Lumboinguinal nerve
| Lumboinguinal nerve | |
|---|---|
|
Cutaneous nerves of the right lower extremity. Front and posterior views. (Lumboinguinal visible at upper left, in green.) | |
|
Cutaneous nerves of the right lower extremity. Front and posterior views. (Lumboinguinal visible at upper left.) | |
| Details | |
| From | genitofemoral nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ramus femoralis nervi genitofemoralis, nervus lumboinguinalis |
| TA | A14.2.07.010 |
| FMA | 16496 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The lumboinguinal nerve, also known as the femoral or crural branch of genitofemoral, is a nerve in the abdomen. The lumboinguinal nerve is a branch of the genitofemoral nerve. The "femoral" part supplies skin to the femoral triangle area.
Structure
The lumboinguinal nerve arises from the genitofemoral nerve. It descends alongside the external iliac artery, sending a few filaments around it, and, passing beneath the inguinal ligament, enters the sheath of the femoral vessels, lying superficial and lateral to the femoral artery. Here, it pierces the anterior layer of the sheath of the vessels and the fascia lata, and supplies the skin of the anterior surface of the upper part of the thigh.[1] :343
On the front of the thigh it communicates with the anterior cutaneous branches of the femoral nerve.
A few filaments from the lumboinguinal nerve may be traced to the femoral artery.
Additional images
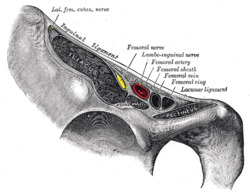 Structures passing behind the inguinal ligament.
Structures passing behind the inguinal ligament.
See also
External links
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 953 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)