Tibial nerve
| Tibial nerve | |
|---|---|
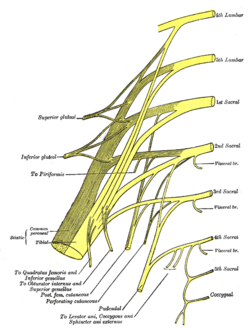 Plan of sacral and pudendal plexuses (Tibial nerve labelled at centre left) | |
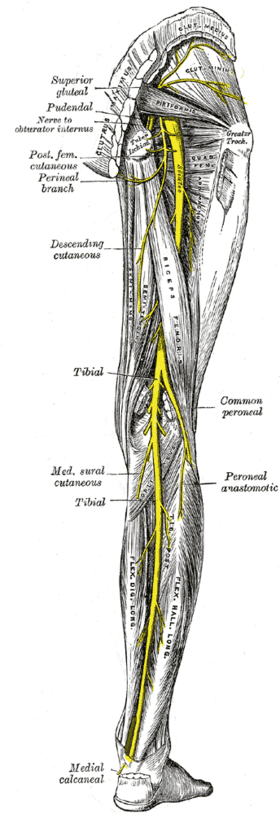 Nerves of the right lower extremity Posterior view. | |
| Details | |
| From | sacral plexus via sciatic nerve |
| To | medial plantar nerve, lateral plantar nerve |
| Innervates |
Origin: flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus Medial: abductor hallucis, flexor digitorum brevis, flexor hallucis brevis, first lumbrical Lateral: quadratus plantae, flexor digiti minimi, adductor hallucis, the interossei, three lumbricals. and abductor digiti minimi |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nervus tibialis |
| MeSH | D013979 |
| TA | A14.2.07.058 |
| FMA | 19035 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.
Structure
Popliteal fossa
Tibia nerve is the larger terminal branch of the sciatic nerve with root values of L4, L5, S1, S2, and S3. It lies superficial (or posterior) to the popliteal vessels, extending from the superior angle to the inferior angle of the popliteal fossa, crossing the popliteal vessels from lateral to medial side. It gives off branches as shown below:[1]
- Muscular branches - Muscular branches arises from the distal part of the popliteal fossa. It supplies the medial and lateral heads of gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris and popliteus muscles. Nerve to popliteus crosses the popliteus muscle, runs downwards and laterally, winds around the lower border of the popliteus to supply the deep (or anterior) surface of the popliteus. This nerve also supplies the tibialis posterior muscle, superior tibiofibular joint, tibia bone, interosseous membrane of leg, and the inferior tibiofibular joint.[1]
- Cutaneous branches - Tibial nerve also gives off a cutaneous nerve called the medial sural nerve from the middle of the popliteal fossa and exits at the inferior angle. It supplies the skin of the lower half of the back of the leg and lateral border of the foot until the tip of the little toe.[1]
- Articular branches - There are three articular branches arises from the upper part of the fossa: superior medial genicular nerve (located on the surface of medial condyle of femur, middle genicular nerve (pierces the posterior capsule of the knee joint to supply the structures located in the intercondylar notch of the femur, and inferior genicular nerve (runs along the upper border of the popliteus to reach the medial condyle of tibia).[1]
Back of the leg
At the inferior angle of the popliteal fossa, tibial nerve passes deep to the tendinous arch of soleus to enter the back of the leg. In the leg, it runs downwards and medially to reach the posteromedial side of the ankle, midway between the medial malleolus and medial tubercle of the calcaneum. It terminates deep to the flexor retinaculum at the origin of the abductor hallucis by dividing into medial and lateral plantar nerves to supply the foot. The tibial nerve gives off several branches to supply the back of the leg:[1]
- Muscular branches - Supplies tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus, and deep part of soleus.[1]
- Cutaneus branches - The medial calcaneal nerve pierces the flexor retinaculum to supply the skin of the back and lower surface of the heel.[1]
- Articular branches - Supplies the ankle joint[1]
Foot
In the foot, the nerve terminates by dividing into medial and lateral plantar branches.
- Medial plantar nerve - It is the larger terminal branch of the tibial nerve. It passes between the abductor hallucis and flexor digitorum brevis to divides further into branches. Its distribution resembles to that of the distribution of median nerve in the hand. Its muscular branches supplies the abductor hallucis, the flexor digitorum brevis, the flexor hallucis brevis and the first lumbrical. Cutaneous distribution of the medial plantar nerve supplies the medial sole and medial three and one half toes through four digital branches. Each digital branch give off a dorsal branch to supply the nail beds on the dorsum. This nerve also gives off articular branches to supply the tarsus and metatasus bones. [1]
- Lateral plantar nerve - It is the smaller terminal branch of the tibial nerve. It courses laterally and forward until the base of fifth metatarsal bone, where it divideds into superficial and deep branches. Its distribution resembles to the distribution of ulnar nerve in the hand. The main trunk of the nerve supplies two muscles: flexor digitorum accessorius and abductor digiti minimi. This nerve also supplies the skin of the sole.[1] The superficial branch is divided into medial and lateral branches. The lateral branch supplies three muscles: flexor digiti minimi, 3rd and 4th interossei, and the skin over the lateral side of the toe. The medial branch communicates with the medial plantar nerve and supplies the skin over the fourth interdigital cleft.[1] The deep branch supplies the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th lumbricals, first and second plantar interossei and adductor hallucis.[1]
Additional images
 Tibial nerve
Tibial nerve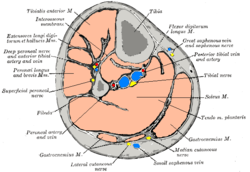 Cross-section through middle of left calf
Cross-section through middle of left calf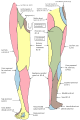 Cutaneous nerves of the right lower extremity. Front and posterior views
Cutaneous nerves of the right lower extremity. Front and posterior views Diagram of the segmental distribution of the cutaneous nerves of the sole of the foot
Diagram of the segmental distribution of the cutaneous nerves of the sole of the foot A schematic of the sacral plexus with the origin of the tibial nerve shown (labeled at the bottom left)
A schematic of the sacral plexus with the origin of the tibial nerve shown (labeled at the bottom left)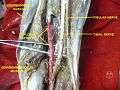 Tibial nerve
Tibial nerve- Tibial nerve
- Tibial nerve
External links
- Tibial_nerve at the Duke University Health System's Orthopedics program
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Krishna, Garg (2010). "Popliteal fossa (Chapter 6)". BD Chaurasia's Human Anatomy (Regional and Applied Dissection and Clinical) Volume 2 - Lower limb, abdomen, and pelvis (Fifth ed.). India: CBS Publishers and Distributors Pvt Ltd. p. 86,87,120, 131. ISBN 978-81-239-1864-8.