Tombigbee River
| Tombigbee River | |
|---|---|
 Tombigbee River at White Bluff (Ecor Blanc) in Demopolis. | |
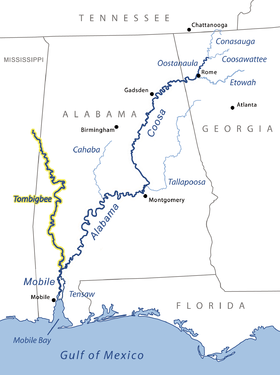 Tombigbee and Alabama river basins. | |
| Country | United States (Alabama, Mississippi) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Main source | Confluence of Tennessee-Tombigbee Waterway and Black Warrior River |
| River mouth | Mobile River, at Mobile, Alabama |
| Length | 200 miles (320 km) |
The Tombigbee River is a tributary of the Mobile River, approximately 200 mi (325 km) long, in the U.S. states of Mississippi and Alabama. Together with the Alabama, it merges to form the short Mobile River before the latter empties into Mobile Bay on the Gulf of Mexico. The Tombigbee watershed encompasses much of the rural coastal plain of western Alabama and northeastern Mississippi, flowing generally southward. The river provides one of the principal routes of commercial navigation in the southern United States, as it is navigable along much of its length through locks and connected in its upper reaches to the Tennessee River via the Tennessee-Tombigbee Waterway.
The name "Tombigbee" comes from Choctaw /itumbi ikbi/, meaning "box maker, coffin maker", from /itumbi/, "box, coffin", and /ikbi/, "maker".[1] The river formed the eastern boundary of the historical Choctaw lands, from the 17th century when they coalesced as a people, to the forced Indian Removal by the United States in the 1830s.[2]
Description


The river begins in northeastern Mississippi in Itawamba County. Historically, the beginning of the river was in northern Monroe County, by the confluence of Town Creek (also known as West Fork Tombigbee River) and East Fork Tombigbee River. Today, however, what was once known as the east fork is now designated as the Tombigbee.[3]
The river flows east through Aberdeen Lake near Aberdeen, and Columbus Lake near Columbus. It flows through Aliceville Lake on the Mississippi-Alabama border, then generally SSE across western Alabama in a highly meandering course, past Gainesville and Demopolis, where it is joined from the northeast by the Black Warrior River. South of Demopolis it flows generally south across southwestern Alabama, past Jackson. It joins the Alabama from the north on the Mobile-Baldwin county line, approximately 30 mi (50 km) north of Mobile, to form the Mobile River.[3]
After the completion of the Tennessee-Tombigbee Waterway in 1985, much of the middle course of the river in northeastern Mississippi was diverted into the new, straightened channel. Above Aberdeen Lake, the waterway flows alongside the original course of the river.
In addition to the Black Warrior, the river is joined by the Buttahatchee River from the east, north of Columbus, Mississippi. To the South of Columbus, Luxapalila Creek joins with the Tombigbee River, approximately 5.2 miles from downtown Columbus. Approximately 10 mi (15 km) north of Gainesville, it is joined from the north by the Sipsey River. At Gainesville, it is joined from the west by the Noxubee River.
The Choctaw National Wildlife Refuge is along the river in southwestern Alabama, approximately 20 mi (30 km) northwest of Jackson.
The upper reaches of the Tombigbee formed the homeland of the formidable Chickasaw. The French official Bienville used the Tombigbee to travel with his forces in his 1736 campaign against the Chickasaw. In the nineteenth century, they were considered one of the Five Civilized Tribes of the Southeast, as they adopted some European-American ways. But Congress still passed the Indian Removal Act of 1830, and ultimately the United States forced the Chickasaw west of the Mississippi to Indian Territory, extinguishing most of their claim to land in the Southeast.
Lock and dams
The Tombigbee River has five lock and dams along its length. Lock & Dams are listed from north to south; the river mile indicates the distance from the mouth of the Mobile River at Mobile Bay.
- John C. Stennis Lock & Dam is located at river mile 334.7
- Tom Bevill Lock & Dam is located at river mile 306.8
- Howell Heflin Lock & Dam is located at river mile 266.1
- Demopolis Lock & Dam is located at river mile 213.2
- Coffeeville Lock and Dam is located at river mile 116.6.[4]
Tributaries
Tributaries that empty directly into the Tombigbee:
- West River
- Bassetts Creek (Washington County)
- Bassett Creek (Clarke County)
- Jackson Creek
- Santa Bogue Creek
- Turkey Creek
- Okatuppa Creek
- Oak Slush Creek
- Big Tallawampa Creek
- Bashi Creek
- Wahalak Creek
- Sucarbowa Creek
- Horse Creek
- Tuckabum Creek
- Beaver Creek
- Kinterbish Creek
- Chickasaw Bogue
- Cotohaga Creek
- Sucarnoochee River
- Spring Creek
- Hall Creek
- Black Warrior River
- Brush Creek
- Trussells Creek
- Noxubee River
- Sipsey River
- Lubbub Creek
- Big Creek
- Luxapallila Creek
- Buttahatchee River
- Bull Mountain Creek
Cahaba Incident
On April 28, 1979, a tugboat named M/V Cahaba was on the Tombigbee near Demopolis, Alabama.[5] The tugboat was trying to guide two coal barges under a flooded side-span of the old Rooster Bridge (removed years later), but the flood current was too strong. The tug and barges approached the drawbridge-section, which failed to re-open fast enough while the river was near flood stage (drawbridges must close and re-open to allow waiting traffic to cross). The fast currents pinned the Cahaba's starboard side against the bridge in high waters. The force was so great that it pulled the boat downward, tilting it beneath the bridge, and fully submerging it in the river.[5] The underwater pressure blew out a port-side window in the pilot house, which began filling with water, while the captain remained at the helm.[5] Soon the tugboat emerged from beneath the other side of the bridge and righted itself, with water pouring from the doorways and decks.[6]
One of the two main ventilator funnels had tilted to the center, yet one engine was still running, and the captain steered to anchor the tugboat in a flooded cornfield. Another downstream tugboat, M/V Tallapoosa, rescued the captain and all three crew members; with the pilot, then secured the two barges of coal. The barges were later towed to Mobile by the same company's towboat M/V Mauvilla. The Mauvilla is otherwise notable for its later involvement in the 1993 Big Bayou Canot train wreck.[5]
Recreation
Pleasure boats, cruising America's Great Loop, use the waterway each year in the fall.
Folklore
The river is closely associated with several steamboat disasters, including the Eliza Battle[7] and James T. Staples.
See also
- List of Alabama rivers
- List of Mississippi rivers
- South Atlantic-Gulf Water Resource Region

References
- ↑ Bright, William (2004). Native American placenames of the United States. University of Oklahoma Press. p. 504. ISBN 978-0-8061-3598-4. Retrieved 11 April 2011.
- ↑ Patricia Galloway, Choctaw Genesis, 1500-1700, University of Nebraska Press, 1998
- 1 2 U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Tombigbee River. Retrieved 14 June 2005.
- ↑ Courtesy U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Mobile District
- 1 2 3 4 Bjarne & Captain Michael L. Smith, "The Tugboat story" Archived 2009-04-16 at the Wayback Machine. (M/V Cahaba), Monet.fi (Finland), January 2006
- ↑ "Cahaba Towboat Incident" Archived 2002-06-03 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Emmet Calhoun (14 August 1942). "Recollections: Eliza Battle". Birmingham News. Retrieved 26 January 2014.