Symbiosis

Symbiosis (from Greek συμβίωσις "living together", from σύν "together" and βίωσις "living")[2] is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasitic. The organisms, each termed a symbiont, may be of the same or of different species. In 1879, Heinrich Anton de Bary defined it as "the living together of unlike organisms". The term was subject to a century-long debate about whether it should specifically denote mutualism, as in lichens; biologists have now abandoned that restriction.
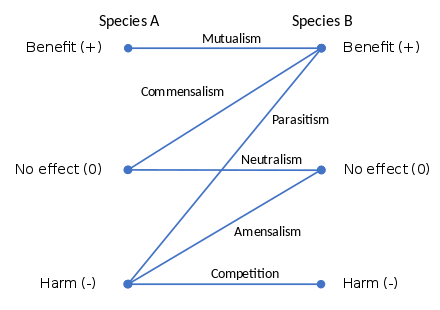
Symbiosis can be obligatory, which means that one or both of the symbionts entirely depend on each other for survival, or facultative (optional) when they can generally live independently.
Symbiosis is also classified by physical attachment; symbiosis in which the organisms have bodily union is called conjunctive symbiosis, and symbiosis in which they are not in union is called disjunctive symbiosis.[3] When one organism lives on the surface of another, such as head lice on humans, it is called ectosymbiosis; when one partner lives inside the tissues of another, such as Symbiodinium within coral, it is termed endosymbiosis.[4][5]
Definition
The definition of symbiosis was a matter of debate for 130 years.[6] In 1877, Albert Bernhard Frank used the term symbiosis to describe the mutualistic relationship in lichens.[7] In 1879, the German mycologist Heinrich Anton de Bary defined it as "the living together of unlike organisms".[8][9] The definition has varied among scientists with some advocating that it should only refer to persistent mutualisms, while others thought it should apply to all persistent biological interactions, in other words mutualisms, commensalism, or parasitism, but excluding brief interactions such as predation.[10] Current biology and ecology textbooks use the latter "de Bary" definition, or an even broader one where symbiosis means all interspecific interactions; the restrictive definition where symbiosis means only mutualism is no longer used.[11]
In 1949, Edward Haskell (1949) proposed an integrative approach, proposing a classification of "co-actions",[12] later adopted by biologists as "interactions".[13][14][15]
Biological interactions can involve individuals of the same species (intraspecific interactions) or individuals of different species (interspecific interactions). These can be further classified by either the mechanism of the interaction or the strength, duration and direction of their effects.[16]
Obligate versus facultative
Relationships can be obligate, meaning that one or both of the symbionts entirely depend on each other for survival. For example, in lichens, which consist of fungal and photosynthetic symbionts, the fungal partners cannot live on their own.[8][17][18][19] The algal or cyanobacterial symbionts in lichens, such as Trentepohlia, can generally live independently, and their symbiosis is, therefore, facultative (optional).[20]
Physical interaction
Endosymbiosis is any symbiotic relationship in which one symbiont lives within the tissues of the other, either within the cells or extracellularly.[5][21] Examples include diverse microbiomes, rhizobia, nitrogen-fixing bacteria that live in root nodules on legume roots; actinomycete nitrogen-fixing bacteria called Frankia, which live in alder root nodules; single-celled algae inside reef-building corals; and bacterial endosymbionts that provide essential nutrients to about 10%–15% of insects.
Ectosymbiosis is any symbiotic relationship in which the symbiont lives on the body surface of the host, including the inner surface of the digestive tract or the ducts of exocrine glands.[5][22] Examples of this include ectoparasites such as lice, commensal ectosymbionts such as the barnacles which attach themselves to the jaw of baleen whales, and mutualist ectosymbionts such as cleaner fish.
Competition

Competition can be defined as an interaction between organisms or species, in which the fitness of one is lowered by the presence of another. Limited supply of at least one resource (such as food, water, and territory) used by both usually facilitates this type of interaction, although the competition may also exist over other 'amenities', such as females for reproduction (in case of male organisms of the same species).[23]
Mutualism

Mutualism or interspecies reciprocal altruism is a long-term relationship between individuals of different species where both individuals benefit.[24] Mutualistic relationships may be either obligate for both species, obligate for one but facultative for the other, or facultative for both.
.jpg)
A large percentage of herbivores have mutualistic gut flora to help them digest plant matter, which is more difficult to digest than animal prey.[4] This gut flora is made up of cellulose-digesting protozoans or bacteria living in the herbivores' intestines.[25] Coral reefs are the result of mutualisms between coral organisms and various types of algae which live inside them.[26] Most land plants and land ecosystems rely on mutualisms between the plants, which fix carbon from the air, and mycorrhyzal fungi, which help in extracting water and minerals from the ground.[27]
An example of mutualism is the relationship between the ocellaris clownfish that dwell among the tentacles of Ritteri sea anemones. The territorial fish protects the anemone from anemone-eating fish, and in turn the stinging tentacles of the anemone protect the clownfish from its predators. A special mucus on the clownfish protects it from the stinging tentacles.[28]
A further example is the goby, a fish which sometimes lives together with a shrimp. The shrimp digs and cleans up a burrow in the sand in which both the shrimp and the goby fish live. The shrimp is almost blind, leaving it vulnerable to predators when outside its burrow. In case of danger the goby touches the shrimp with its tail to warn it. When that happens both the shrimp and goby quickly retreat into the burrow.[29] Different species of gobies (Elacatinus spp.) also clean up ectoparasites in other fish, possibly another kind of mutualism.[30]
A non-obligate symbiosis is seen in encrusting bryozoans and hermit crabs. The bryozoan colony (Acanthodesia commensale) develops a cirumrotatory growth and offers the crab (Pseudopagurus granulimanus) a helicospiral-tubular extension of its living chamber that initially was situated within a gastropod shell.[31]
Many types of tropical and sub-tropical ants that have evolved very complex relationships with certain tree species.[32]
Endosymbiosis
In endosymbiosis, the host cell lacks some of the nutrients which the endosymbiont provides. As a result, the host favors endosymbiont's growth processes within itself by producing some specialized cells. These cells affect the genetic composition of the host in order to regulate the increasing population of the endosymbionts and ensure that these genetic changes are passed onto the offspring via vertical transmission (heredity).[33]
A spectacular example of obligate mutualism is the relationship between the siboglinid tube worms and symbiotic bacteria that live at hydrothermal vents and cold seeps. The worm has no digestive tract and is wholly reliant on its internal symbionts for nutrition. The bacteria oxidize either hydrogen sulfide or methane, which the host supplies to them. These worms were discovered in the late 1980s at the hydrothermal vents near the Galapagos Islands and have since been found at deep-sea hydrothermal vents and cold seeps in all of the world's oceans.[34]
As the endosymbiont adapts to the host's lifestyle the endosymbiont changes dramatically. There is a drastic reduction in its genome size, as many genes are lost during the process of metabolism, and DNA repair and recombination, while important genes participating in the DNA to RNA transcription, protein translation and DNA/RNA replication are retained. The decrease in genome size is due to loss of protein coding genes and not due to lessening of inter-genic regions or open reading frame (ORF) size. Species that are naturally evolving and contain reduced sizes of genes can be accounted for an increased number of noticeable differences between them, thereby leading to changes in their evolutionary rates. When endosymbiotic bacteria related with insects are passed on to the offspring strictly via vertical genetic transmission, intracellular bacteria go across many hurdles during the process, resulting in the decrease in effective population sizes, as compared to the free living bacteria. The incapability of the endosymbiotic bacteria to reinstate their wild type phenotype via a recombination process is called Muller's ratchet phenomenon. Muller's ratchet phenomenon together with less effective population sizes leads to an accretion of deleterious mutations in the non-essential genes of the intracellular bacteria.[35] This can be due to lack of selection mechanisms prevailing in the relatively "rich" host environment.[36][37]
Commensalism

Commensalism describes a relationship between two living organisms where one benefits and the other is not significantly harmed or helped. It is derived from the English word commensal, used of human social interaction. It derives from a medieval Latin word meaning sharing food, formed from com- (with) and mensa (table).[24][38]
Commensal relationships may involve one organism using another for transportation (phoresy) or for housing (inquilinism), or it may also involve one organism using something another created, after its death (metabiosis). Examples of metabiosis are hermit crabs using gastropod shells to protect their bodies, and spiders building their webs on plants.
Parasitism
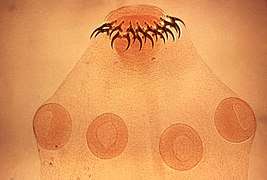
In a parasitic relationship, the parasite benefits while the host is harmed.[39] Parasitism takes many forms, from endoparasites that live within the host's body to ectoparasites and parasitic castrators that live on its surface and micropredators like mosquitoes that visit intermittently. Parasitism is an extremely successful mode of life; as many as half of all animals have at least one parasitic phase in their life cycles, and it is also frequent in plants and fungi. Moreover, almost all free-living animal species are hosts to parasites, often of more than one species.
Mimicry
Mimicry is a form of symbiosis in which a species adopts distinct characteristics of another species to alter its relationship dynamic with the species being mimicked, to its own advantage. Among the many types of mimicry are Batesian and Müllerian, the first involving one-sided exploitation, the second providing mutual benefit. Batesian mimicry is an exploitative three-party interaction where one species, the mimic, has evolved to mimic another, the model, to deceive a third, the dupe. In terms of signalling theory, the mimic and model have evolved to send a signal; the dupe has evolved to receive it from the model. This is to the advantage of the mimic but to the detriment of both the model, whose protective signals are effectively weakened, and of the dupe, which is deprived of an edible prey. For example, a wasp is a strongly-defended model, which signals with its conspicuous black and yellow coloration that it is an unprofitable prey to predators such as birds which hunt by sight; many hoverflies are Batesian mimics of wasps, and any bird that avoids these hoverflies is a dupe.[40][41] In contrast, Müllerian mimicry is mutually beneficial as all participants are both models and mimics.[42][43] For example, different species of bumblebee mimic each other, with similar warning coloration in combinations of black, white, red, and yellow, and all of them benefit from the relationship. [44]
Amensalism
Amensalism is an asymmetric interaction where one species is harmed or killed by the other, and one is unaffected by the other.[45][46] There are two types of amensalism, competition and antagonism (or antibiosis). Competition is where a larger or stronger organism deprives a smaller or weaker one from a resource. Antagonism occurs when one organism is damaged or killed by another through a chemical secretion. An example of competition is a sapling growing under the shadow of a mature tree. The mature tree can rob the sapling of necessary sunlight and, if the mature tree is very large, it can take up rainwater and deplete soil nutrients. Throughout the process, the mature tree is unaffected by the sapling. Indeed, if the sapling dies, the mature tree gains nutrients from the decaying sapling. An example of antagonism is Juglans nigra (black walnut), secreting juglone, a substance which destroys many herbaceous plants within its root zone.[47]
A clear case of amensalism is where sheep or cattle trample grass. Whilst the presence of the grass causes negligible detrimental effects to the animal's hoof, the grass suffers from being crushed. Amensalism is often used to describe strongly asymmetrical competitive interactions, such as has been observed between the Spanish ibex and weevils of the genus Timarcha which feed upon the same type of shrub. Whilst the presence of the weevil has almost no influence on food availability, the presence of ibex has an enormous detrimental effect on weevil numbers, as they consume significant quantities of plant matter and incidentally ingest the weevils upon it.[48]
Cleaning symbiosis
Cleaning symbiosis is an association between individuals of two species, where one (the cleaner) removes and eats parasites and other materials from the surface of the other (the client).[49] It is putatively mutually beneficial, but biologists have long debated whether it is mutual selfishness, or simply exploitative. Cleaning symbiosis is well-known among marine fish, where some small species of cleaner fish, notably wrasses but also species in other genera, are specialised to feed almost exclusively by cleaning larger fish and other marine animals.[50]
Co-evolution

Symbiosis is increasingly recognized as an important selective force behind evolution;[4][51] many species have a long history of interdependent co-evolution.[52]
Symbiogenesis
Eukaryotes (plants, animals, fungi, and protists) developed by symbiogenesis from a symbiosis between bacteria and archaea.[4][53][54] Evidence for this includes the fact that mitochondria and chloroplasts divide independently of the cell, and the observation that some organelles seem to have their own genome.[55]
The biologist Lynn Margulis, famous for her work on endosymbiosis, contended that symbiosis is a major driving force behind evolution. She considered Darwin's notion of evolution, driven by competition, to be incomplete and claimed that evolution is strongly based on co-operation, interaction, and mutual dependence among organisms. According to Margulis and her son Dorion Sagan, "Life did not take over the globe by combat, but by networking."[56]
Co-evolutionary relationships
Mycorrhizas
About 80% of vascular plants worldwide form symbiotic relationships with fungi, in particular in arbuscular mycorrhizas.[57]
Pollination

Flowering plants and the animals that pollinate them have co-evolved. Many plants that are pollinated by insects (in entomophily), bats, or birds (in ornithophily) have highly specialized flowers modified to promote pollination by a specific pollinator that is correspondingly adapted. The first flowering plants in the fossil record had relatively simple flowers. Adaptive speciation quickly gave rise to many diverse groups of plants, and, at the same time, corresponding speciation occurred in certain insect groups. Some groups of plants developed nectar and large sticky pollen, while insects evolved more specialized morphologies to access and collect these rich food sources. In some taxa of plants and insects the relationship has become dependent,[58] where the plant species can only be pollinated by one species of insect.[59]

Acacia ants and acacias
_with_Beltian_bodies%2C_Caves_Branch_Jungle_Lodge%2C_Belmopan%2C_Belize_-_8505045055.jpg)
The acacia ant (Pseudomyrmex ferruginea) is an obligate plant ant that protects at least five species of "Acacia" (Vachellia)[lower-alpha 1] from preying insects and from other plants competing for sunlight, and the tree provides nourishment and shelter for the ant and its larvae.[60][61]
See also
Notes
- ↑ The acacia ant protects at least 5 species of "Acacia", now all renamed to Vachellia: V. chiapensis, V. collinsii, V. cornigera, V. hindsii and V. sphaerocephala.
References
- ↑ Miller, Allie. "Intricate Relationship Allows the Other to Flourish: the Sea Anemone and the Clownfish". AskNature. The Biomimicry Institute. Retrieved 15 February 2015.
- ↑ συμβίωσις, σύν, βίωσις. Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert; A Greek–English Lexicon at the Perseus Project
- ↑ "symbiosis." Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. Philadelphia: Elsevier Health Sciences, 2007. Credo Reference. Web. 17 September 2012
- 1 2 3 4 Moran 2006
- 1 2 3 Paracer & Ahmadjian 2000, p. 12
- ↑ Martin, Bradford D.; Schwab, Ernest (2012), "Symbiosis: 'Living together' in chaos", Studies in the History of Biology, 4 (4): 7–25.
- ↑ "symbiosis". Oxford English Dictionary (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press. September 2005. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- 1 2 Wilkinson 2001
- ↑ Douglas 1994, p. 1
- ↑ Douglas 2010, pp. 5–12
- ↑ Martin, Bradford D.; Schwab, Ernest (2013), "Current usage of symbiosis and associated terminology", International Journal of Biology, 5 (1): 32–45., doi:10.5539/ijb.v5n1p32
- ↑ Haskell, E. F. (1949). A clarification of social science. Main Currents in Modern Thought 7: 45–51.
- ↑ Burkholder, P. R. (1952) Cooperation and Conflict among Primitive Organisms. American Scientist, 40, 601-631. link.
- ↑ Bronstein, J. L. (2015). The study of mutualism. In: Bronstein, J. L. (ed.). Mutualism. Oxford University Press, Oxford. link.
- ↑ Pringle, E. G. (2016). Orienting the Interaction Compass: Resource Availability as a Major Driver of Context Dependence. PLoS Biology, 14(10), e2000891. http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2000891.
- ↑ Wootton, J.T.; Emmerson, M. (2005). "Measurement of Interaction Strength in Nature". Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics. 36: 419–44. doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.36.091704.175535. JSTOR 30033811.
- ↑ Isaac 1992, p. 266
- ↑ Saffo 1993
- ↑ Douglas 2010, p. 4
- ↑ Muggia, Lucia; Vancurova, Lucie; Škaloud, Pavel; Peksa, Ondrej; Wedin, Mats; Grube, Martin (2013). "The symbiotic playground of lichen thalli - a highly flexible photobiont association in rock-inhabiting lichens". FEMS Microbiology Ecology. 85 (2): 313–323. doi:10.1111/1574-6941.12120.
- ↑ Sapp 1994, p. 142
- ↑ Nardon & Charles 2002
- ↑ Begon, M., J.L. Harper and C.R. Townsend. 1996. Ecology: individuals, populations, and communities, Third Edition. Blackwell Science Ltd., Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA.
- 1 2 Paracer & Ahmadjian 2000, p. 6
- ↑ "symbiosis." The Columbia Encyclopedia. New York: Columbia University Press, 2008. Credo Reference. Web. 17 September 2012.
- ↑ Toller, Rowan & Knowlton 2001
- ↑ Harrison 2005
- ↑ Lee 2003
- ↑ Facey, Helfman & Collette 1997
- ↑ M.C. Soares; I.M. Côté; S.C. Cardoso & R.Bshary (August 2008). "The cleaning goby mutualism: a system without punishment, partner switching or tactile stimulation". Journal of Zoology. 276 (3): 306–312. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.2008.00489.x.
- ↑ Klicpera, A; PD Taylor; H Westphal (1 Dec 2013). "Bryoliths constructed by bryozoans in symbiotic associations with hermit crabs in a tropical heterozoan carbonate system, Golfe d'Arguin, Mauritania". Mar Biodivers. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 43 (4): 429–444. doi:10.1007/s12526-013-0173-4. ISSN 1867-1616.
- ↑ Piper, Ross (2007), Extraordinary Animals: An Encyclopedia of Curious and Unusual Animals, Greenwood Press.
- ↑ Latorre, A.; Durban, A.; Moya, A.; Pereto, J. (2011). The role of symbiosis in eukaryotic evolution. Origins and evolution of life – An astrobiological perspective. pp. 326–339.
- ↑ Cordes et al. 2005
- ↑ Moran, N. A. (1996). "Accelerated evolution and Muller's ratchet in endosymbiotic bacteria". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 93 (7): 2873–2878. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.7.2873. PMC 39726. PMID 8610134.
- ↑ Andersson, Siv G.E; Kurland, Charles G (1998). "Reductive evolution of resident genomes". Trends in Microbiology. 6 (7): 263–8. doi:10.1016/S0966-842X(98)01312-2. PMID 9717214.
- ↑ Wernegreen, J.J. (2002). "Genome evolution in bacterial endosymbionts of insects". Nature Reviews Genetics. 3 (11): 850–861. doi:10.1038/nrg931. PMID 12415315.
- ↑ Nair 2005
- ↑ Paracer & Ahmadjian 2000, p. 7
- ↑ Vane-Wright, R. I. (1976). "A unified classification of mimetic resemblances". Biological Journal of the Linnean Society. 8: 25–56. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8312.1976.tb00240.x.
- ↑ Bates, Henry Walter (1861). "Contributions to an insect fauna of the Amazon valley. Lepidoptera: Heliconidae". Transactions of the Linnean Society. 23 (3): 495–566. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.1860.tb00146.x. ; Reprint: Bates, Henry Walter (1981). "Contributions to an insect fauna of the Amazon valley (Lepidoptera: Heliconidae)". Biological Journal of the Linnean Society. 16 (1): 41–54. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8312.1981.tb01842.x.
- ↑ Müller, Fritz (1878). "Ueber die Vortheile der Mimicry bei Schmetterlingen". Zoologischer Anzeiger. 1: 54–55.
- ↑ Müller, Fritz (1879). "Ituna and Thyridia; a remarkable case of mimicry in butterflies. (R. Meldola translation)". Proclamations of the Entomological Society of London. 1879: 20–29.
- ↑ Mallet, James (2001). "Causes and consequences of a lack of coevolution in Mullerian mimicry". Evolutionary Ecology. 13: 777–806. doi:10.1023/a:1011060330515.
- ↑ Toepfer, G. "Amensalism". In: BioConcepts. link.
- ↑ Willey, Joanne M.; Sherwood, Linda M.; Woolverton, Cristopher J. (2013). Prescott's Microbiology (9th ed.). pp. 713–738. ISBN 978-0-07-751066-4.
- ↑ The Editors of Encyclopædia Britannica. (n.d.). Amensalism (biology). Retrieved September 30, 2014, from http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/19211/amensalism
- ↑ Gómez, José M.; González-Megías, Adela (2002). "Asymmetrical interactions between ungulates and phytophagous insects: Being different matters". Ecology. 83 (1): 203–11. doi:10.1890/0012-9658(2002)083[0203:AIBUAP]2.0.CO;2.
- ↑ Losey, G.S. (1972). "The Ecological Importance of Cleaning Symbiosis". Copeia: 820–833. doi:10.2307/1442741.
- ↑ Poulin, Robert; Grutter, A. S. (1996). "Cleaning symbiosis: proximate and adaptive explanations" (PDF). BioScience. 46 (7): 512–517. doi:10.2307/1312929.
- ↑ Wernegreen 2004
- ↑ Paracer & Ahmadjian 2000, pp. 3–4
- ↑ Brinkman et al. 2002
- ↑ Golding & Gupta 1995
- ↑ "Symbiosis". Bloomsbury Guide to Human Thought. London: Bloomsbury Publishing Ltd, 1993. Credo Reference. Web. 17 September 2012.
- ↑ Sagan & Margulis 1986
- ↑ Schüßler, A.; et al. (2001), "A new fungal phylum, the Glomeromycota: phylogeny and evolution", Mycol. Res., 105 (12): 1416, doi:10.1017/S0953756201005196.
- ↑ Harrison 2002
- ↑ Danforth & Ascher 1997
- 1 2 Hölldobler, Bert; Wilson, Edward O. (1990). The ants. Harvard University Press. pp. 532–533. ISBN 0-674-04075-9.
- ↑ National Geographic. "Acacia Ant Video". Archived from the original on 2007-11-07.
Bibliography
- Cordes, E.E.; Arthur, M.A.; Shea, K.; Arvidson, R.S.; Fisher, C.R. (2005), "Modeling the mutualistic interactions between tubeworms and microbial consortia", PLoS Biol, 3 (3): 1–10, doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0030077, PMC 1044833, PMID 15736979
- Brinkman, F.S.L.; Blanchard, J.L.; Cherkasov, A.; Av-gay, Y.; Brunham, R.C.; Fernandez, R.C.; Finlay, B.B.; Otto, S.P.; Ouellette, B.F.F.; Keeling, P.J.; et al. (2002), "Evidence That Plant-Like Genes in Chlamydia Species Reflect an Ancestral Relationship between Chlamydiaceae, Cyanobacteria, and the Chloroplast", Genome Research, 12 (8): 1159–1167, doi:10.1101/gr.341802, PMC 186644, PMID 12176923
- Danforth, B.N.; Ascher, J. (1997), "Flowers and Insect Evolution" (PDF), Science, 283 (5399): 143, doi:10.1126/science.283.5399.143a, retrieved 2007-09-25
- Douglas, Angela (1994), Symbiotic interactions, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-854294-1
- Douglas, Angela (2010), The Symbiotic Habit, New Jersey: Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-11341-8
- Facey, Douglas E.; Helfman, Gene S.; Collette, Bruce B. (1997), The Diversity of Fishes, Oxford: Blackwell Science, ISBN 0-86542-256-7
- Golding, RS; Gupta, RS (1995), "Protein-based phylogenies support a chimeric origin for the eukaryotic genome", Mol. Biol. Evol., 12 (1): 1–6, doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040178, PMID 7877484
- Harrison, Rhett (2002), "Balanced mutual use (symbiosis)", Quarterly journal Biohistory, 10 (2)
- Harrison, Maria J. (2005), "Signaling in the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis", Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 59: 19–42, doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.58.030603.123749, PMID 16153162
- Lee, J. (2003), "Amphiprion percula", Animal Diversity Web, retrieved 2007-09-29
- Isaac, Susan (1992), Fungal-plant interactions, London: Chapman & Hall, ISBN 0-412-36470-0
- Moran, N.A. (2006), "Symbiosis", Current Biology, 16 (20): 866–871, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.019, PMID 17055966
- Nardon, P.; Charles, H. (2002), "Morphological aspects of symbiosis", Symbiosis: Mechanisms and Systems. Dordercht/boson/London, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Cellular Origin, Life in Extreme Habitats and Astrobiology, 4: 15–44, doi:10.1007/0-306-48173-1_2, ISBN 1-4020-0189-4
- Paracer, Surindar; Ahmadjian, Vernon (2000), Symbiosis: An Introduction to Biological Associations, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-511806-5
- Nair, S. (2005), "Bacterial Associations: Antagonism to Symbiosis", in Ramaiah, N., Marine Microbiology: Facets & Opportunities, National Institute of Oceanography, Goa, pp. 83–89, retrieved 2007-10-12
- Saffo, M.B. (1993), "Coming to terms with a field: Words and concepts in symbiosis", Symbiosis, 14 (1–3)
- Sagan, Dorion; Margulis, Lynn (1986), Origins of sex: three billion years of genetic recombination, New Haven, Conn: Yale University Press, ISBN 0-300-03340-0
- Sapp, Jan (1994), Evolution by association: a history of symbiosis, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-508821-2
- Toller, W. W.; Rowan, R.; Knowlton, N. (2001), "Repopulation of Zooxanthellae in the Caribbean Corals Montastraea annularis and M. faveolata following Experimental and Disease-Associated Bleaching", The Biological Bulletin, 201 (3): 360–373, doi:10.2307/1543614, JSTOR 1543614, PMID 11751248
- Vinn, O. & Mõtus, M.-A. (2014). "Endobiotic Rugosan Symbionts in Stromatoporoids from the Sheinwoodian (Silurian) of Baltica". PLoS ONE. 9 (2): e90197. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090197. PMC 3934990. PMID 24587277. Retrieved 2014-01-09.
- Wernegreen, J.J. (2004), "Endosymbiosis: lessons in conflict resolution", PLOS Biology, 2 (3): e68, doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0020068, PMC 368163, PMID 15024418
External links
- TED-Education video – Symbiosis: a surprising tale of species cooperation.

