas Hofmann (2008). Phosphoric Acid and Phosphates. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_465.pub3.
- 1 2 Destainville, A., Champion, E., Bernache-Assollant, D., Laborde, E. (2003). "Synthesis, characterization and thermal behavior of apatitic tricalcium phosphate". Materials Chemistry and Physics. 80 (1): 269–277. doi:10.1016/S0254-0584(02)00466-2. ISSN 1742-7061. – via ScienceDirect (Subscription may be required or content may be available in libraries.)
- 1 2 3 4 Rey, C.; Combes, C.; Drouet, C.; Grossin, D. (2011). "1.111 - Bioactive Ceramics: Physical Chemistry". In Ducheyne, Paul. Comprehensive Biomaterials. 1. Elsevier. pp. 187–281. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-055294-1.00178-1. ISBN 978-0-08-055294-1. – via ScienceDirect (Subscription may be required or content may be available in libraries.)
- ↑ Dorozhkin, Sergey V. (December 2012). "Amorphous calcium (ortho)phosphates". Acta Biomaterialia. 6 (12): 4457–4475. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2010.06.031. ISSN 1742-7061. – via ScienceDirect (Subscription may be required or content may be available in libraries.)
- ↑ Yashima, M.; Sakai, A.; Kamiyama, T.; Hoshikawa, A. (2003). "Crystal structure analysis of beta-tricalcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2 by neutron powder diffraction". rnal of Solid State Chemistry. 175: 272-p277.
- 1 2 Carrodeguas, R.G.; De Aza, S. (2011). "α-Tricalcium phosphate: Synthesis, properties and biomedical applications". Acta Biomaterialia. 7 (10): 3536–3546. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2011.06.019. ISSN 1742-7061. – via ScienceDirect (Subscription may be required or content may be available in libraries.)
- ↑ Yacoubou, Jeanne, MS. Vegetarian Journal's Guide To Food Ingredients "Guide to Food Ingredients". The Vegetarian Resource Group, n.d. Web. 14 Sept. 2012.
- ↑ Daculsi, G.; Legeros, R. (2008). "17 - Tricalcium phosphate/hydroxyapatite biphasic ceramics". In Kokubo, Tadashi. Bioceramics and their Clinical Applications. Woodhead Publishing. pp. 395–423. doi:10.1533/9781845694227.2.395. ISBN 978-1-84569-204-9. – via ScienceDirect (Subscription may be required or content may be available in libraries.)
- ↑ Salinas, Antonio J.; Vallet-Regi, Maria (2013). "Bioactive ceramics: from bone grafts to tissue engineering". RSC Advances. Royal Society of Chemistry. 3 (28): 11116–11131. doi:10.1039/C3RA00166K. Retrieved 15 February 2015. (Subscription required (help)).
- ↑ Elliott, J.C. (1994). "3 - Hydroxyapatite and Nonstoichiometric Apatites". Studies in Inorganic Chemistry. 18. Elsevier. pp. 111–189. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-81582-8.50008-0. ISSN 0169-3158. Retrieved 15 February 2015. – via ScienceDirect (Subscription may be required or content may be available in libraries.)
- ↑ Vallet-Regí, M.;Rodríguez-Lorenzo, L.M. (November 1997). "Synthesis and characterisation of calcium deficient apatite". Solid State Ionics. 101–103, Part 2: 1279–1285. doi:10.1016/S0167-2738(97)00213-0. – via ScienceDirect (Subscription may be required or content may be available in libraries.)
- ↑ Bonjour JP, Carrie AL, Ferrari S, Clavien H, Slosman D, Theintz G, Rizzoli R (March 1997). "Calcium-enriched foods and bone mass growth in prepubertal girls: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial". J. Clin. Invest. 99 (6): 1287–94. doi:10.1172/JCI119287. PMC 507944. PMID 9077538.
- ↑ Straub DA (June 2007). "Calcium supplementation in clinical practice: a review of forms, doses, and indications". Nutr Clin Pract. 22 (3): 286–96. doi:10.1177/0115426507022003286. PMID 17507729.
- ↑ Paderni S, Terzi S, Amendola L (September 2009). "Major bone defect treatment with an osteoconductive bone substitute". Musculoskelet Surg. 93 (2): 89–96. doi:10.1007/s12306-009-0028-0. PMID 19711008.
- ↑ Moore DC, Chapman MW, Manske D (1987). "The evaluation of a biphasic calcium phosphate ceramic for use in grafting long-bone diaphyseal defects". Journal of Orthopaedic Research. 5 (3): 356–65. doi:10.1002/jor.1100050307. PMID 3040949.
- ↑ Lange TA, Zerwekh JE, Peek RD, Mooney V, Harrison BH (1986). "Granular tricalcium phosphate in large cancellous defects". Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Science. 16 (6): 467–72. PMID 3541772.
- ↑ Cao H, Kuboyama N (September 2009). "A biodegradable porous composite scaffold of PGA/beta-TCP for bone tissue engineering". Bone. 46 (2): 386–95. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2009.09.031. PMID 19800045.
- ↑ Erbe EM, Marx JG, Clineff TD, Bellincampi LD (October 2001). "Potential of an ultraporous beta-tricalcium phosphate synthetic cancellous bone void filler and bone marrow aspirate composite graft". European Spine Journal. 10 Suppl 2: S141–6. doi:10.1007/s005860100287. PMC 3611552. PMID 11716011.
- ↑ Bansal S, Chauhan V, Sharma S, Maheshwari R, Juyal A, Raghuvanshi S (July 2009). "Evaluation of hydroxyapatite and beta-tricalcium phosphate mixed with bone marrow aspirate as a bone graft substitute for posterolateral spinal fusion". Indian Journal of Orthopaedics. 43 (3): 234–9. doi:10.4103/0019-5413.49387. PMC 2762171. PMID 19838344.
- ↑ Kundu, B; Lemos A; Soundrapandian C; Sen PS; Datta S; Ferreira JMF; Basu D (2010). "Development of porous HAp and β-TCP scaffolds by starch consolidation with foaming method and drug-chitosan bilayered scaffold based drug delivery system". J Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 21 (11): 2955–69. doi:10.1007/s10856-010-4127-0. PMID 20644982.
