Second Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights
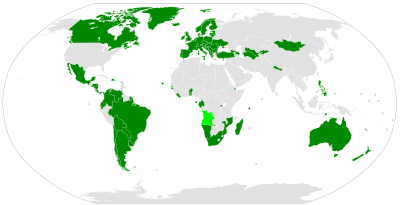
The Second Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, aiming at the abolition of the death penalty is a side agreement to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights. It was created on 15 December 1989 and entered into force on 11 July 1991. As of September 2018, the Optional Protocol has 86 states parties. In addition, Angola has signed, but not ratified the Protocol.[1]
The Optional Protocol commits its members to the abolition of the death penalty within their borders, though Article 2.1 allows parties to make a reservation allowing execution "in time of war pursuant to a conviction for a most serious crime of a military nature committed during wartime".[2] (Brazil, Chile, El Salvador). Cyprus, Malta and Spain initially made such reservations, and subsequently withdrew them. Azerbaijan and Greece still retain this reservation on their implementation of the protocol, despite both having banned the death penalty in all circumstances. (Greece has also ratified Protocol no.13).
See also
References
- ↑ "Parties to the Second Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, aiming at the abolition of the death penalty". United Nations Treaty Collection. Retrieved 2011-09-12.
- ↑ http://www1.umn.edu/humanrts/instree/b5ccprp2.htm